Understanding 5G Disaggregation Options: Option 2 vs Option 7 and Their Variants
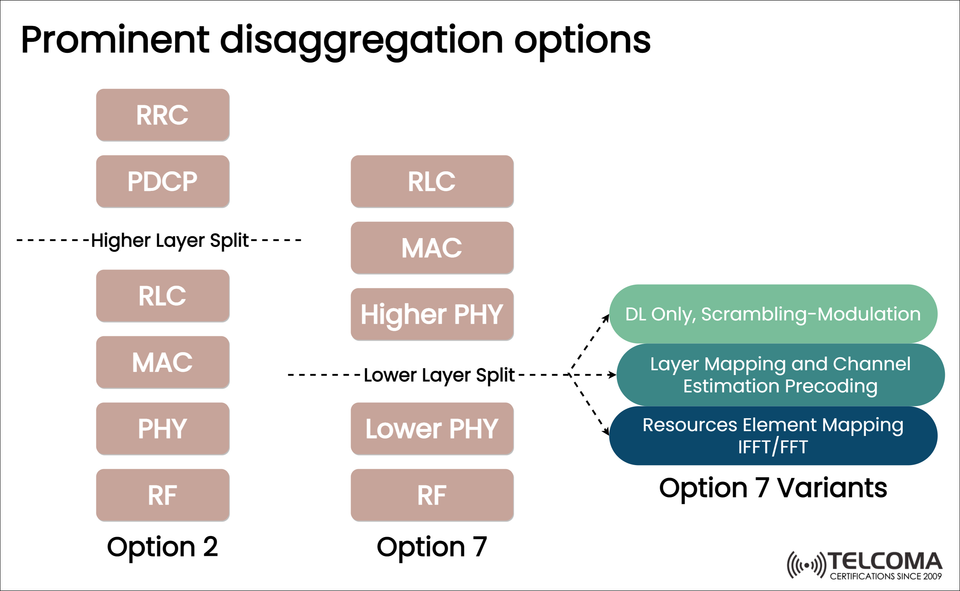

🔍 Principal Disaggregation Choices in 5G: Understanding Option 2, Option 7, and Their Options
As we move forward with the advancement of 5G and Open RAN architectures, the ability to effectively disaggregate the RAN (Radio Access Network) will become crucial to develop flexible, vendor-neutral and cost-efficient networks. Disaggregating the RAN protocol stack allows you to separate the functional blocks of the RAN, to allow different vendors or components to take the responsibility of certain layers. In this blog, we explore the principal Option 2 and Option 7 splits, along within their Options – see the image above.
📦 What is RAN Disaggregation?
RAN disaggregation is the act of decoupling the RAN protocol stack into neutral, deployable units, which will provide flexibility of deployment and interoperability. It is essential for:
Open RAN Architectures
Cloud-native RAN deployments
Lowering CAPEX/OPEX through functional splitting deploys
The splits are standardized through 3GPP and ORAN Alliance with the current most used splits being Option 2 and similar Option 7 splits.
📘 Option 2: Higher Layer Split
The Option 2 definition indicates a split occurs and between the PDCP and RLC layers of the protocol stack.
🔹 Functional Split:
Layer Placement
RRC, PDCP Central Unit (CU)
RLC, MAC, PHY, RF Distributed Unit (DU)
🔹 Characteristics
Interface: F1
Most widely utilized in 5G NSA, SA deployments
Centralized control with distributed radio processing, which simplifies CU-DU integration + vendor
🔹 Applications:
Centralized synchronization
Enhanced mobility management
Cloud-native CU's
🔹 Functional Split:
Layer Location
RRC to Higher PHY Central Unit (CU) or DU
Lower PHY, RF Radio Unit (RU)
🔹 Interface: Eg. ORAN Fronthaul (eCPRI, Open Fronthaul)
🔹 Benefits
Good for Open RAN deployments
Lowers fronthaul bandwidth as compared to Option 8 (CPRI)
Supports intelligent RU with offload of lower PHY
🧬 Option 7 Variants
The cut or split in Option 7 can be further categorized depending on where the cut is made within the PHY-layer:
Variant Description
DL Only, Scrambling-Modulation CU/DU performs as above (to modulation); RU does the rest
Layer Mapping and Channel Estimation Pre-coding Split at channel estimation and precoding functions
Resource Element/RE Mapping / IFFT/ FFT Fine-grained split at RE mapping and FFT functions
📍 How variants matter
These variants allow for some flexibility in deployment especially in the case of fronthaul constraints. This is important as the vendor can simply choose the split point depending on:
Latency constraints
Transport Network capabilities
Cost-performance thresholds
📊 Option 2 vs Option 7: Comparison Table
Feature Option 2 Option 7
Split Point PDCP-RLC PHY-PHY
Interface F1 eCPRI or proprietary
Level of Centralization High Medium
Fronthaul Requirement Moderate Stringent
Open RAN Suitability Moderate
Conclusion
The emergence of 5G disaggregation is transforming the telecommunications ecosystem, allowing for flexibility, scale, and multi-vendor deployment options. We are specifically excited about the roles that Items 2 and 7 will play:
Item 2 is all about providing a better experience with centralized, software-only deployment.
