Understanding 5G MEC System Architecture: Components, Functions, and Benefits

🧠 In-Depth: 5G MEC System Architecture
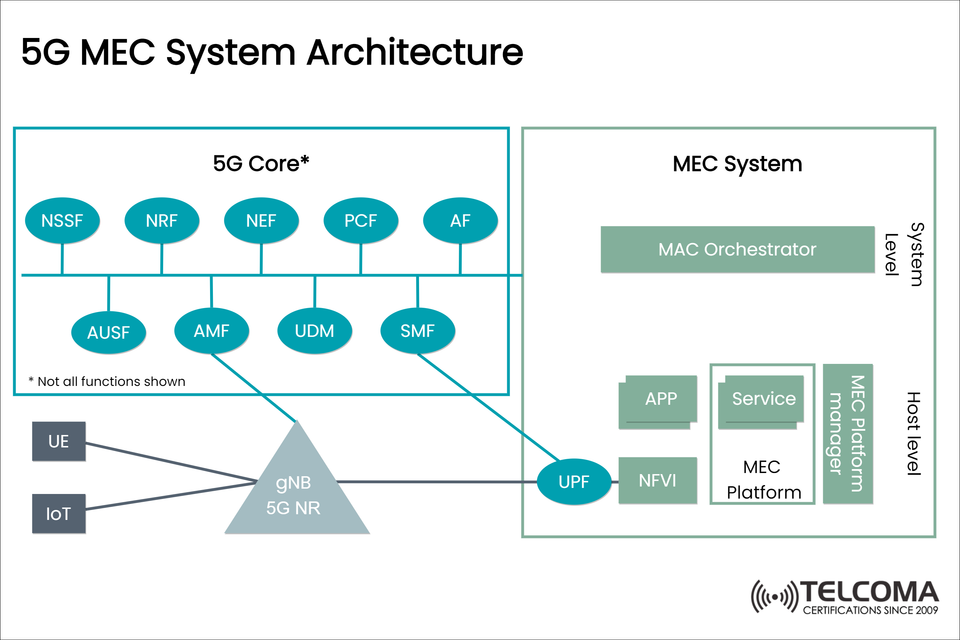
As 5G networks are growing in scope and scale, Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) is going to be very important in order to achieve ultra-low latency, localized processing, and real-time services. In this blog post I will provide a close look into the 5G MEC system architecture based on the diagram that I uploaded above.
Whether you are an architect, RAN engineer, or strategic telecom consultant, you want to understand how MEC is laid out and how it operates so that you can deliver edge-native applications and ensure service level agreements (SLAs) are intact.
📌 What is 5G MEC?
Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) allows cloud-computing capabilities to be closer to the user by moving network functions and application processing to the edge of the network at or around the gNB (5G NR base station). This decreases latency and enables context-aware services.
🧱 5G MEC System Airthitecture: Main Components
The architecture is divided into two main domains:
🔹 1. 5G Core Network
This includes control plane and user plane functions identified by 3GPP specifications. In the image, the main components are as follows:
Function Description
NSSF Network Slice Selection Function
NRF Network Repository Function
NEF Network Exposure Function
PCF Policy Control Function
AF Application Function
AUSF Authentication Server Function
AMF Access and Mobility Management Function
UDM Unified Data
🔹 2. MEC System
The MEC portion takes care of running applications and services as roles at the edge of the network. It is further categorized into:
🏗 Host Level Components
NFVI (Network Function Virtualization Infrastructure): the physical tier in a virtualized layer.
MEC Platform: the way that the edge applications run.
MEC Platform Manager: takes care of the lifecycle of the platform and its configuration.
Applications: these include the services offered like XR, V2X, cloud gaming, video analytics, etc.
⚙ System Level Components
MAC Orchestrator: it manages the MEC environment across sites and across nodes; manages and ensures resources are used accordingly.
🔌 How It All Connects
The data flow looks like this:
UEs and IoT Devices connect to the gNB.
Control plane signaling is controlled by the 5G core (AMF, SMF, PCF etc.).
User plane traffic gets routed through the UPF to the MEC platform.
