Understanding Cisco SD-WAN Architecture: Management, Control, and Data Planes Explained

🛰️ Introduction: Today's Enterprise Network Dilemma
As enterprises become even more distributed and cloud-native, the traditional WAN architecture, which is inflexible, complex, and costly, can no longer keep pace. Software Defined WAN (SD-WAN) offers a way forward, allowing organizations to take control of the traffic going into and out of their networks and provide a means to leverage a wide variety of circuits while simplifying the overall WAN architecture.
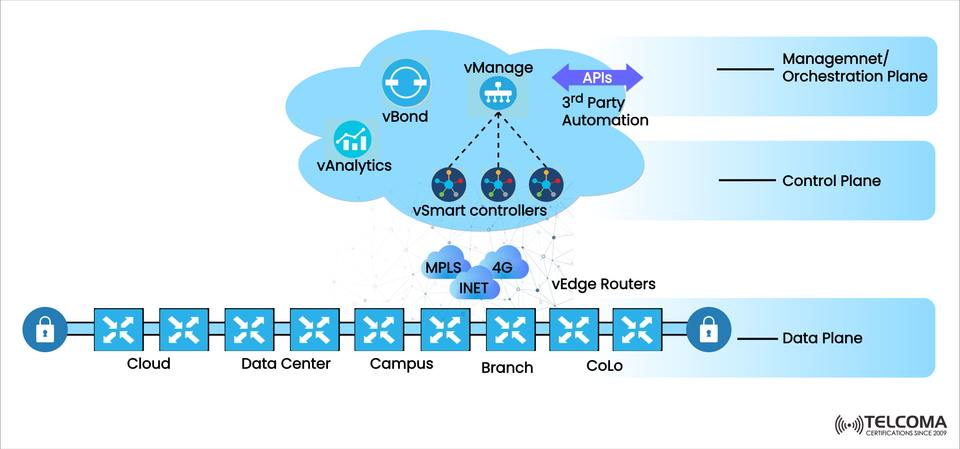
In this blog I will demonstrate how Cisco's SD-WAN architecture works, shown in the diagram above and break down each section consisting of management, control and data planes.
🔍 Overview of Cisco SD-WAN Architecture
Cisco's SD-WAN solution consists of several architectural components and functions that are distributed across three distinct planes:
📊 1. Management/Orchestration Plane
Component: vManage
This plane consists of centralized configuration, monitoring, policy creation, and managed access to a dashboard.
Key Functions:
Centralization of GUI/CLI to manage vEdge routers and controllers
API interfaces to utilize third-party automation
Push policies to vSmart controllers
Other tools found in this plane:
vAnalytics: Provides insight into performance and suggestions for WAN optimization
APIs: Facilitate NetOps and DevOps integrations
📡 2. Control Plane
Component: vSmart Controllers
The control plane handles routing intelligency, distributing policy information to the endpoint devices, and establishing secure overlay networks within cloud-native and distributed environments.
Key Functions:
Route advertisement and path selection using Overlay Management Protocol (OMP)
Policy enforcement for example SLA-based routing
Distribution of security keys
Co-ordinating with vBond to onboard edge devices
Additional component: vBond
- Data Plane
Component: vEdge Routers
The actual packet forwarding occurs in this layer. vEdge routers are found in enterprise locations (branch, CoLo, cloud, data center) and:
- Create secure IPsec tunnels
- Transport data over MPLS, Internet (INET) and 4G LTE
Enforce routing policies that were established in the control plane
Each connection is encrypted end-to-end ensuring integrity and confidentiality.
