Understanding 5G NR RRC Reconfiguration Procedure: Step-by-Step Signaling Explained

5G NR RRC Reconfiguration: A Step-by-Step Signaling Guide
The 5G NR RRC Reconfiguration process is essential for setting up the radio connection and enabling data sessions for User Equipment (UE). It links the radio access network (gNB) to the 5G Core (5GC), which helps to ensure smooth service delivery and the setup of PDU sessions.
This article outlines each step of the process, using the signaling diagram provided to illustrate the interactions between UE, gNB, and various 5GC components like AMF, SMF, and UPF.
Understanding RRC Reconfiguration in 5G
The Radio Resource Control (RRC) protocol manages signaling between the UE and gNB. When registering and establishing a session, RRC Reconfiguration messages are exchanged to set up radio bearers, measurement parameters, and security contexts.
In the 5G environment, RRC Reconfiguration is usually initiated after the UE receives the NAS Registration Accept message from the AMF through the gNB. This transition ensures the UE goes into connected mode with all necessary configurations in place for data communication to begin.
Key Players in RRC Reconfiguration
Entity Description
UE (User Equipment): The 5G device asking for network access and configuration.
gNB (Next Generation NodeB): The 5G base station that manages radio resources and communicates signaling to the 5GC.
5GC (5G Core Network): Includes AMF, SMF, UPF, PCF, and AUSF, responsible for session management, mobility, authentication, and policy control.
Explaining the Signaling Flow
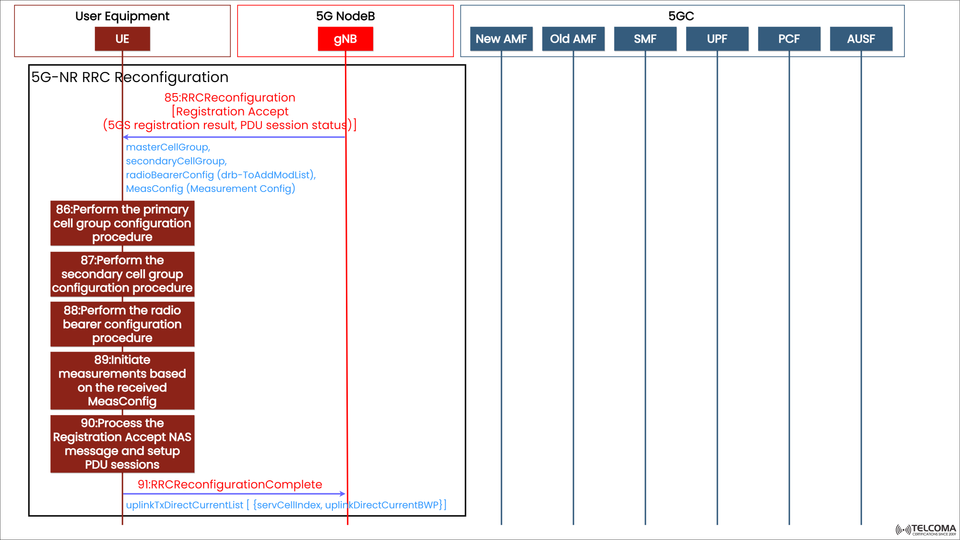
The diagram displays the signaling flow for 5G NR RRC Reconfiguration, mainly concentrating on the interaction between UE and gNB, while the 5GC components remain inactive during this phase.
Key steps involve:
Step 85: RRC Reconfiguration Message (Downlink from gNB to UE)
Message Name: RRC Reconfiguration
Purpose: Carries the Registration Accept message and prepares the UE for further operations.
Contents:
master Cell Group
secondary Cell Group
radio Bearer Config (drb-To Add Mod List)
Meas Config (Measurement Config)
5GS registration result and PDU session status
This message lets the UE know:
The network has accepted its registration.
Which bearers and radio configurations need to be established.
The measurement configurations necessary for mobility and handover decisions.
Essentially, it’s the instructions from the network for the UE setup and data session start.
Step 86: Configuring the Primary Cell Group
Once the UE gets the RRC Reconfiguration message, it starts the configuration process. First up is the primary cell group — this involves setting up the master cell group (MCG), which is responsible for:
Control-plane signaling.
