Understanding SD-WAN Architecture: Layers, Services, and Cloud Integration
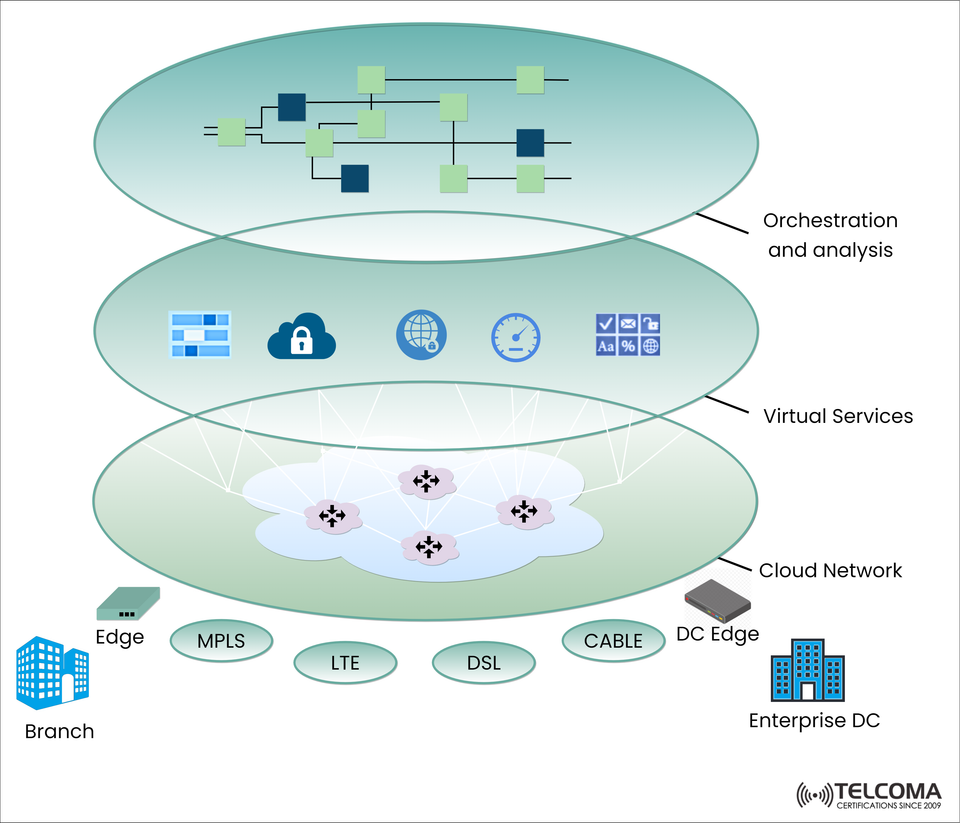

🌐 Understanding the SD-WAN Framework: Cloud, Virtual Services, and Orchestration
With today's networks becoming more dynamic and cloud-native, Software-Defined Wide Area Networking, or SD-WAN is a game-changing technology to satisfy modern enterprises. The graphic above shows the SD-WAN architecture levels, where SD-WAN connects Enterprises' branches to data centers and/or cloud services via:
Intelligent Routing, Virtualized Services, and Orchestrated Control.
In this article, we'll take a look at the layers of Cloud Network, Virtualized Services, and Orchestration & Analysis to understand how SD-WAN works in real-world telecoms & enterprise environments.
1️⃣ Cloud Network Layer: Connectivity
At the base layer of the architecture is the Cloud Network Layer that is responsible for Connectivity between:
Branches
Enterprise data centers (DCs)
Public/private cloud architecture
Transport can be performed over the following options,
MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching)
LTE (Long-Term Evolution)
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)
Cable broadband
Notable points:
Abstracts physical transport types
Allows for hybrid WAN
Redundant path selection based on failovers or performance
🔌 Example: A Branch office may utilize an LTE connection and an MPLS connection to centrally connect to an enterprise data center based on the applications sensitivity and bandwidth requirements.
2️⃣ Virtual Services Layer: Network Intelligence in Action
The middle layer holds the virtualized network functions (VNFs) enabling the software-driven services like:
Firewall and traffic inspection
Secure web gateways
WAN optimization
Load balancing
Application-aware routing
Benefits:
Limiting dependency on physical devices
Increased flexibility and quick provisioning
Security and QoS on specific applications
🛡️ Security Integration: virtual services layer integrates natively with encryption, secure tunneling, and threat detection.
