Understanding SD-WAN Architecture: How Enterprises Connect Smarter and Faster

🌐 Understanding SD-WAN Architecture: Intelligent, Flexible, and Cloud-Enabled Networking
With the digital transformation, traditional WANs just aren't enough to meet business demands. As companies increasingly rely on cloud-based services such as Google Workspace, AWS, Office 365, Dropbox, and other SaaS applications, the need for intelligent and agile networks is greater than ever.
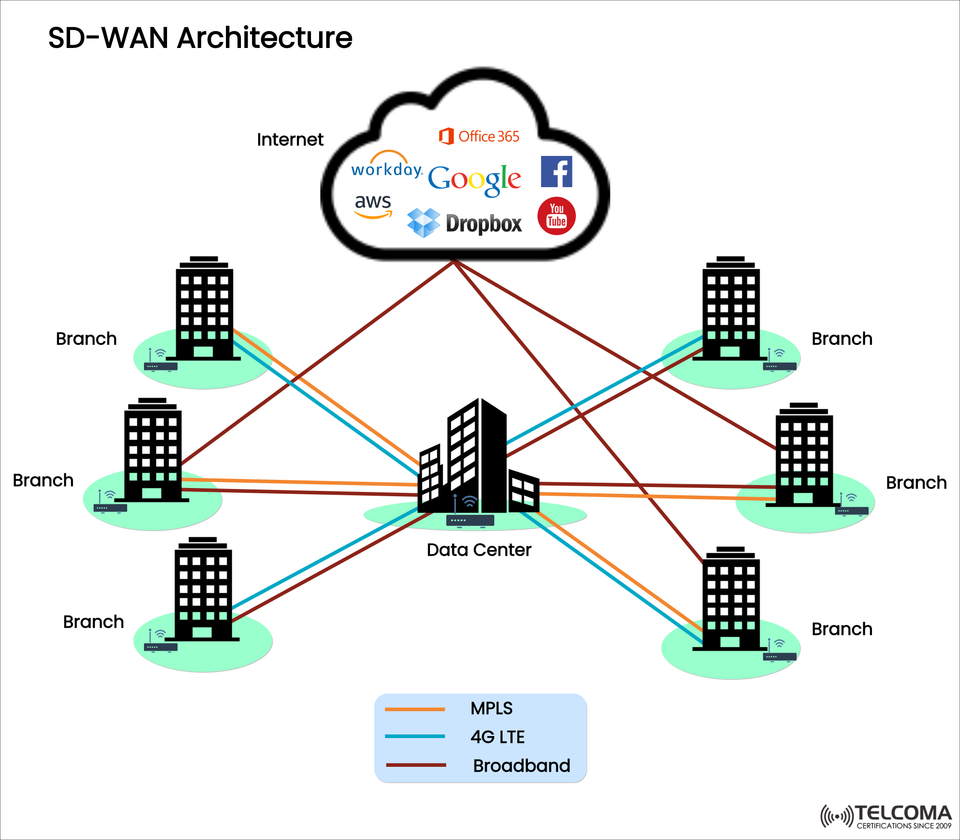
This is where, SD-WAN (Software-Defined WAN) comes into play. The diagram above illustrates the modern SD-WAN architecture and how the branch connects to the data centers, and cloud services, using MPLS, 4G LTE, and Broadband links.
🧠 So What is SD-WAN Architecture?
SD-WAN is a way to decouple the hardware of the network from its controller and enables dynamic path selection, centralized management, and cloud integration.
The SD-WAN image above represents several key architectural elements:
Multiple branch locations connecting back to a central data-center
Combination of three transport mediums:
MPLS (brown lines) — traditional leased-line for mission-critical applications
4G LTE (blue lines) — mobile backup or flexible transport for failover
Broadband (orange lines) — cost-effective medium for high-bandwidth, access
Direct connectivity from branch offices to cloud-applications (e.g. Google, AWS, Dropbox, Office 365)
🔑 Key Functions of SD-WAN Architecture
- Transport-agnostic
SD-WAN supports hybrid connectivity, utilizing:
MPLS for reliable, low-latency services
LTE for mobility and redundancy
Broadband for scalable bandwidth
- Cloud-Optimized Access
Branches can securely connect to cloud apps independently without needing traffic to go through HQ, which reduces latency and improves the experience for users. - Centralized Control & Visibility
Policies can be managed from one location, which means:
Application-aware routing.
Monitoring of traffic in real-time.
Enforcing of security.