Inter-Plane Communication Overview
Plane Primary Function Key Components Communication
Management
Policy/config management vManage, vAnalytics API, Web UI
Control
Route, policy distribution vSmart, vBond OMP
Data
Packet forwarding vEdge routers IPsec Tunnels
End-to-End Security in Cisco SD-WAN
Cisco SD-WAN leverages a Zero Trust model, meaning that every device must authenticate before joining the fabric. Encryption is enabled:
- Between vEdges
- Between vEdges and cloud services
- For data-in-transit and control messages
Security Advantages include: - Minimizes the risk of man-in-the-middle attacks
- Branch-to-branch isolation
- Secure cloud breakout without backhaul
API and Automations Integrations
Through vManage's APIs, Cisco SD-WAN can enable: - Configuration templates at scale
- Automated changes to the network
- Real-time monitoring integrations (e.g., Splunk, Grafana)
📦 Use Cases of Cisco SD-WAN
Use Case Description
Cloud Access Optimization Direct, policy-based breakout to SaaS applications
Secure Remote Branch Encrypt WAN flow without overreliance on MPLS
Application-Aware Routing Dynamic failover and quality of service per application
WAN Cost Reduction Leverage broadband/4G instead of costly MPLS lines
🧠 Conclusion:
Why Cisco SD-WAN is Different
Cisco's SD-WAN architecture has clearly defined data, control and management plane allowing for the scalability, security and programmability you want in your WAN. Flexibility in deployments, strong cloud integration allows telecom professionals to build high performing, cost-effective and future proof WANs.
Whether you deploy networks in your role as an engineer or are involved with a company strategy decision to invest in data networks, it is important to understand this architecture is core to taking full advantage of the SD-WAN solution.
📈 Advanced Insights: Cisco SD-WAN to Traditional WAN
One of the best ways to understand the improvements that Cisco SD-WAN over traditional WAN architectures is to see the particular features that make it stand out:
Feature Traditional WAN Cisco SD-WAN
Traffic Routing Static and manual Dynamic and application aware
Security Perimeter based End to end IPsec based and Zero Trust
Integration of Cloud Services Poor - via backhaul Direct cloud breakout
Cost High (MPLS reliance) Reduced - support for internet/4G
Management Site by site Centralized (vManage)
Take Time Weeks/months Hours/days
📡 Cisco SD-WAN + SASE: Substantial Future
Cisco SD-WAN has the ability to integrate with Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) frameworks for security and networking in a unified way across the WAN edge.
Combined with Cisco Umbrella, Cisco SD-WAN provides:
Security delivered in the cloud
Secure internet access for users in remote sites
Streamlined policy enforcement
💬 Final Thoughts
Cisco SD-WAN provides the flexibility, scalability, and intelligence that an enterprise will need. It's cloud-first, policy-based approach allows enterprises to:
Lower operational cost
Improve application performance
Connect users and workloads safely from anywhere
🛠️ Best Practices for Deploying Cisco SD-WAN
Here are some best practices recommended by Cisco that will help ensure your SD-WAN implementation is successful:
- Plan for a Phased Migration
Start off with pilot sites (e.g., branches that do not represent anything too big or important).
Monitor network performance on these sites and then rollout larger scale. - Have Redundant Controllers
Have at least a couple of vSmart, vBond, and vManage controllers deployed in other PoPs or regions to support high-availability operation. - Segment Traffic by VPNs
Take advantage of VPNs and separate different traffic types (e.g., voice, guest, PCI-apps) in their own different VPNs all from one SD-WAN deployment. - Use Application-Aware Routing
Establish policies that are based on SLAs and use application-aware routing to prioritize critical applications and dynamically change based on performance degradation. - Enable Real-Time Analytics
Work with vAnalytics to monitor SLA counts, use patterns, and current performance bottlenecks.
🧭 Common Use Cases for Cisco SD-WAN
Cisco SD-WAN is used in various industries and enterprise sizes. Below are some representative use cases:
Use Case Description
Cloud-First Architecture Direct breakout to apps, such as Salesforce, Office 365, AWS
Retail WAN Modernization Secure, reliable access to hundreds of stores
MPLS Cost Take Out Transitioning to broadband/4G while having SLAs
Remote Work Enablement Deployment of vEdge/CPEs remotely to home offices
Multi-Cloud Access Policy control across Azure AWS, GCP traffic.
