Understanding A1 Interface and AI Integration in O-RAN Architecture
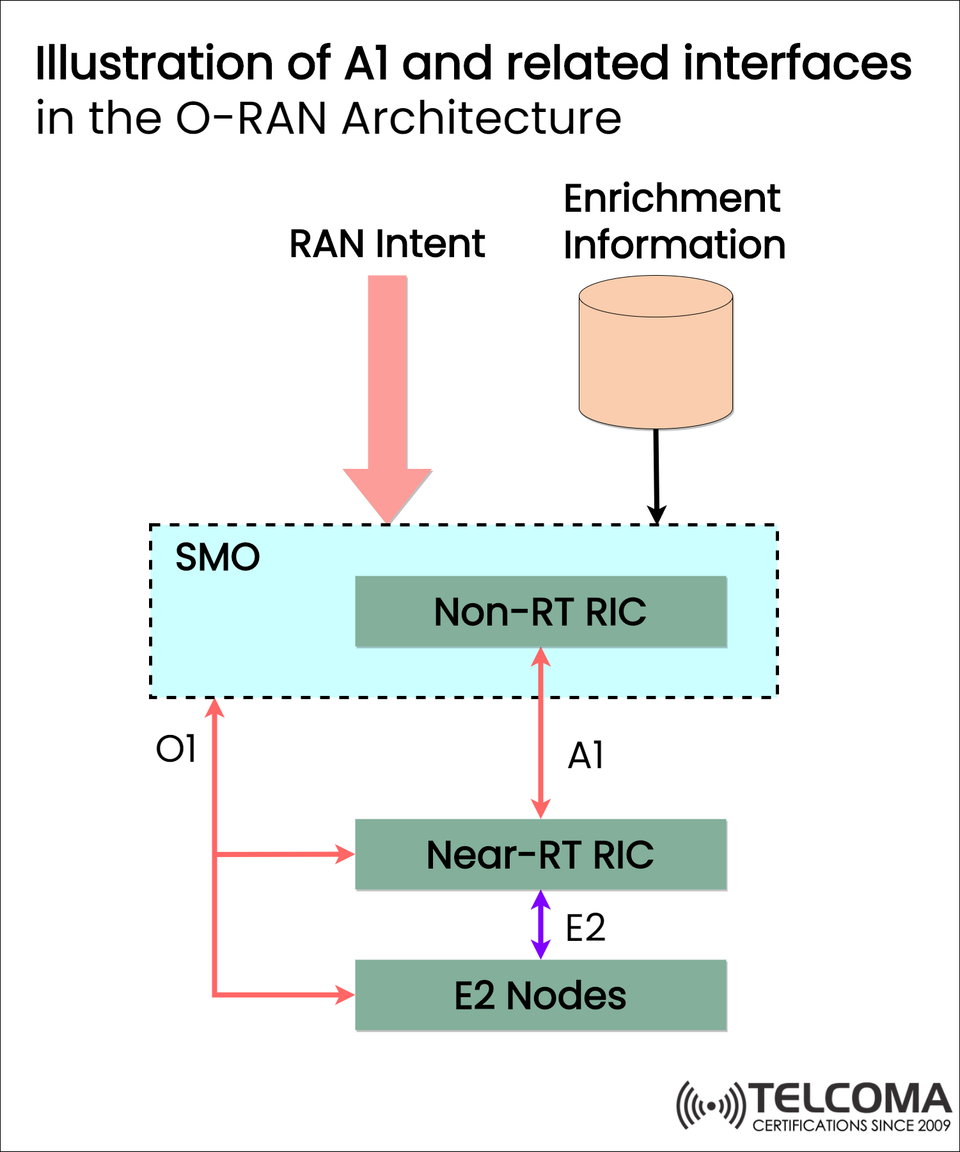

🔍 A Closer Look: A1 interface and AI in the O-RAN Architecture
As 5G necessitates networks that are increasingly smart and dynamic, Open RAN (O-RAN) introduces several powerful components such as the A1 interface and RIC (RAN Intelligent Controller). These components enable the application of AI to make intelligent decisions for both real-time and non-real-time network optimization.
The video description included a diagram with a simplified but accurate depiction of the AI-related interfaces of the O-RAN architecture, namely, how the A1, O1, and E2 interfaces evolved together between the various RIC layers and E2 Nodes.
🧠 O-RAN AI Architecture Components Defined
- 🟦 SMO (Service Management and Orchestration)
- Centralized Management layer of the O-RAN.
- Handles the O1 interface to manage and configure E2 nodes and RIC(s).
- Informs Non-RT RIC of RAN intent.
- Incorporates information from outside data sources, e.g. enrichment.
- 🟩 Non-RT RIC (Non-Real-Time RAN Intelligent Controller)
- Operates outside of 1 second timescale.
- Creates AI/ML model training, policy creation, long term optimization.
- Informs Near-RT RIC of policy and guidance behavior through A1 interface.
- Ingests enriching data, like traffic patterns, subscriber behavior.
- 🟦 Near-RT RIC (Near-Real-Time RIC)
- Operates in a timescale of 10 ms to 1 second.
- Executes xApps for RRM (Radio Resource Management) and SON (Self Organizing Network) functions like load balancing, handover optimization.
- Receives xApps from the O-RAN architecture.