MEC Applications can process data locally or together with the cloud.
In each case, the MEC environment enables network slicing, service awareness, and contextual processing at the very edge—which can be applied to mission-critical use cases.
🚀 Why 5G MEC Is Important: Value and Use Cases
🌍 Value
Ultra-low latency (for immediate, real-time applications)
Reduced number of load on the core network network
Better availability, reliability, and QoS
Content delivery closer to users
Greater data privacy and sovereignty
📦 Use Cases
- Autonomous driving (V2X)
- AR/VR & cloud gaming
- Industrial automation & robotics
- Video analytics & surveillance
- Smart grids & utilities
📈 MEC in the Wider 5G Ecosystem
MEC isn't a standalone new technology. It works with technologies such as:
- vRAN and O-RAN: Allows for deployable network functions that can be dynamically deployed.
- Network Slicing: Support different industry requirements for the edge services.
- AI/ML at the Edge: Enables predictive analytics and possibly automation.
As illustrated in the picture above, MEC enables seamless operational and functional interoperability with the Service-Based Architecture (SBA) of the 5G core and associated ecosystem with the ability to efficiently scale.
🛠️ Architectural Design Considerations for 5G MEC Implementation
To implement MEC is much more than putting the equipment or servers in the same physical location as the gNBs. Below are the following design considerations and challenges;
✅ Critical Design Considerations
Traffic Steering: Leverage UL CL (Uplink Classifier) and PDU session anchoring with UPF to redirect traffic at the edge to MEC (local).
⚠️ Issues of MEC Implementation
Issue Mitigation Plan
Placement of network functions Adopt a hierarchical MEC use case with Central/Edge tiers
Application orchestration Use ETSI-compliant MEC Orchestrators
Integration with existing infrastructure Implement hybrid MEC–cloud models with interworking
Mobility & session persistence Utilize context transfer
📡 Use Cases for 5G MEC
5G MEC is of greatest value when implemented as latency-sensitive and data-intensive workloads, and here it is easy to see how many industries benefit from these innovations:
🚗 Automotive (V2X)
MEC enables local processing of vehicle data for applications such as cooperative collision avoidance and real-time communication with traffic signals.
🕶️ Augmented & Virtual Reality
Edge rendering processes visuals on local edge compute, which helps minimize lag time for XR situational awareness, such as when used for training simulations, remote collaboration, using telemedicine, or even participating in remote surgery.
🏭 Smart Manufacturing
MEC provides deterministic latency for robotic control, Machine vision, Predictive maintenance, etc.
🏥 Healthcare
MEC enables diagnostic imaging and remote robotic surgery by processing data locally.
🔄 The UPF Role in MEC Implementation
One of the greatest challenges of MEC integration is to utilize the User Plane Function (UPF) for local data breakout.
🔹 UPF Activities in MEC:
Termination of user plane traffic for PDU sessions
Forwarding packets to MEC applications/platforms
Anchoring PDU sessions in architectural context for localized services
Routing of traffic, QoS enforcement, and buffering.
🧰 MEC System Components Overview
There is a summarized table displaying the MEC System components and their roles:
Component Layer Function
MAC Orchestrator System Level Manages multiple MEC hosts and resources
MEC Platform Host Level Runs edge apps and exposes APIs
MEC Platform Manager Host Level Manage MEC app lifecycle and configuration
NFVI Host Level Provides compute/storage resources
Edge Apps/Services Host Level Real MEC applications (e.g. analytics and AR)
🔮 MEC Future in 5G and Beyond
MEC is important to being 6G ready and supports AI-driven networks, autonomous systems, and real-time digital twins. Here are elements to monitor:
Federated Edge Clouds that interconnected MEC nodes across domains (e.g. enterprise, municipality, etc.)
✅ Conclusion
5G MEC System Architecture is the foundation layer of future telecom service products and services. It changes how and where data is processed using the network from a more compute-in-the-network paradigm. It adds intelligence no longer needing to reside in centralized data centres. The MEC transition of intelligence to the edge of the network to process data is hoped to deliver lower latency and new applications and service experience benefits regardless of verticals.
