The Industry Framework for Next-Generation Digital Ecosystems: How AI, IoT, and XR Transform Connectivity
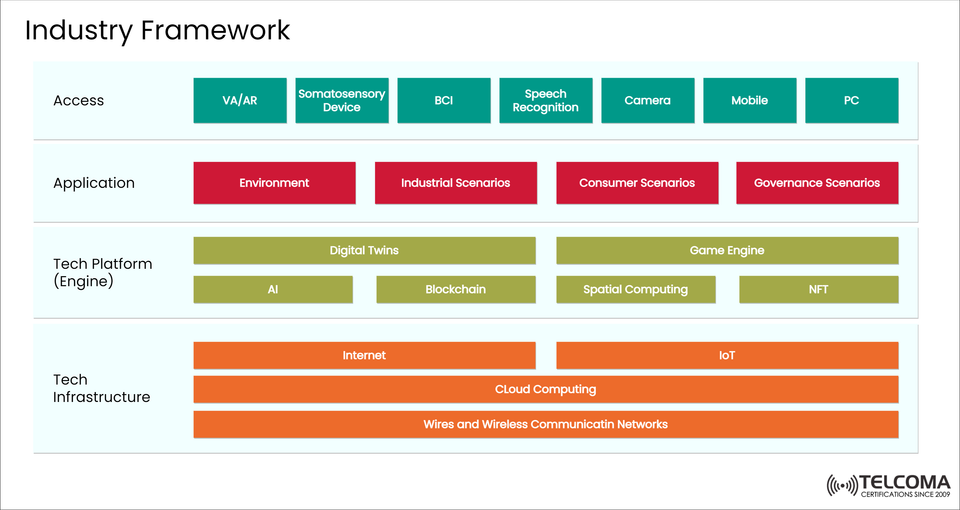

The Industry Framework Driving Digital Transformation: A Look from Telecom and Tech
The digital landscape is changing fast. New tech like AI, blockchain, IoT, XR (extended reality), and 5G are coming together to create fresh opportunities across various sectors.
The Industry Framework shown above captures this shift—illustrating how tech infrastructure, platforms, and access interfaces support innovative applications in industrial, consumer, and governance contexts.
For those in telecom and tech, this framework is like a roadmap for a connected, smart, and immersive future.
The Foundation: Tech Infrastructure Layer
At the base of the Industry Framework is the Tech Infrastructure layer, which serves as the backbone for connectivity and computing, enabling all kinds of digital innovation.
Key Components:
Component | Description
Wired and Wireless Communication Networks | Comprises fiber optics, 5G/6G, satellite, and Wi-Fi networks that provide ultra-reliable, low-latency connections.
Cloud Computing | Delivers scalable computing and storage solutions for real-time data analytics, AI training, and immersive applications.
Internet | Acts as the universal layer for connectivity, allowing devices, applications, and platforms to work together.
IoT (Internet of Things) | Links billions of smart devices, sensors, and systems, sending real-time data to AI-driven decision engines.
All these parts create the digital nervous system of various industries, supporting real-time data exchange, immersive experiences, and intelligent automation.
Telecom’s Role:
Telecom networks are crucial here, offering:
Ultra-low latency via 5G and upcoming 6G
Network slicing to cater to specific industrial needs
Edge computing for local data processing
Extensive IoT connectivity to support smart infrastructure
Without a solid telecom foundation, the higher layers—like applications and AI platforms—would struggle to operate efficiently.
The Tech Platform (Engine) Layer: Fueling Intelligence and Immersion
Next up is the Tech Platform (Engine) layer, which supplies the computational engines, frameworks, and protocols that drive innovation.
This layer takes raw data and turns it into intelligence, simulations, and interactive experiences using a blend of advanced technologies.
Core Technologies in This Layer:
AI (Artificial Intelligence): Powers automation, pattern recognition, natural language processing, and predictive analytics across various applications.
Blockchain: Offers decentralized trust mechanisms for secure transactions, identity verification, and transparent governance.
Digital Twins: Create virtual replicas of real systems (like factories or cities) for simulation, monitoring, and optimization.
Spatial Computing: Merges physical and digital environments with AR/VR/MR, allowing real-world interaction with digital info.
Game Engines: Tools like Unreal Engine and Unity provide immersive 3D environments and interactive scenarios.
NFT (Non-Fungible Tokens): Enable ownership, authentication, and trading of digital assets across immersive and decentralized platforms.
This platform layer is the engine room of innovation, where telecom data meets smart algorithms, leading to applications that range from smart manufacturing to engaging learning experiences.
The Application Layer: Real-World Use Cases Across Industries
The Application Layer is the visible side of digital transformation—where technology directly influences human activities and industry workflows.
