Understanding 5G System Architecture: 5G Core Services (SBA) + IMS Core Explained

Demystifying 5G Core Architecture: Service-Based Architecture (SBA), and the IMS Core
As 5G continues to cause disruption (and there is likely more to be expected), in addition to other industry players promoting their 5G capabilities, it will be important for all those who are coming to grips with not only 5G but its supporting 5G Core architecture to understand everything that 5G is to offer.
5G Core - Overview and Synthetic Architecture
The 5G Core (5GC) is based off and has leveraged a Service-Based Architecture (SBA), which is a more modern and cloud-native architecture that offers higher levels of flexibility, scalability and interoperability in mobile networks than previously seen in any other generation of architecture.
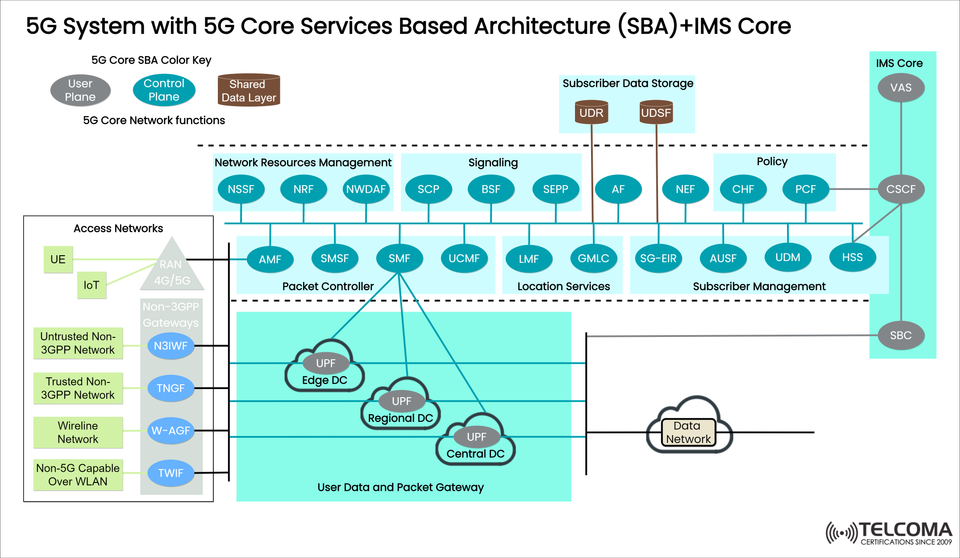
In this post, we will illustrate and explain what the image shown represents, and will outline how the 5G SBA infrastructure can fit into the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) Core to create a strong and performant core network.
What is NOT Service-Based Architecture (SBA)?
SBA is the foundation of the 5G core network (5GC), and was divided into the massive connectivity, ultra-low latency, and the enabled use of network slicing.
The previous networking paradigm, network functions (NFs) would use either Diameter or SIP, or some other protocol to allow one NF to talk to another NF; with Service-Based Architecture, communication between services is modular and service-oriented.
🔑 Key Takeaways:
- decoupled architecture that allows scale independently
- cloud-native functions that allows containerized deployment
-support for Network Slicing - inter-service communication is simplified
Core Elements of 5G SBA + IMS Core Architecture
As shown in the image, we have presented a complete high-level overview of the 5G core, with the general division of Control Plane/ User Plane/ Shared Data Layer. For a brief review of the architecture, component by component:
- Access Networks (AN)
User Equipment (UE) connects via:
RAN (Radio Access Network) – 4G/5G
Non-3GPP Gateways (for example, N3IWF, TNGF, W-AGF, TWIF)
IoT and wireline networks
Covers trusted and untrusted non-3GPP access
- User Plane Function (UPF)
User data and packet routing to/from data networks
Hosted in:
Edge DC (low latency)
Regional DC
Central DC
- Control Plane Functions (Blue in Image)
Session management and signaling and mobility functions:
Function Description
AMF access and mobility management
SMF session management function
SMSF sms over nas support
AUSF authentication server
UDM user data management
PCF policy control function
CHF charging function
NEF network exposure function
AF application function
NRF NF repository function
NSSF network slice selection
NWDAF analytics function
BSF binding support
SEPP security edge proxy
LMF location management
UCNF / UCMF unified charging/configuration management
GMLC, SG-EIR location and equipment identity
SCP service communication proxy
1. Shared Data Layer
UDR (Unified Data Repository) is where subscriber and policy data is stored.
UDSF (Unstructured Data Storage Function) is where temporary or application specific data is stored.
IMS Core Integraton
5G's IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem) provides signal based service for voice services, video services, and messaging services:
• CSCF (Call Session Control Function): The basic Core SIP signaling
• SBC (Session Border Controller): Service based management of borders for media and signaling
• HSS (Home Subscriber Server): Legacy user authentication
• VAS (Value Added Services): Value Added services
IMS only works with 5GC for VoNR (Voice over New Radio) and multimedia/voice services over 5G.
Why Does SBA + IMS Core Matter for 5G
This network architecture allows service providers to provide many new opportunities for:
• Seamless scale with cloud-native network functions (NFs)
• Fast and reliable services with UPFs local to the service delivery
• Latency and performance of applications including voice services
• Secure and robust security and policy management
• Interoperability against many vendors and network types
Conclusion
The intrinsic value of 5G Service-Based Architecture (SBA) and IMS Core, combining the promises of 5G connectivity from ultra-fast data connections, to user experience improvements to real-time and scalable services is giving operators the ability to create agile, high-performance networks for the future.
If you work in telecommunications, or are simply interested in the telecommunication space, understanding this architecture is important to see how 5G is changing communications globally!
Keywords:
5G SBA, 5G Core Network, IMS Core, Service Based Architecture, UPF, SMF, AMF, NRF, Network Slicing, VoNR, Telecom Architecture, 5G Components.
Deployment Approaches for a 5G SBA and IMS Core
As operators transition to fully cloud-native deployments, it is important to understand how to design SBA and IMS elements.
✅ Recommendations for Deployments
Edge-first UPF Deployments: users can benefit from low-latency applications (e.g. AR/VR, autonomous vehicles)
Centralized UDR/UDSF: keeps subscriber data centralized for user access and policy control
Containerized NFs: Supports microservices, allowing for independent updates and scaling
Multi-cloud or hybrid deployments: provides resiliency, scale, and compliance with applicable regulations
Security Considerations for an SBA-based 5G Core
5G security is a significant concern, as it becomes more exposed with more APIs and integration points.
🔐 Security Layers for 5G Core:
SEPP (Security Edge Protection Proxy): protects inter-PLMN traffic (i.e. roaming)
NEF: controls exposure to external applications
AUSF + UDM + PCF = provides authentication, user profiling, and policy enforcement.
TLS(Transport Layer Security): protects all SBA service communication.
5G Core and IMS Core Interworking: Why this is important
It is important to emphasis that while SBA takes care of data and control functions, IMS is still critical as the most popular 5G services (voice, messaging, and video, etc) are imagined to be provided via IP data over the 5G core. This connection of SBA to IMS components (CSCF, HSS, SBC, VAS) enables total service support from the 5G standalone (SA) architecture.
What is Next: Evolution of SBA and IMS Core in 6G
While 5G SBA and IMS are on the cutting edge today, they are also foundational pillars for 6G where even more AI/ML driven autonomous networking will evolve.
Looking Ahead:
Complete AI-native core functions (NWDAF evolution)
Real-time orchestration and automation
Quantum-safe encryption standards
Increased integration with satellite networks and NTN (Non-Terrestrial Networks)