- E2 Nodes
Moves distributed network functions (gNodeBs, O-RAN components).
Facilitate control decisions and telemetry to Near-RT RIC.
Directed (in part) by O1 from SMO.
Key Interfaces in O-RAN AI workflow
Interface Role Participants
A1 Policy-based control and guidance Non-RT RIC ⇄ Near-RT RIC
O1 Configuration and fault/performance management SMO ⇄ E2 Nodes, RICs
E2 Real-time control, telemetry and feedback Near-RT RIC ⇄ E2 Nodes
Ai Role in O-RAN architecture
Model Training: AI/ML models in the Non-RT RIC are trained with enrichment data (traffic patterns, network KPIs)
Policy Guidance: AI/ML models generate policies which are pushed down to the Near-RT RIC via the A1 Interface ready for execution.
Dynamic Optimisation: The Near-RT RIC evaluates established real-time xApps which fine-tune RAN parameters in response to AI input.
Feedback Loop: E2 Nodes relay information back through the E2 into the Near-RT RIC providing feedback to enable a closed-loop optimisation loop.
Benefits of A1 and AI Integration in O-RAN
Vendor agnostic optimisations built on standardized interfaces.
Centralized intelligence created from AI driven policies.
Flexible RAN orchestration across multi-vendor consortiums.
Closed-loop automation enables real-time variations in response to actual network conditions.
Conclusion: Pathway to Autonomous RAN
The combination of AI and the A1 interface in O-RAN is a huge step towards self-optimizing, open, intelligent 5G networks. With distinct boundaries between the Non-RT and Near-RT layers as outlined in O-RAN specifications, operators can create automation opportunities, lower costs, and improve performance in heterogeneous RANs.
Architecting next generation RAN systems involves telecom architects, network engineers and AI practitioners, all of whom need to be cognizant of the A1 interface and its role.
Real World Examples of A1 Interface in O-RAN
A1 is not simply a concept - it is already being deployed in the real world across numerous unique and interesting contexts where telecom operators are investing in open, disaggregated, and intelligent networks. Here are the notable examples:
Closed-Loop Automation
A1 enables the Non-RT RICs to send policies to the Near-RT RICs which can utilize its real-time telemetry to take near real-time action. This creates a 'closed-loop' between the long-term insights gained by AI and the immediate actions taken in real-time based upon those insights.
Traffic Steering and Load Balancing
Operators are using AI models leveraging Non-RT RICs to predict high traffic areas. These signals are forwarded via the A1 interface to the Near-RT RIC where the xApps can update.
📚 Major Standards and Governance Organizations
O-RAN Alliance: Defines RIC specifications and A1/E2/O1 interfaces.
3GPP: Provides complementary standards across RAN's functionality that O-RAN depends on.
ETSI ZSM & ONAP: Worked on SMO, and zero-touch orchestration principles that are relevant to O-RAN deployments.
🔐 Security Considerations in A1 and AI
While A1 provides new flexibility in the management of RANs, it still requires a strong security model:
Policy Integrity: Ensure only authorized and validated policies are pushed from Non-RT to Near-RT RICs.
Interface Security: All A1 communications should be across an encrypted communications channel (e.g., TLS or equivalent).
Model Explainability: AI models being utilized for decision making in RAN must be auditable to ensure there is no unintended behavior.
🛠 Future Improvements coming
Dynamic A1 Policy: Allows A1 policy to be changed dynamically without reboot or disruption.
Federated Learning: Allowing AI models to be trained across numerous sites while preserving data privacy.
Multi-domain: A1 policy must be able to coordinate across RAN/core/transport layers for end-to-end service.
Why the A1 Interface is the Cornerstone of Modern RAN
Component Role
SMO Manages complete O-RAN ecosystem through O1
Non-RT RIC Manages AI/ML models, long-term strategy
Near-RT RIC Manages medium-term strategy
RAN Delivers services on radio environment
O-RAN Delivers services across the entire RAN architecture.
🔮 Final Remarks
The A1 interface, with Non-RT and Near-RT RICs, is the forward-looking end game for smart, agile and AI-based 5G networks. It's not just about performance improvements, it is a key enabler of unprecedented levels of automation, flexibility, and openness across telecom infrastructure.
For operators, integrators, and developers of AI, it will be crucial to understand how A1 will be the enabler of intelligent coordination in order to build the next generation of scalable and resilient mobile networks.
✅ Summary:
The A1 Interface as the Enabler of AI-led RAN
With the continued realization of 5G, the desire for intelligent, flexible, and automated RAN operations will be paramount in the operating model. The A1 interface in O-RAN architecture can play a critical role to:
Connect long-term, AI-driven insights with near-real-time network control
Support disaggregation and vendor agnostic approaches
Enable policy-driven RAN optimization and automation
Improve scalability through centralized intelligence and decentralized execution
For telecommunications operators and network strategists, effective latitude of the A1 interface will truly enable the advancement of Open RAN - not just for reduced costs, but of smarter, more effective, and flexible wireless networks.
🔍 SEO Summary & Quick Reference
🔑 Key Concepts:
A1 interface O-RAN
Non-RT RIC and Near-RT RIC
AI in 5G RAN
RAN automation architecture
E2 interface O-RAN
Service Management and Orchestration
