The Service-Driven 5G Architecture Explained: A Deep Dive for Telecom Professionals
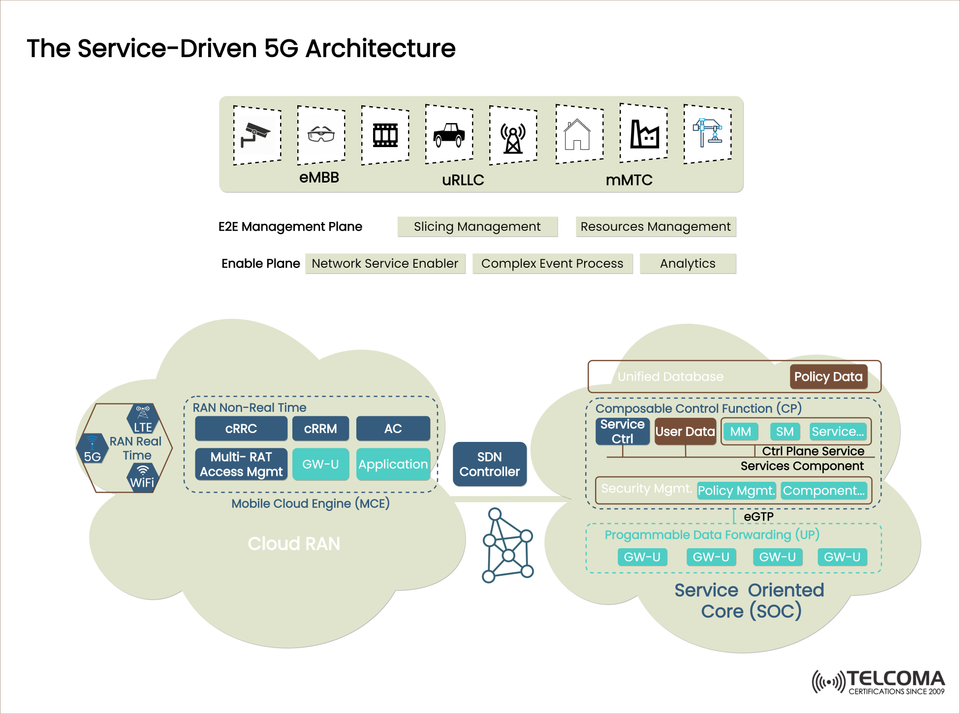

The Official Service-Driven 5G Architecture: A Detailed Overview for Telecommunication Professionals
With the arrival of 5G all the paradigms for how we plan, implement and optimize networks changed. At the heart of this change is the Service-Driven 5G Architecture. This is a modular, scalable architecture that will support a broad range of services including eMBB, uRLLC and mMTC. In this post we unpack the layered stack and components of this architecture so Telecom professionals and technical enthusiasts will be able to gain a deeper understanding of how 5G networks are engineered and orchestrated.
Understanding 5G Service Types
The service driven 5G architecture supports many types of use cases by using three broad categories of service types:
eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband): High speed mobile internet services for applications such as HD video over-the-top streaming and virtual / augmented reality.
uRLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication): Mission critical services for things like autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and industrial automation.
mMTC (Massive Machine-Type Communication): Large-scale IoT solutions for use cases like smart cities, industrial automation, and smart agriculture.
These services require dynamic and flexible, real-time network characteristics which is very complex challenge and it is met with the sophisticated 5G service architecture.
Core Layers of the Service-Driven 5G Architecture
The architecture is composed of a set of logical layers, each with its own function:
- E2E Management Plane
The E2E Management Plane is responsible for managing the end-to-end life cycle for both network slices and network resources. The E2E Management Plane includes:
Slicing Management: allocating a logical network slice that meets certain service constraints.
Resource Management: managing network resources in real time across all domains. - Enable Plane
The Enable Plane provides intelligent assistance to the network functions through the:
Network Service Enabler
Complex Event Processing
Analytics
The enable plane also provides a mechanism for proactive decision-making and self-optimisation of the entire network.
Technical Building Blocks
This architecture uses Cloud RAN, SDN, and SOC in precisely this manner to render services to the Customer of Things with maximum effectiveness and efficiency, and flexibility.
Cloud RAN (Radio Access Network)
RAN Real-Time: Provides support for Edge based LTE, 5G and Wi-Fi operations.
