TSN Support in 5G Systems: Enabling Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication

TSN Support in the 5G System
With 5G technology making waves, industries are really transforming how communication systems back mission-critical applications. A key player in this shift is Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN).
TSN builds on standard Ethernet, offering reliable communication by ensuring bounded latency, low jitter, and high reliability. When you pair it with 5G Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (URLLC), TSN supercharges fields like industrial automation, autonomous vehicles, robotics, and real-time control.
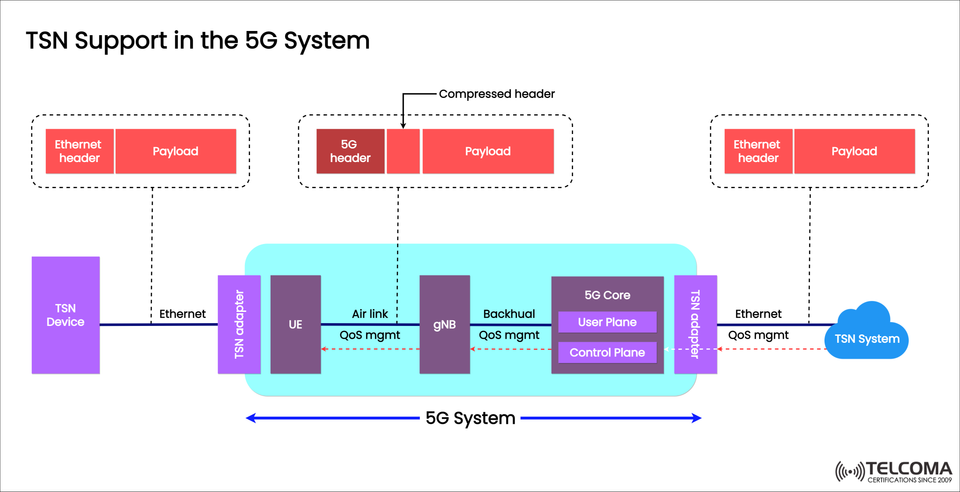
The diagram above illustrates how TSN support fits into the 5G system, showing how Ethernet packets travel through the 5G user plane and control plane, all while managing end-to-end Quality of Service (QoS).
What is Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN)?
TSN refers to a range of IEEE 802.1 standards that aim to enhance Ethernet for deterministic, low-latency communication. Some of the standout TSN features include:
Traffic Scheduling: Makes sure critical packets get the priority they need.
Bounded Latency: Guarantees that packets arrive within specific timeframes.
Low Jitter: Minimizes variations in packet delays.
Redundancy: Implements parallel paths to boost reliability.
Industries like automotive (in-vehicle networks), manufacturing (industrial IoT), and energy (smart grids) are all jumping on the TSN bandwagon.
Why Combine TSN with 5G?
Ethernet TSN shines in wired scenarios, but it does struggle with issues around mobility, scalability, and flexibility. Merging TSN with wireless 5G systems offers businesses:
Mobility: Devices can move freely without being tied down by Ethernet cables.
Coverage: 5G expands TSN reach across factories, campuses, and cities.
QoS Management: 5G has built-in features to prioritize TSN traffic through its URLLC capabilities.
Scalability: Supports thousands of devices without needing extra wiring.
TSN and 5G together create a solid foundation for Industry 4.0 and critical infrastructure communications.
TSN Support Architecture in 5G
The diagram shows how TSN packets make their way through the 5G system step by step:
- TSN Device to TSN Adapter
TSN devices (like sensors and controllers) kick things off by generating Ethernet frames with an Ethernet header and payload.
These packets then head to a TSN adapter, which prepares them for 5G transport.
- User Equipment (UE)
The UE, which includes the TSN adapter, takes in the Ethernet packets.
Here, Ethernet headers might get compressed and wrapped into 5G frames with a header that's specific to 5G.
QoS management actually starts at the air interface to make sure TSN deadlines are hit.
- gNB (5G Base Station)
The gNB is in charge of air-link QoS, scheduling resources for those time-sensitive packets.
These packets then move over the backhaul with QoS guarantees intact.
