Understanding Open RAN Architecture: Key Components, Interfaces, and Intelligence Layers

📡 Open RAN Architecture: Disaggregated, Intelligent, and Open by Design
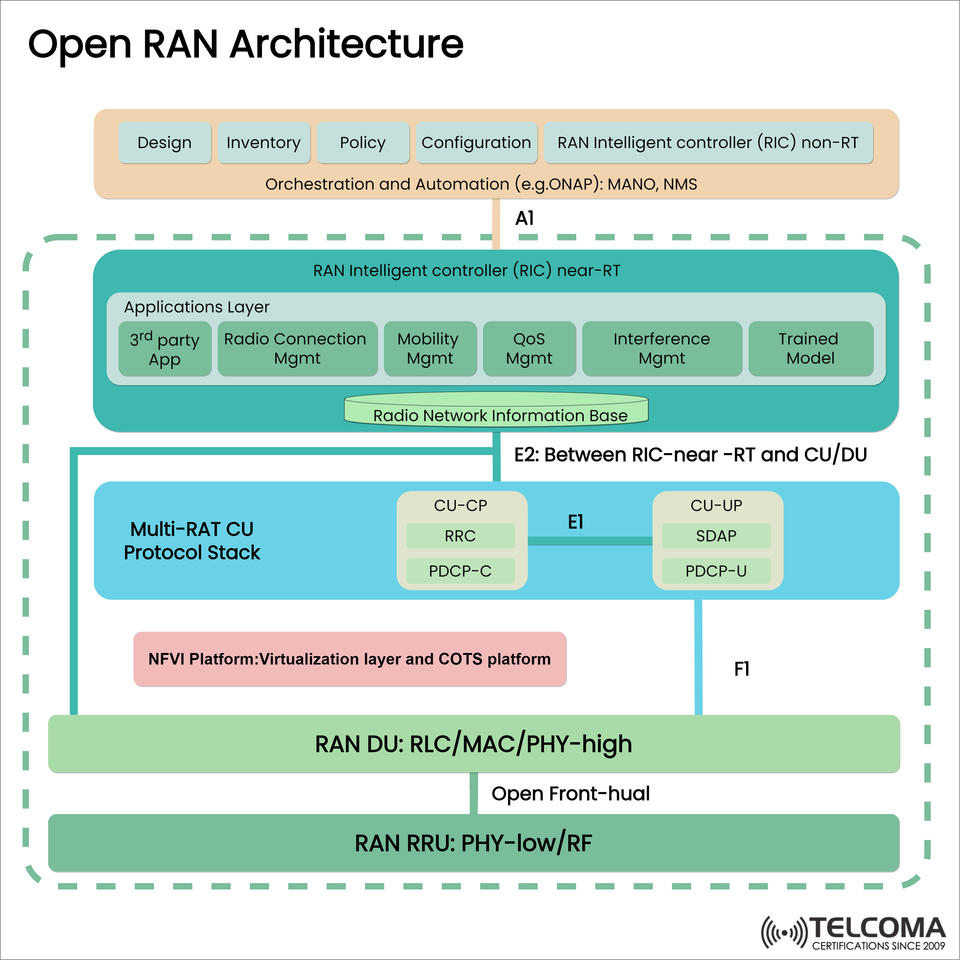
Open RAN (Radio Access Network) architecture is an innovative paradigm shift in mobile network design. Open RAN is also disaggregated, intelligent, and open by design breaking the mold of today’s vendor locked and proprietary systems through a disaggregated RAN function and incorporating intelligent and open interfaces. This disaggregation of functions provides distinct advantages in the Open RAN implementation allowing for more flexibility in the choice of vendors and their solutions with interoperability and real-time optimizations, which are necessary for the 5G and 6G future.
🔍 Components of the Open RAN Architecture
- RAN Intelligent Controllers (RICs)
The RICs provide the necessary intelligence to the RAN in real time with the assistance of Real Time and Non Real Time operations.
Non-RT RIC (upper layer):
<1s response time
Uses the A1 interface.
Typical functions include policy management, design, inventory, and configuration (typical integrated with ONAP/MANO).
Near-RT RIC (mid-layer):
10ms – 1s; connects to CU and DU via E2 interface
Houses apps for mobility mgmt, QoS, inter-cell interferance mgmt, and AI/ML models.
- Multi-RAT Central Unit (CU)
CU-CP (Control Plane): RRC and PDCP-C layer functions
CU-UP (User Plane): SDAP and PDCP-U functions
Interfaces
E1: Between CU-CP and CU-UP
E2: For interaction with Near-RT RIC
- Distributed Unit (DU)
Performs the lower-layer protocols: RLC, MAC, PHY-high
Based on the vendor's F1 interface to CU
Sits on NFVI world in terms of virtualization and with support for COTS - Radio Unit (RU)
Handles PHY-low and RF layers
Responsible for connecting to the DU via the Open Fronthaul interface
The hardware implementation is capable of determining how, and allow for interoperability through standardized physical interfaces.
