Understanding Split Option 7-2x in O-RAN Fronthaul: Architecture, Functions, and Benefits

🔍 Introduction: Overview of Split Option 7-2x
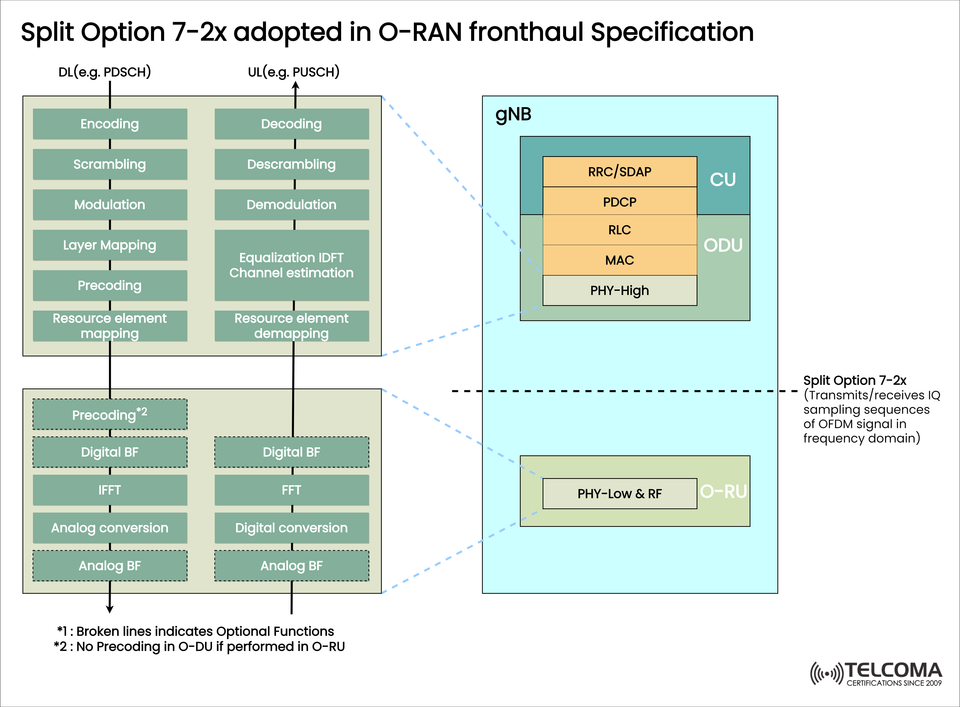
Split Option 7-2x is a functional split architecture specified in O-RAN (Open Radio Access Network) fronthaul specifications. It splits the gNB (next-generation Node B) baseband processing functionality between the O-DU (Distributed Unit) and O-RU (Radio Unit)—mainly at the PHY (Physical) layer.
Split Option 7-2x is a common functional split option for 5G NR deployments as it provides a good level of centralization and fronthaul bandwidth utilization.
🏗️ Functional Overview of Split Option 7-2x
The image specifies how the PHY functions are split between the O-DU and O-RU. Here is the breakdown:
🔹 O-DU (Distributed Unit) Functions
The upper PHY (PHY-High) is located in the O-DU and has the following functions:
Encoding / Decoding
Scrambling / Descrambling
Modulation / Demodulation
Layer Mapping
Precoding (optional - could move to RU)
Resource Element Mapping / Demapping
This keeps any frequency-domain processing in O-DU before sending information to the RU.
🔸 O-RU (Radio Unit) Functions
Meanwhile, the lower PHY (PHY-Low) is in the O-RU and has the following functions:
FFT / IFFT
Digital Beamforming
Digital ↔ Analog Conversion
Analog Beamforming
RF Transmission / Reception
These functions accomplish time-domain and RF processing to ultimately transmit a signal to the real-world.
🧠 Technical Highlights
Component Functionality
PHY-High (O-DU) Frequency-domain functions (scrambling, modulation, etc.)
PHY-Low (O-RU) Time-domain + RF functions (FFT/IFFT, beamforming)
Precoder Can reside in O-DU or O-RU depending on the solution.
Split Point - Between frequency and time: IQ samples are transmitted.
💡 Why Use Split Option 7-2x?