- 5G Core (User Plane and Control Plane)
User Plane (UP): Takes care of packet forwarding, ensuring latency-sensitive traffic has top priority.
Control Plane (CP): Handles policies, synchronization, and QoS enforcement for TSN flows.
- TSN Adapter and TSN System
Once at the exit point, packets are decapsulated and returned to their original Ethernet header and payload format.
They’re then sent to the destination TSN system (like industrial control servers or automation systems).
QoS Management in TSN over 5G
A big part of integrating TSN with 5G is about managing Quality of Service effectively.
Air Link QoS: The gNB scheduler gives TSN packets their own time slots and bumps them up the priority list compared to non-critical traffic.
Backhaul QoS: Traffic shaping and prioritization are consistent throughout the 5G network.
Core QoS: The 5G Core ensures end-to-end QoS policies are in place to deliver dependable performance across the system.
Ethernet QoS: TSN adapters on both ends translate 5G QoS parameters back into TSN priorities.
This smooth integration helps keep TSN flows reliable and predictable even over wireless connections.
Key Benefits of TSN Support in 5G
- Deterministic Communication
Guarantees bounded latency and reliability, which is crucial for real-time control.
- Mobility with Reliability
TSN running over 5G lets mobile robots, drones, and vehicles keep up real-time communications without being tethered.
- End-to-End QoS
5G provides a cohesive QoS framework right from the device to the core, mapped effectively into TSN streams.
- Convergence of IT and OT
Bridges the gap between Operational Technology (OT) and Information Technology (IT) networks in various industries.
- Flexibility and Scalability
Cuts down on the need for extensive wiring, supporting large-scale, cost-effective setups.
TSN over 5G: Industrial Use Cases
Smart Factories
Real-time control of robots via reliable wireless connections.
Augmented Reality (AR) for maintenance tasks with guaranteed low latency.
Automotive
Expanding in-vehicle communication through 5G for coordinated driving.
Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication with TSN guarantees.
Energy and Utilities
TSN-enabled smart grids ensure dependable power distribution and grid synchronization.
Healthcare
Real-time patient monitoring and remote robot-assisted surgeries boasting low latency and reliability.
TSN over 5G vs Traditional Ethernet TSN
Feature Ethernet TSN (Wired)TSN over 5G (Wireless)Mobility Not supported Fully supported Latency Deterministic, very low Deterministic with 5G URLLC Deployment Cost High (extensive cabling)Lower (wireless, scalable)Coverage Limited to physical cabling Wide-area, indoor and outdoor Scalability Limited by wiring constraints High, supports thousands of nodes Use Cases Industrial automation, AVB Industry 4.0, robotics, V2X, IoT
Challenges in Implementing TSN over 5G
Even though the promise is there, integrating TSN into 5G comes with its hurdles:
Synchronization: Keeping precise timing across wireless connections is tricky.
Resource Allocation: Needs sophisticated scheduling algorithms in the gNB for managing TSN traffic.
Standardization: Full integration of TSN and 5G relies on evolving standards from 3GPP.
Cost: Requires advanced hardware and network upgrades to achieve reliable performance.
Future Outlook: TSN and 6G
As we move past 5G and into 6G development, TSN is likely to stay at the forefront of deterministic communications. Here's what we can expect:
Improved Synchronization Methods: Better precision for industrial uses.
AI-driven QoS Management: Smarter resource allocation that adapts to traffic patterns.
Edge Integration: Merging TSN with edge computing for super-fast responses.
Broader Standards: A wider embrace of TSN-5G standards across sectors.
Conclusion
TSN support in the 5G system is a crucial milestone in fostering ultra-reliable, low-latency communication across wireless networks. By carrying Ethernet-based TSN traffic with solid end-to-end QoS guarantees, 5G extends deterministic networking to mobile, scalable, and adaptable environments.
From smart factories and self-driving vehicles to power systems and healthcare, TSN over 5G is opening up exciting opportunities in Industry 4.0 and crucial communications. There are still some challenges to tackle, but the future points to a world where TSN and 5G (and eventually 6G) intersect to deliver seamless, reliable, and mobile connectivity for all sorts of demanding applications.
