Understanding Open RAN Architecture: Components, Interfaces, and Benefits
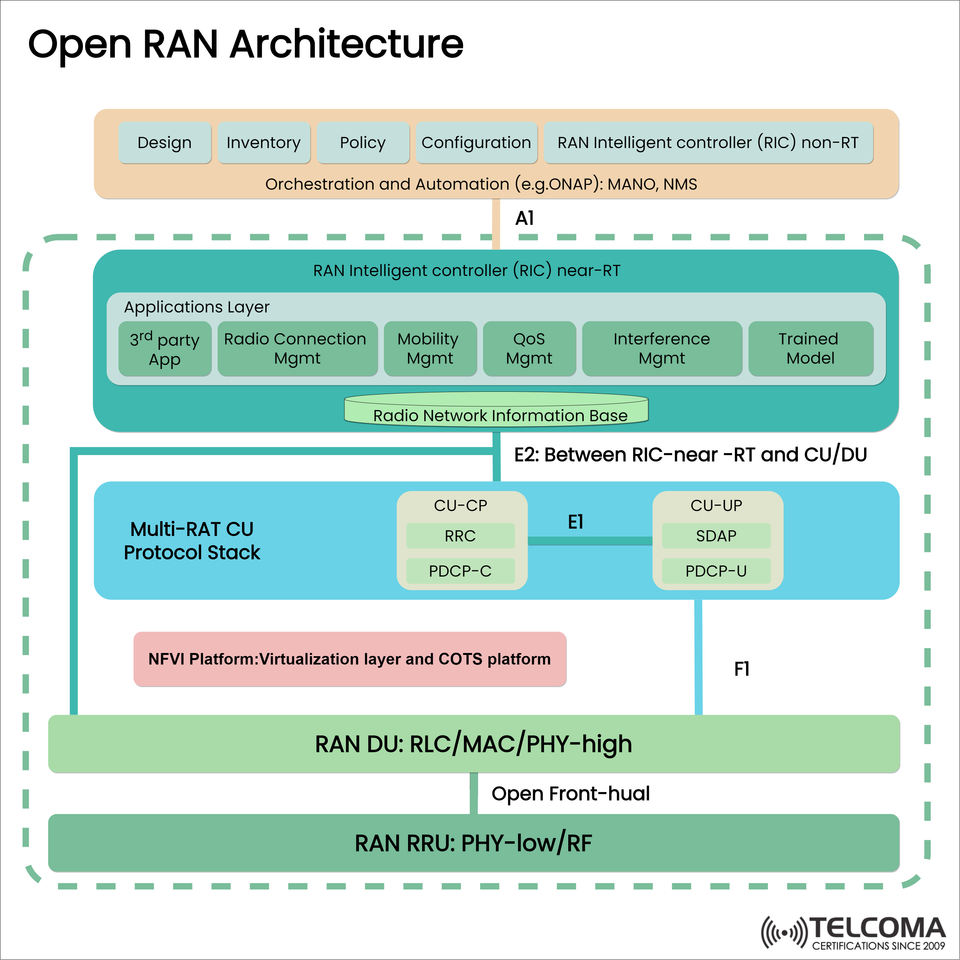

Open RAN Architecture: Components, Interfaces, and Virtualization
Open RAN (Radio Access Network) is changing the face of telecommunications through advantages of openness, interoperability, and intelligence across the RAN ecosystem. Open RAN pushes for disaggregation of hardware and software, which allows for multi-vendor deployments and increases flexibility of a network.
📌 What is Open RAN Architecture?
Open RAN is a modular and open network architecture that separates both hardware and software components of the RAN. Open RAN is fundamentally different from traditional monolith RAN architectures in that they enable:
Vendor-neutral interfaces
Flexible deployment between cloud-native platforms
Enhanced automation with AI/ML models
Better cost savings with commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) hardware
🧱 Core Components of the Open RAN Architecture
Component Description
RIC (non-RT) Conducts non-real-time tasks including policy, design, inventory, configuration available using the A1 interface.
RIC (Near-RT) Conducts near-real-time tasks like interference and mobility management and can utilize AI/ML to optimize the process.
CU (Central Unit) Disaggregated into Control Plane (CU-CP) and User Plane (CU-UP), which handles SDAP, RRC, and PDCP.
DU (Distributed Unit) Distributes tasks that require time-sensitive decisions.