Main Application Domains:
Category | Description
Environment | Covers smart cities, environmental monitoring, and digital sustainability projects using IoT and AI.
Industrial Scenarios | Includes manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and energy sectors that utilize digital twins and automation.
Consumer Scenarios | Encompasses entertainment, gaming, shopping, and social experiences enhanced by XR and blockchain.
Governance Scenarios | Focuses on e-governance, digital identity management, and secure citizen data services.
Examples of Applications:
Smart Manufacturing: AI and IoT keep track of equipment health and automate processes in real-time.
Immersive Retail: AR shopping apps let customers visualize products in a virtual space.
Digital Healthcare: Remote surgeries and diagnostics use 5G and XR interfaces.
Smart Governance: Blockchain guarantees transparency in managing public records.
These applications depend heavily on data intelligence, low-latency connectivity, and AI-driven automation, making telecom networks vital to their success.
The Access Layer: Connecting Users and Machines
The Access Layer is where people, machines, and digital environments come together. It sets the stage for how users connect with and experience applications and platforms.
Access Technologies in the Framework:
Technology | Function
VR/AR (Virtual and Augmented Reality) | Enables immersive visualization and interaction in 3D spaces.
Somatosensory Devices | Convert physical movements and gestures into digital commands.
BCI (Brain-Computer Interface) | Facilitates direct communication between the brain and digital systems.
Speech Recognition | Translates spoken words into actionable data for hands-free operation.
Cameras & Sensors | Gather environmental and spatial data for computer vision uses.
Mobile Devices & PCs | Serve as the main points of access for consumers and businesses alike.
This layer shapes user experience (UX) and human-machine interaction (HMI), relying on low latency, high bandwidth, and AI-driven edge processing—areas where telecom innovation plays a key role.
The Interplay Between Layers: Crafting a Unified Digital Ecosystem
The Industry Framework showcases a vertically integrated architecture—where each layer builds on the one beneath:
Tech Infrastructure delivers connectivity and computational resources.
Tech Platforms harness these resources to trigger AI, blockchain, and XR engines.
Applications leverage these technologies to generate value in industrial, consumer, and governance settings.
Access Interfaces allow for smooth interactions between users and digital systems.
This layered approach guarantees scalability, interoperability, and adaptability, helping organizations innovate quickly without starting from scratch on foundational systems.
Interdependencies Example:
A smart factory gathers sensor data through IoT (infrastructure).
AI (platform) evaluates this data to forecast equipment failures.
An industrial application displays results via an AR headset (access).
Such multi-layer integration is only achievable through coordinated collaboration among telecom networks, cloud platforms, and AI systems.
The Role of Telecom Networks in the Industry Framework
Telecom networks are more than just data channels—they're drivers of intelligence and automation across the framework.
Telecom Contributions Include:
5G/6G Connectivity: Guarantees reliable communication for industrial automation and XR experiences.
Edge Computing: Brings processing closer to users, cutting down latency and network congestion.
Network Slicing: Enables tailored virtual networks for different uses (like healthcare vs. gaming).
IoT Integration: Links billions of devices across sectors, providing real-time data to AI platforms.
Data Security and Privacy: Ensures safe data transfer with encryption, authentication, and decentralized structures.
By aligning with this framework, telecom operators can shift from being mere connectivity providers to intelligent digital service enablers.
Future Outlook: Convergence and Standardization
The future of digital industries hinges on convergence—where AI, IoT, XR, and blockchain function under unified standards and interoperable frameworks.
Key Trends to Watch:
6G Evolution: Set to enable terabit-per-second speeds and ultra-low latency for fully immersive experiences.
Quantum Networking: Boosting security and computation speed.
Federated AI: Allowing AI models to collaboratively learn while keeping sensitive data private.
Sustainable Networks: Building eco-friendly infrastructure leveraging energy-efficient technologies.
Global telecom organizations like 3GPP, ITU, and IEEE are already working on interoperability standards to bring this ecosystem together.
Conclusion: Shaping the Future of Connected Intelligence
The Industry Framework demonstrates how modern technologies—from AI and blockchain to IoT and XR—interconnect through telecom infrastructure to establish an intelligent, immersive, and decentralized digital ecosystem.
Every layer—from core infrastructure to user access—is crucial in determining how industries function, consumers engage, and governments operate in this connected world.
For telecom professionals, this framework offers both a chance and a challenge: to evolve networks into intelligent platforms that provide real-time insights, immersive experiences, and promote digital sustainability.
In this new age of connected intelligence, those who grasp and harness the full potential of this layered architecture will lead the next wave of digital transformation.