RAN Non-Real-Time Components:
cRRC: Centralized RRC component of RAN architecture
cRRM: Centralized RAN Resource Management
AC: Access Control
Multi-RAT Access Management: Multi-radio access technology participating management
GW-U: Gateway User Plane
Application Layer: application scoped logic, and interfaces to perform RAN functions
SDN Controller
It acts as the brain to control traffic and routing between the RAN and Core, enabling:
Dynamic path management
Network slice enforcement
Real-time configuration
Service-Oriented Core (SOC)
Divided into two main Planes:
Control Plane (CP)
Composable Control Functions:
Service Control
User Data
MM (Mobility Management)
SM (Session Management)
Service Functions
Unified Database & Policy Data
Security Management, Policy Management, and Component Management
User Plane (UP)
Details of programmable Data Forwarding – making use of multiple instances of GW-U to steer user data
Details of eGTP Support – provides encapsulated tunneling for mobility and session continuity
Quick Reference Table
Component Functionality
eMBB / uRLLC / mMTC Core service categories supported by 5G
Cloud RAN Allows for configured RAN functions as both real-time and non-real-time processes
SDN Controller Centralized control of routing and slicing for the Network
Service-Oriented Core (SOC) Modular core network that separates plan and data bi-plane
Enable Plane Intelligence (Analytics, CEP and service enablers)
E2E Management Plane (slicing and resource allocation and management across the network )
Why This Architecture Matters
- Scalability: Modular design supports massive deployments and dynamic scaling.
- Agility: Network slicing and SDN allow fast adaptation to service demands.
- Efficiency: Virtualization and programmability reduce operational overhead.
- Security: Built-in policy and security management for trusted communication.
Real-World Use Cases for Service-Driven 5G Architecture
With its modular and programmable design, this 5G Architecture can accommodate multiple practical applications and deployments across many industries.
🏥 Healthcare
Remote Surgery: Supported by ultra-reliable, low-latency communications (uRLLC)
Telemedicine & Diagnostics: Using enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB)
🚗 Automotive
Autonomous Vehicles: Real-time vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communications
Traffic Management Systems: Integration of massive IoT sensors (mMTC)
🏙️ Smart Cities
Smart Grids & Utilities: Real-time control & monitoring of infrastructure
Public Safety & Surveillance: Real-time, high-resolution video streaming
🏭 Manufacturing
Industrial Automation: High-density sensor networks and low-latency control.
Digital Twins: Real-time synchronization of physical assets to virtual models.
Industry Context: Why Telco Providers Are Moving Toward This Architecture
Telecom providers need to address the current pressures to drill-down to:
- Deliver faster service deployment.
- Supply network slices that enterprises can customize to their business.
- Realize cost savings through virtualization, and
- Meet security or government policy requirements.
The Service Driven 5G Architecture allows them to meet these strategically and operationally as it relates to service. The infrastructure is adaptable to development opportunities concerning Multi-RAT access, real-time analytics, and programmable gateways. The architecture is both futureproof and aligned with business goals.
Concluding Thoughts
While 5G rolls out across the globe, understanding Service-Driven 5G Architecture is all important for everyone shaping the networks of the future. Through standardizing Service-driven 5G architecture, we can inform stakeholders of the layers needed for flexible, intelligent, and future-proof networks commencing with a cloud-native core, progressing through to dynamic RAN control and service enablement layers.
For telecommunications practitioners, this is not just theory, but the operational basis for revenue-generating services, intelligent automation, and next-generation digital infrastructure.
Industry Relevance: Why Telecom Operators Are Adopting This Architecture
Telecom operators are under pressure to deliver:
Faster service deployments
Customizable network slices for enterprises
Cost Savings through operational virtualization
Security and policy compliance
Each of these requirements can be satisfied with the Service-Driven 5G Architecture. Capabilities like Multi-RAT access, real-time analytics and programmable gateways result in infrastructure that is future-proof and aligned with a business.
Key Future Enhancements:
- AI/ML for Real-Time Optimization: Integrated into analytics and event processing
- 6G Readiness: Architectural concepts like disaggregated networks and edge intelligence pave the way for beyond-5G evolution
- Dynamic Network Slicing-as-a-Service (NSaaS): On-demand, enterprise-driven slices for private networks
- Security Automation: Policy-based, real-time security enforcement using AI-driven systems
Conclusion
The Service-Driven 5G Architecture is more than a technical blueprint—it’s the enabler of the next generation of digital services. By combining Cloud RAN, SDN control, and a service-oriented core, telecom operators can meet the demands of modern applications and services with flexibility, intelligence, and precision. As 5G continues to evolve, understanding this architecture is essential for telecom professionals aiming to lead in this fast-paced industry.