🔁 Key Interfaces in Open RAN
An understanding of the standard interfaces is critical to interoperability:
A1 Interface - Ties the non-RT RIC to the near-RT RIC to provide orchestration and policy-based control
E2 Interface - Ties the near-RT RIC to the CU/DU which allows for the exchange of real-time control information
E1 Interface - Provides communication between CU-CP and CU-UP
F1 Interface - Provides communication between the CU and DU
Open Front-Haul—Supports the interoperability of the DU and RRU using open standards
🧠 RIC Layers: Intelligent Control
Near-RT RIC Manages time-critical applications such as:
Radio connection management
Mobility management, including QoS (Quality of Service)
Interference management
ML (Machine Learning) models that have been trained to make real-time performance improvements
Non-RT RIC Responsible for long-range, strategic decision making, including:
Network policy control
Configuration and inventory management
Integration with orchestration platforms such as ONAP, MANO, and NMS
🖥️ Virtualization & NFVI Layer
The NFV Infrastructure (NFVI) abstracts the physical hardware and enables:
Dynamic scaling of the network functions
Flexibility to execute in public/private clouds
A variety of vendor-neutral COTS (Commercial Off-The-Shelf) deployment platforms
This decouples the network functions from vendor hardware and opens the door for innovation and cost savings.
🌐 Advantages of Open RAN
✅ Vendor Interoperability: Combine solutions from different vendors
✅ Scalability: Deploy functions in the form of virtualized network functions, or as containerized applications
✅ AI-driven Optimization: Real-time optimization based on machine learning, with RIC models
✅ Cost Efficiency: Leverage Commercial Off The Shelf (COTS) hardware and open interfaces.
✅ Faster Innovation: Open Interfaces and APIs enable quicker integration of solutions.
🏁 Closing Thoughts
Open RAN architecture represents a disruptive change to the telecoms industry by unlocking the closed RAN ecosystem. Open RAN provides operators the velocity, scale, and agility network operators are looking for to enable next generation mobile networks, such as 5G and beyond, through disaggregation, virtualized network functions, and deliberately decoupling layers with AI-driven control.
For engineers at telecoms, systems integrators, or those curious about technology, it will be imperative to understand this new layering and modular approach (slicing) to RAN as Open RAN becomes the industry norm.
🔧 Open RAN Implementation Considerations
Open RAN is more than an architectural change; it represents operational change. Here are items that telecommunications professionals need to consider:
- Interoperability Testing
Different vendors may effect open interfaces lurch differently and therefore you will need to conduct extensive interoperability testing to ensure that components such as CU, DU, and RRU interwork. - Security Issues
Disaggregated architectures have an increased attack surface.
Secures all of the interfaces (A1, E1, F1, E2) - authentication, encryption, and integrity protection. - Latency Sensitivity
Real-time applications (handovers, scheduling etc.) are latency sensitive based on sensor data exchange between DU and RRU in the location and time.
Your fronthaul network will become more critical especially in 5G and beyond. - RIC Application (xApp and rApp) Development
You will have flexibility with xApps (near-RT) and rApps (non-RT) as a plug-and-play piece of intelligence.
Network Vendors or third parties can develop xApps and rApps targeting use cases (anomaly detection, traffic steering).
💼 Use Cases for Open RAN
Use Case Description
Rural & Remote Connectivity Lower cost opens the door for sustain deployment in very low-ARPU (average revenue per user) environments.
Private 5G Networks Enterprises will be able to build custom designed networks that enable their modular components.
Smart Cities AI-enabled RIC can impact adaptive coverage, traffic shaping, and dynamic QoS.
Multi-Vendor 5G Rollouts Operators will extend best-of-breed solutions without vendor lock-in by going open.
🧩 Tools and Platforms Recommendations
In support of Open RAN deployments, we identify the following tools and platforms that (or could) provide value to telecom operators:
ONAP (Open Network Automation Platform), orchestration and management
O-RAN Software Community (OSC), open-source components like RIC, SMO
Kubernetes and CNFs for deploying container-network functions
Intel FlexRAN or NVIDIA Aerial SDK, providing high-performance DU builds
📘 Glossary of Terms
Term Meaning
RIC RAN Intelligent Controller
CU/DU Central Unit / Distributed Unit
RRU Radio Remote Unit
NFVI Network Functions Virtualization Infrastructure
E1/F1/E2/A1 standard open RAN interfaces
xApp/rApp Apps running on near-RT RIC, and non-RT RIC, respectively
SDAP/RRC/PDCP protocol layers in 5G NR stack
📈 Future Vision
Open RAN is likely to transform operator practice of creating and evolving networks:
Leading telecom operators (Vodafone, Telefónica, Rakuten) are already embracing Open RAN.
Governments and standards organizations (O-RAN Alliance) are supporting open innovation.
With 6G on the horizon, the fundamental flexibility allowed through Open RAN will be critical for developing future intelligent, autonomous networks.
✅ Final Thoughts
Open RAN Architecture creates openness in telecom, while enabling innovation through modularity and standards. For network operators, it provides:
A means to accelerate 5G deployments
A means to lower CapEx and OpEx
A platform to include AI-enabled intelligence for smarter networks.