✅ Key Benefits
Interoperability: Enables plug and play across hardware vendors (open ecosystems)
Fronthaul Bandwidth: Transmission of frequency-domain IQ reduces CPRI load
Beamforming: Digital or analog BF either in RU or DU
Centralized Processing: Simplicity RAN manage and optimize
⚠️ Considerations for Implementation
It requires accurate synchronization between DU and RU:
Fronthaul latency and jitter management are critical:
Not particularly well-suited for ultra-low latency use cases unless fronthaul is fiber.
🛠️ Where is it Deployed?
Split Option 7-2x is most prevalent in:
5G NR NSA and SA deployments
Urban macro and small cell sites
vRAN and Cloud RAN architectures
Working in multi-vendor environments
This split enables network operators to mix and match software-defined DUs with hardware RUs, enabling innovation and cost benefits.
📊 Summary Table: Split Option 7-2x at a Glance
Feature Description
O-DU Processing Layer PHY-High (frequency-domain tasks)
O-RU Processing Layer PHY-Low & RF (time-domain and RF tasks)
Fronthaul Interface Type eCPRI / RoE (packet-based, low-latency)
Typical Deployment Models O-RAN, vRAN, Cloud RAN
Key Performance Impact Fronthaul bandwidth efficiency
Main Challenge Synchronization and latency control
🌐 Cultural Implementation of Option 7-2x in O-RAN
Operators, vendors, and others are in different states of alignment with the O-RAN standards and the use of Option 7-2x today is being explored in:
Greenfield 5G Deployments: Countries who have little legacy infrastructure are able to deal an advantage exponentially in building out cloud-native 5G stack - to date, Australia have done so with Option 7-2x.
Private 5G Networks: Enterprises and industrial campus' use this split option as part of their localized control for rapid software iterations/re-enforcing, and retaining potential option for RF hardware re-use.
Neutral Host networks are infrastructure natively multi-access edge computing (MEC) compatible with more flexibility for siting core data locations.
📖 Further Reading and Standards References
For readers who want to explore more, here are some useful resources:
📘 O-RAN WG4 Fronthaul Working Group specifications
📘 3GPP TS 38.401 - NG-RAN Architecture
📘 Small Cell Forum Functional Split Options whitepaper
📘 Intel FlexRAN 7-2x architecture papers
🧭 Final Notes
Split Option 7-2x sits at the intersection of performance, openness, and scalability in the design choices confronting a modern 5G RAN. For operators making the transition to disaggregated, software-defined RAN architectures from increasingly monolithic architectures, the use of Split Option 7-2x provides:
Reduced fronthaul load state
Interoperable hardware ecosystems
Flexible RU deployments
A state of readiness for a future of cloud-native RAN
Whether you are a telecom engineer, a network architect, or vendor structuring new frameworks, adopting and understanding the principles of Split Option 7-2x should be an essential building block for delivering flexible ct networks in a future proof way underpinned by underlying open technologies.
🔄 Summary Table: Split Option 7-2x Functional Distribution
Layer Function (DU – O-DU) Function (RU – O-RU)
PHY-High Encoding, Scrambling, Modulation, Layer Mapping, Precoding*, RE Mapping N/A
PHY-Low Optional Precoding, Digital Beamforming, IFFT FFT, Digital Beamforming, Analog conversion, Analog beamforming
RF N/A RF Transmission/Reception
🧩 Why does Split Option 7-2x matter in Open RAN?
This functional split serves to overlay elements of O-RAN aim to provide inter-compatibility with:
✅ Vendor Interoperability
✅ Decreased latency overheads
✅ Decoupling between DU and RU vendors
✅ Reduced CapEx through the use of commercially available?? Hardware
📌 Key Takeaways
Split Option 7-2x specifies a logical interface between PHY High (DU) and PHY Low (RU) layers of a gNB.
It facilitates frequency-domain IQ sample transfer over fronthaul to reduce latency and fronthaul data rates.
It has been successfully employed in O-RAN architectures to enable disaggregated, interoperable, cost-effective 5G deployments.
With respect to precoding, this is a flexible function and can be positioned anywhere to maximize either compute or fronthaul bandwidth based on the deployment objectives.
🔚 Conclusion
Split Option 7-2x is a discriminating choice in the disaggregation of 5G network functions. It provides the ability for operators to scale wisely with complex PHY operations centralized, radio hardware lean, and operational flexibility.
By also enabling frequency-domain IQ transmission, option 7-2x reduces the fronthaul load with no loss of control or quality. As 5G stabilizes and O-RAN is more entrenched, Option 7-2x may evolve into the de facto architecture for scalable, open, and efficient radio access networks.
