Understanding SDN Architecture in 5G Networks: A Deep Dive into ONF and 5G Integration

🧠 SDN Architecture and 5G: The Future of Programmable Networks
As 5G continues to mature, ultralow latency, mass connectivity, and high flexibility no longer suit themselves to traditional rigid network infrastructures. Software-Defined Networking (SDN) is the technology that will fundamentally change 5G deployments.
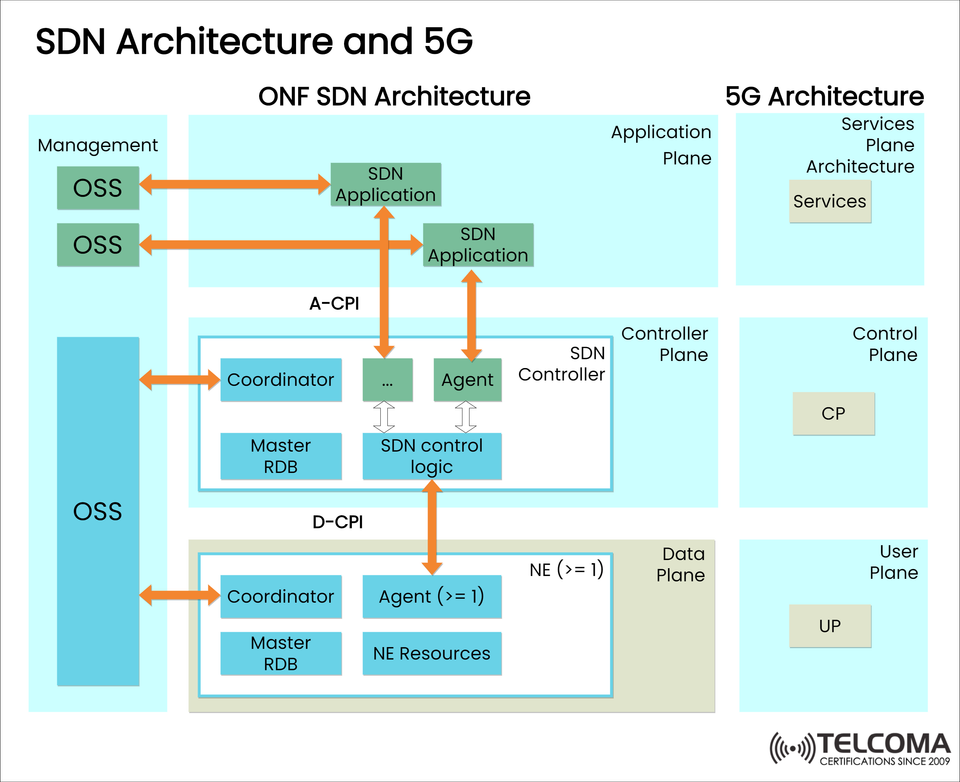
The diagram below provides an overview of how the SDN architecture through the ONF (Open Networking Foundation) integrates with 5G network stack to show how abstraction and programmability is processed across management, control, and data planes.
🔍 What Is SDN in 5G?
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) is a networking technique that separates the data plane from the control plane for easier management and automation of networks. In the 5G ecosystem SDN will enable dynamic service provisioning, centralized control, and real-time network slicing.
🔧 Explanation of ONF SDN Architecture Components
- SDN Applications (Application Plane)
These are focused on top-level decision making.
They communicate with the SDN controller via Application-Controller Plane Interface (A-CPI).
They are connected to OSS (Operations Support Systems) for orchestration and monitoring.
- SDN Controller (Controller Plane)
SDN's 'brain'.
This includes:
Coordinator: Coordinates a number of agents and keeps them consistent.
Agent: An agent interfaces with specific data-plane elements.
SDN Control Logic: Maps logic to enforce the policy.
Master RDB: A single Resource Database (RDB) for everything.
- NE and D-CPI (Data Plane)
NE (Network Elements): Can be anything physical or virtual, examples include switches, routers or base stations.
Agent (≥1): Enables one or more endpoints to connect.
D-CPI (Data-Controller Plane Interface): This connects data plane components to the controller, where the instructions flow in a southern direction.
Master RDB and NE Resources: Maintain the current operational state and capabilities of the hardware resources.
🛰️ SDN vs Traditional Networking in 5G
Feature Traditional Networking SDN in 5G
Control Distributed Centralized
Configuration Manual Automated
Scalability Static Highly Scalable
Network Slicing Limited Full support
Use of OSS Basic fault & config Deep Integration & orchestration
🧩 Connection to the 5G Architecture
On the right side of the diagram, one can see how this SDN model maps to the 5G Service-Based Architecture (SBA)
Services Plane - Artifact of SDN applications
Control Plane (CP) - Controlled by SDN controllers
User Plane (UP) - The user plane is influenced directly by NE (network elements) on the data plane via agents
With this interoperability, a network can leverage slicing, MEC (multi-access edge computing), and zero-touch provisioning that arise in the advanced 5G use cases.