- Improved Redundancy and Uptime
By allowing multiple paths (LTE, broadband, MPLS), SD-WAN means:
Failover can occur during link failures.
Load balancing can lead to better performance.
📊 SD-WAN Architecture vs Traditional WAN
Feature Traditional WAN (MPLS-centric) SD-WAN
Transport Type Typically MPLS MPLS + LTE + Broadband
Cloud Access Through HQ only Direct from branches
Management Distributed, manual Centralized, automated
Cost High More cost efficient
Application Awareness No Yes
Flexibility Low High
Redundancy Limited to few links Multi-link failover
⚙️ Use Cases of SD-WAN Architecture
Retail chains that are connecting their stores with real-time inventory applications.
Healthcare providers that need to gain access to secure cloud-based patient records.
Banks that need to provide SD-WAN as a solution for maintaining uptime across multiple ATM machines and branches.
Remote offices that require fast time to deploy and secure access to corporate applications.
✅ Conclusion: The Future is SD-WAN
The evolution of how enterprises connect and manage their networks is here, and going strong. SD-WAN architecture delivers the flexibility, performance and cloud-first capabilities modern businesses require today. The combination of MPLS, LTE, and broadband provides the resilience and cost-effectiveness that the future demands.
🔍Technical Benefits of an SD-WAN Design
- Application-aware routing
SD-WAN can discover applications in real-time and dynamically route them based on the best-suited link:
MPLS for VoIP and latency-sensitive apps
Broadband for bulk data or streaming
4G LTE for mobility or backup connectivity
This solution is designed to provide the best possible end-user experience while maximizing bandwidth use. - Traffic Segmentation and QoS
Traffic policies for prioritizing include the ability to:
Guarantee the performance of mainstream apps such as Office 365 or Salesforce
Mitigate non-critical data traffic taking too much bandwidth
Segment and protect tenant network traffic for security & compliance (e.g. PCI DSS for financial services) - Zero-touch provisioning (ZTP)
With ZTP, enterprises can deploy completely new branch devices without physically visiting the location. Just plug the SD-WAN device in:
It will authenticate to the orchestrator
It will pull down configured templates
It will connect to the WAN in minutes.
This makes life much easier for distributed enterprises or those with limited staff in IT.
🧩 Things to consider for changes
As organizations transition from traditional WAN to SD-WAN, think about the following:
🛠️ Integration with everything
During this migration, hybrid WAN will be the most common model: MPLS + SD-WAN co-existing together.
Leverage your existing MPLS while contracts last, transition to broadband/LTE.
📍 Scalability
You will want to ensure the SD-WAN solution can service thousands of sites.
You will also want multi-cloud support (Azure, AWS, GCP).
📊 Monitoring and Analytics
Real-time dashboards that provide bandwidth usage, link health, and app performance
Ability to provide AI/ML powered insights for predictive network management
🔐 SD-WAN and Security: Built-In Value
Traditional WAN models backhaul all traffic to a central data center for security inspection adding latency and complexity.
SD-WAN provides:
Direct Internet Breakout with a security stack (firewall, URL filtering, IPS)
Secure Tunnels with IPsec / SSL encryption for each branch connection
Cloud-delivered security (SASE - Secure Access Service Edge) from vendors such as, Zscaler, Palo Alto, Cisco Umbrella
Security Benefits
Encrypted links ensure data confidentiality
Role-based access control provides network governance
Real-time threat detection using cloud firewalls and analytics.
📈 Real World Impact: What Enterprises Are Getting
Advantage Benefits
Lower WAN Costs Utilize Broadband and LTE instead of MPLS which is costly
Faster Cloud Access Direct-to-cloud access versus backhaul to HQ before accessing cloud
Better User Experience Lower latency, apps can also be routed directly
Improved Business Continuity Multiple links to failover and provide resilience
Improved IT Agility Rapid site onboarding and policy rollout.
🏁 Conclusion:
SD-WAN is the Future of Modern Enterprise Connectivity
The reveal of the shift in enterprise architecture is evident—the move from static, structured MPLS networks to fluid and dynamic cloud based multi-transport methods through SD-WAN.
Under an SD-WAN model:
Your branches can connect directly to SaaS, PaaS and IaaS applications
Your IT group has central control and visibility
Your network is secure, adaptable and future proof
🔗 Additional Resources (Optional Resources)
SD-WAN vs MPLS: Understanding the Differences
What is SASE and How Does it Relate to SD-WAN
Checklist: Is Your Enterprise Ready for SD-WAN?