Item 7 and its variants are about enabling granular control of the RAN and optimizing fronthaul in Open RAN deployments.
Deployment Implications for Item 2 and Item 7
Item 2 - Centralized Deployment Model
Item 2 was generally for Cloud-RAN deployments in centralized Radio Access Networks (RAN) where the CU is placed closer to the core network or as a dedicated instance in cloud data centers. The Cloud-RAN deployment model has certain efficiencies to offer:
Simplified transport: The F1 interface is more permissive to higher latencies (10-20 ms).
Cloud-native CU deployment: Cloud-native CU facilitates scalability, automation, and cost reductions.
Simplified integration process for the vendors: A centralized CU allows the network operator to mix and match DU and CU vendor product offerings and improves their prospects for identifying a suitable Open RAN.
Deployment Advice: Centralized deployment is ideal for a scenario where there is a suitable urban area for centralized CU with good backhaul and central office resources.
Item 7 - Distributed Deployment with Fronthaul Efficiency
Item 7 deployment is essential for fronthaul optimization and other low-latency scenario deployments such as:
Smart factories
Smart stadiums
Urban densities
Since Item 7 splits the PHY, Item 7 deployments require:
Time-sensitive fronthaul transport (1 ms or less).
Genealogy synchronizing hardware between DU and RU (via IEEE 1588v2 or GPS).
More sophisticated RU hardware less PHY processing.
🤝 Vendor Ecosystem and Industry Adoption
Open RAN and O-RAN Alliance
The O-RAN Alliance is a strong proponent of Option 7.2x, as the open fronthaul interface specification for O-RAN allows multi-vendor interoperability across:
Distributed Units (DUs)
Radio Units (RUs)
Open RAN vendors like Parallel Wireless, Mavenir, and Rakuten Symphony are actively deploying Option 7 variants in their disaggregated RAN solutions.
Cloud Providers in CU Deployments
Hyperscalers (e.g. AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) preferred Option 2 based on their existing cloud infrastructure so that both CU and parts of DU functions can be deployed in cloud regions. They would allow the CU component to connect to DU options in order to integrate into a core and transport layer essentially by allowing a centralized approach.
🔮 Future Trends in RAN Disaggregation
As 5G evolves and 6G emerges, watch for:
- Dynamic Split Selection
AI/ML-driven selection of split points based on real-time network conditions. - 6G Intelligent RAN (xRAN)
Will continue moving toward more disaggregated models, even split functions; capabilities such as function-as-a-service will be possible.
Also next-generation architectures with advanced splits that adapt streams in real-time in conjunction with cloud-edge convergence. - Integration with RIC (RAN Intelligent Controller)
In Open RAN, the RIC will enable additional orchestration and optimization of split functions, applications of RIC will be most relevant under Option 7 architectures.
📌 Final Takeaways
Key Takeaway Details
Option 2 High-layer split, suitable for central deployment in the cloud, and the F1 interface
Option 7 Lower-layer split, allows for fronthaul optimization and RU-DU separation
Variants of Option 7 Ability to set fine-grained controls, flexibility, and performance tuning
Open RAN Alignment Option 7.2x is the best example of aligned Open RAN fronthaul interfaces
Future-proofing Disaggregated architecture allows for software driven RAN, AI driven orchestration, and cloud-native evolution