3️⃣ Orchestration and Analysis Layer: Central brain of the network
At the top of the stack, the Orchestration and Analysis Layer offers a centralized cloud-based control plane that:
Automates provisioning and policy updates
Monitors network performance and SLAs
Traffic pattern analytics, alerts
AI/ML optimized routing decisions
📊 Orchestration Tools Typically Provide:
Role-based dashboards
Real-time analytics
Application usage
Policy-based automation
⚙️ This layer is key to achieving Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP) and multi-branch scalability.
🔄 How the SD-WAN Layers Work Together
Layer Function Technologies Used
Cloud Network Basic connectivity MPLS, LTE, DSL, Cable
Virtual Services Network functions VNFs, SD-security, SD-routing
Orchestration & Analysis Management & insight Centralized controllers, AI/ML
Each layer is logically decoupled but operationally dependent on each other, to form a complete and agile enterprise wide area network (WAN) solution.
Real-World Use Case: Branch-to-Cloud Connectivity
Context:
A retail chain with 100 branches across the country requires secure and resilient connectivity to both a cloud ERP system and its core data center.
With SD-WAN:
Branches employ both DSL and LTE for dual transport.
Virtual firewalls monitor all traffic at the sites.
The centrally controller orchestrates policy updates while monitoring utilization.
Result: Reduced cost, increased uptime, and easier network management.
Benefits of SD-WAN Architecture:
Transport-agnostic connectivity
Centralized visibility and control
Dynamic path-selection with app performance
Increased security with segmentation and encrypted transport
Simplified operations using cloud-based orchestration
Conclusion
The layered SD-WAN architecture outlined in the image represents a model for the modern enterprise network – agile, secure, cloud-ready, and centrally manageable. By decoupling hardware from software, and allowing for services to be virtualized, SD-WAN gives telecom operators and IT teams never-before-seen levels of control and efficiency.
As organizations continue to digitally transform, keeping this architecture in mind is essential for anyone involved in network planning, operations, or security.
Advanced SD-WAN Features and Capabilities
To cover SD-WAN capabilities beyond basic architecture, some examples of advanced capabilities that can assist organizations in maximizing performance, security, and operational efficiencies include the following :
🔀 Application-Aware Routing
Prioritizes critical applications (such as VoIP, video conferencing, or ERP) over optimal network paths.
Uses Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) to recognize the type of traffic.
🔐 End-to-End Encryption
Encryption of all traffic passing over public or hybrid links (IPsec, SSL).
Protects data transiting over the SD-WAN fabric whether using DSL or broadband.
📶 Link Health Monitoring
Enforces latency, jitter, and packets dropped over links.
Reroutes any traffic that exceeds the threshold.
📍 Network Segmentation
Allows traffic micro-segmentation to sever departments or devices.
Improves compliant security for targeted industries (e.g., finance, healthcare).
🏢 SD-WAN Deployment Models
There are various ways to deploy SD-WAN depending on your business needs:
Deployment Type Description Best for
On-Premises SD-WAN appliances at branch ng to be controlled on-site or through the cloud Managing your own large enterprise with an IT organization
Cloud-Managed SD-WAN is completely managed from a service provider’s cloud platform Small or medium-size enterprises or managing internationally distributed enterprises
Cloud-Hybrid Mix of service provider-hosted and on-site appliances Enterprise in transition
🔀 Application-Aware Routing
Prioritizes critical applications (such as VoIP, video conferencing, or ERP) over optimal network paths.
Uses Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) to recognize the type of traffic.
🔐 End-to-End Encryption
Encryption of all traffic passing over public or hybrid links (IPsec, SSL).
Protects data transiting over the SD-WAN fabric whether using DSL or broadband.
📶 Link Health Monitoring
Enforces latency, jitter, and packets dropped over links.
Reroutes any traffic that exceeds the threshold.
📍 Network Segmentation
Allows traffic micro-segmentation to sever departments or devices.
Improves compliant security for targeted industries (e.g., finance, healthcare).
🏢 SD-WAN Deployment Models
There are various ways to deploy SD-WAN depending on your business needs:
Deployment Type Description Best for
On-Premises SD-WAN appliances at branch ng to be controlled on-site or through the cloud Managing your own large enterprise with an IT organization
Cloud-Managed SD-WAN is completely managed from a service provider’s cloud platform Small or medium-size enterprises or managing internationally distributed enterprises
Cloud-Hybrid Mix of service provider-hosted and on-site appliances Enterprise in transition