Core network access via the primary cell.
Managing the serving cell.
This ensures the UE connects to the main anchor cell that handles the signaling and initial traffic.
Step 87: Configuring the Secondary Cell Group
Next, if dual connectivity or carrier aggregation is supported, the UE will configure the secondary cell group (SCG).
The SCG is usually connected to another gNB or an additional cell to enhance throughput and coverage. This enables:
Split bearer operation.
Load balancing between cells.
Improved data rates via NR-DC (Dual Connectivity).
Step 88: Setting Up the Radio Bearer Procedure
Here, the UE prepares the Data Radio Bearers (DRBs) based on the configuration provided in the message. Each DRB is tied to a data session (PDU session) and specifies:
Logical channel mapping.
QoS parameters (QoS Flow IDs).
Security and integrity protection.
These bearers create the data path for user-plane traffic between the UE and UPF (via gNB).
Step 89: Starting Measurements Based on Meas Config
The Measurement Configuration (Meas Config) part of the RRC Reconfiguration message tells the UE to start network measurements. Generally, these include:
RSRP (Reference Signal Received Power)
RSRQ (Reference Signal Received Quality)
SINR (Signal-to-Interference-plus-Noise Ratio)
These measurements help the network decide when to execute a handover or beam switching for optimal connectivity.
Step 90: Processing NAS Registration Accept and Setting Up PDU Sessions
This step connects the radio and core domains. The UE processes the NAS Registration Accept (found within the RRC Reconfiguration message) and starts setting up PDU sessions with the 5G Core.
NAS layer handles the 5GS registration confirmation.
Session Management Function (SMF) and User Plane Function (UPF) get engaged via the gNB for establishing the data path.
Once the PDU sessions are live, the UE can send IP packets through the 5GC.
In short, this step finishes the end-to-end connection between the UE and the data network.
Step 91: RRC Reconfiguration Complete (Uplink from UE to gNB)
When all configurations are successfully applied, the UE responds with an RRC Reconfiguration Complete message to the gNB.
This message confirms that:
Cell group configurations worked.
Radio bearers are up and running.
Measurement configurations are active.
PDU sessions are set up and operational.
It includes parameters like:
uplink Tx Direct Current List {serv Cell Index, uplink Direct Current BWP}
This acknowledgment signifies that the RRC Reconfiguration phase is successfully completed.
Importance of RRC Reconfiguration in 5G
The RRC Reconfiguration process is crucial for multiple reasons:
✅ It allows UE to shift from registration to active data communication.
✅ Sets up radio bearers with distinct QoS configurations.
✅ Establishes measurement parameters for mobility and radio optimization.
✅ Integrates NAS procedures (like registration accept) with the RRC setup.
✅ Supports dual connectivity and flexible spectrum usage.
Comparing LTE and 5G RRC Reconfiguration
FeatureLTE5G NR Bearer Type DRB, SRBSRB, DRB with QoS flows Network Entities e NB, MM Eg NB, AMF, SMFNAS Embedding Registration Accept (Attach Accept)5GS Registration Accept Dual Connectivity Limited (EN-DC)Native NR-DC Support Measurement Control Cell-specific Beam and cell-level measurements
The 5G NR RRC Reconfiguration takes what LTE had and builds on it with features like beam-based measurements, QoS flow mapping, and multi-cell coordination, boosting flexibility and efficiency.
Practical Considerations for Engineers
For telecom professionals, getting a handle on this procedure is essential for:
Network optimization: Tuning measurement configurations to enhance mobility.
Troubleshooting: Pinpointing problems in registration or PDU session setups.
Testing & simulation: Validating UE reactions during configuration and connectivity phases.
5G network planning: Ensuring a smooth integration between RAN and Core.
Conclusion
The 5G NR RRC Reconfiguration procedure is fundamental to 5G connectivity. It bridges the radio and core domains by configuring the UE, establishing bearers, and enabling end-to-end PDU sessions.
From registration acceptance to session activation, each step ensures the UE is ready to efficiently and securely exchange user-plane data. For network engineers and telecom experts, mastering this process is vital for optimizing 5G performance and providing a seamless experience for users.