🌐 Open RAN Interfaces: Interoperability
Interface Description Functional Purpose
A1 Non-RT RIC → Near-RT RIC Policy, guidance, ML models
E2 Near-RT RIC → CU/DU Real-time control, telemetry, actions
E1 CU-CP ↔ CU-UP Splits user and control planes
F1 CU ↔ DU Functional split interface
Open Fronthaul DU ↔ RU Hardware abstraction, RF control
⚙️ Orchestration & Automation
Open RAN architecture practices automation layers such as
ONAP (Open Network Automation Platform)
MANO (Management and Orchestration)
NMS (Network Management System)
Can enable zero-touch provisioning, continuous optimization, full Lifecycle Management of network functions across multiple vendors.
ℹ️ Why Open RAN is Important
Advantages:
✅ Vendor Neutrality: Combine and match components supplied by different manufacturers
✅ Cost Savings: Reduce CAPEX and OPEX, through purchasing COTS hardware
✅ Network Flexibility: Change configurations in real time through intelligent RIC layers
✅ Innovation at the Edge: Leverage AI/ML models at the edge to optimize performance
✅ Automation Ready: Easily integrated into DevOps, CI/CD pipelines
📚 Conclusion
Open RAN is more than just technology, it captures the essence of the benefits of openness, modular, and smart networks. When we decompose traditional RAN into CU, DU, RU, and RIC, we provide the ultimate level of flexibility operators can use to build, east and optimize network performance. Whether enhancing your existing 4G with network and COTS hardware, or rolling out future 5G or 6G networks, Open RAN architecture is a future-proof approach to build intelligent, efficient, and interoperable mobile networks.
📰 Open RAN Use Cases
Operator / Project Use Case Highlight
Rakuten Mobile (Japan) An end-to-end 5G Open RAN architecture Cloud-native, fully virtualized RAN
Vodafone (Europe, Africa) Open RAN deployment of 4G coverage in rural areas Unlocks vendor diversity and low-cost rural extension
Dish Network (USA) Building a greenfield 5G network using Open RAN Utilizing T-Mobile's Cloud-native core and RAN, requires full automation for critical functions
Airtel / Jio (India) Exploring Open RAN for a 5G rollout Reduced vendor and reliance on vendor profits, it is cheaper.
🔄 Open RAN Architecture: Component Overview
Component Function Interface
Non-RT RIC Long-term policies, AI model training, orchestration A1
Near-RT RIC Real-time control and optimization E2
CU-CP / CU-UP Control/User plane split with defined 5G functions E1
DU Implementation of lower RAN layers (MAC, RLC, PHY-high using E2) F1
RU Radio frequency and lower PHY (radio front-end) Open Fronthaul
NFVI Layer Provides virtualization capabilities for CU/DU functionality —
Apps on RIC Tertiary applications providing with QoS, Mobility, Interference management —
🧭 Conclusion: The Open RAN the Future of RAN Development
Open RAN has transformed the way mobile networks are constructed, optimized and managed. By decoupling hardware from software, introducing intelligent RIC/s and open, interoperable interfaces, operators are able to innovate faster, lower costs and future-proof their networks for 5G, 6G and bigger.
✅ Actionable Takeaways
Think of adopting Open RAN if you desire a varied vendor landscape and future scalability.
Consider using AI/ML with RIC to build real-time optimization into your networks.
Begin your orchestration journey with investment towards management-layer tools such as ONAP that automate operational functions.
Consider hybrid deployment scenarios like starting with rural or private networks, focal point, or scaling to city-wide features.
🌟 Strategic Advantages of Open RAN
Open RAN has many business and operational advantages that permit operators to modernize and future-proof their networks.
✅ 1. Cost Savings
Relying on Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) hardware lowers CAPEX.
Vendor competition helps lower software licensing costs.
Shared infrastructure models lower deployment costs.
✅ 2. Vendor Diversity
No vendor lock-in.
Use vendors with best-of-breed solutions.
Makes it easier to replace and update each component when necessary.
✅ 3. Faster Innovation Cycles
Open APIs and interfaces offer faster integration of AI/ML applications.
Rely on continuous updates of RIC-based applications.
Open source development allows improvements to community-led solutions.
✅ 4. Improved Automation and Intelligence
Near-RT and Non-RT RICs can automate decisions and how resources are provisioned.
Makes closed-loop automation for self-optimizing networks (SON) possible.
Provides support for predictive maintenance and real-time anomaly detection.
📚 Conclusion: Open RAN is the Best Path Forward
With Open RAN changing the way mobile networks are built—through open and intelligent interoperability, it offers operators:
An opportunity to innovate with RICs and AI-based applications.
Improved operational costs and service agility.
Tailored deployments with different use cases in rural, urban and enterprise settings.