🚦Advantages of SDN in the 5G Networks
✅ Centralized control and the traffic management capabilities
✅ Network slicing for enterprise and IoT use cases
✅ Faster package development cycles through automation
✅ Standardized and open APIs for interoperability across multiple vendors
✅ Real-time orchestration with OSS/BSS
🔗 Related Areas:
NFV (Network Function Virtualization): Takes it a step further by virtualizing network functions - for example, firewalls, load balancers, etc. and fits well with SDN.
ONAP (Open Network Automation Platform): Supports real-time, policy-driven orchestration and automation.
O-RAN (Open Radio Access Network): Provides openness and intelligence to the radio access network.
📘 Recommended Standards and Frameworks:
ONF SDN Architecture 2.0; 3GPP TS 23.501 (5G System Architecture); ETSI NFV specifications.
🎓 Learning Path for Telecom Professionals
And then here is a recommended learning path to enable you to master SDN inherently with 5G:
Step Focus Area Expected Outcomes
1️⃣ Fundamentar knowledge of SDN Understand SDN concept and terminology
2️⃣ 5G Core Architecture Understand the components of the 5G Service-Based Architecture
3️⃣ SDN in 5G use cases Understand dynamic slicing, MEC, and automation
4️⃣ Hands-on labs Use simulators or emulators to create SDN/5G setups
5️⃣ Certification (for example TELCOMA, ONF) Validation of skills and readiness for industry.
🗣️ Final thoughts: Leading into the future of programmability
NDN & SDI represent a true turning point in the industry for a programming-centric shift away from hardware in telecommunications. Combining the software controllable network capabilities via SDN with subsequent transformation via 5G to a modern layer of access and transport provide the
combination of creating:
Dynamic resource allocation (i.e. seamless resource allocation to meet traffic demand)
Cross-domain orchestration (i.e. automation horizontally across systems)
Massive scalability (i.e. increased & resilient capacity demands)
End-to-end automation (i.e. an agnostic, open framework reducing vendor lock-in)
This shift offers new levels of flexibility and automation towards enabling future application use cases, such as autonomy, smart cities, the Internet of Things (IoT) and augmented/virtual reality.
🧭 Join us in the SDN & 5G Transition
If you are a designer, engineer, technologist, or strategist, there is no path available but clear competitive necessity to change & adapt to SDN — and in conjunction with 5G networks.
🚀 Find out more!
TELCOMA offers training programs (and certifications) in SDN & 5G that show in practical ways how to engage SDN architectures in 5G networks.
🧲 Keywords to Target (to leverage SEO):
SDN in 5G
ONF SDN architecture
5G network slicing
SDN control plane
programmable telecom networks
A-CPI and D-CPI explained
SDN applications in telecom
software-defined networking 5G use cases
✅ Call to Action: Pave the Way for 5G with SDN
Combining SDN with 5G is creating a new era in telecommunications—not only re-configurable, but also better, faster, smarter, and more efficient.
Commit to knowledge and skill investment in SDN
Use network tools with programmable capability
Engage with the ONF and open source communities
Use SDN labs that are 5G ready
What is the difference between the ONF SDN architecture and traditional architectures?
The ONF SDN architecture moves away from traditional static technology architectures that used a model of embedded code in a network device, and it allows for separation of the control and data planes, centralizing control.
What are A-CPI and D-CPI?
A-CPI(Application-Controller Plane Interface): This interface allows SDN applications to interface with the SDN controller.
D-CPI (Data-Controller Plane Interface): This interface connects the SDN controller to the network elements and is responsible for the interactions with the network elements.
Can SDN enable 5G slicing and automation?
Yes, SDN is a fundamental architecture for implementing slicing across a 5G network, automating service and resource provisioning, and multi-tenancy isolation and Quality of Service (QoS) guarantees.
In what way does SDN enhance OSS integration for 5G?
SDN leverages programmable APIs and real-time telemetry to enhance the integration of OSS with automated fault, configuration, and performance management capabilities.
To Conclude: Building Smarter Networks
As telecom operators and their suppliers move into a domain of zero-touch automation, AI-driven operations, and agile service provision, SDN and 5G present themselves as the foundational technologies that allow networks to self-optimize, elastically scale, and evolve into intelligent networks to meet application demands.
