Understanding the 6G Ecosystem: Components, Stakeholders, and AI Integration
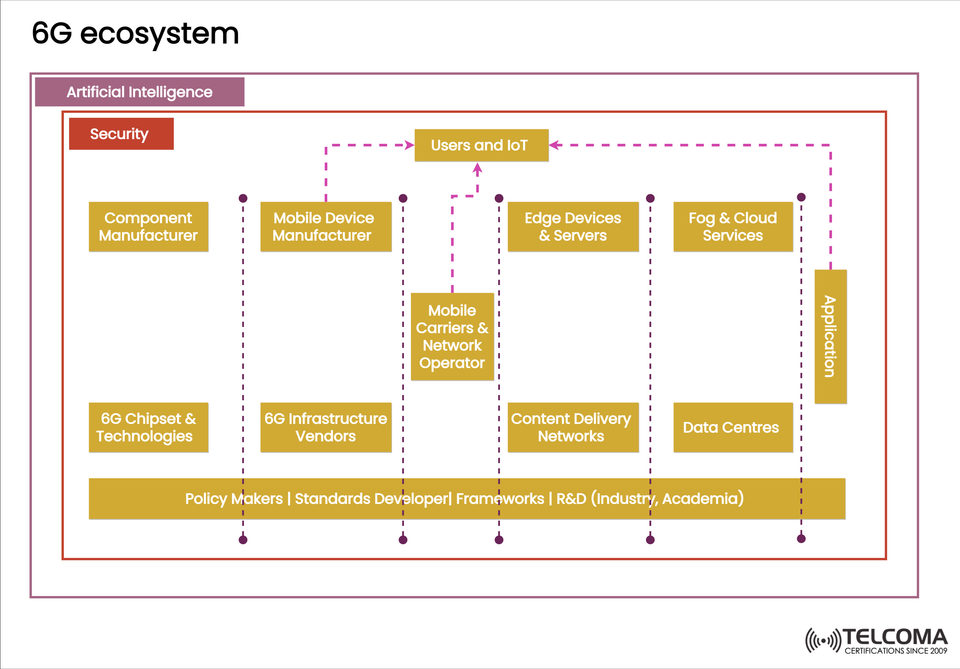

The 6G Ecosystem: Laying the Groundwork for Next-Gen Connectivity
As the global telecom sector gears up for 6G, expected to debut around 2030, it’s evident that this ecosystem is way more intricate than what we've seen before. Unlike 5G, which primarily aimed for faster speeds, lower latency, and improved connectivity, 6G introduces a system that deeply integrates artificial intelligence (AI), security, and collaboration across industries.
The diagram illustrating the 6G ecosystem shows how different players, technologies, and frameworks unite to create the foundation of the network. In this article, we’re going to break down each part, explain what it does, and relate it to the larger vision of 6G.
Artificial Intelligence at the Heart of 6G
At the pinnacle of this ecosystem is Artificial Intelligence (AI), highlighting its key role in 6G networks. In contrast to 5G, where AI was more of an add-on, in 6G it’s going to be an integral part of every layer of the network.
AI in 6G will take charge of:
Autonomous Network Operations: Networks that can optimize, heal, and configure themselves on their own.
Traffic Forecasting: Anticipating user demand and adjusting resources accordingly.
Edge Intelligence: Running AI models on local devices and servers to cut down on latency.
Security Enhancements: Spotting and neutralizing threats in real-time.
By embedding AI right into the ecosystem, 6G will provide smarter, more adaptable, and robust infrastructure.
Security as a Core Layer
Just below AI, the framework emphasizes Security as a critical component. It embodies the zero-trust architecture necessary for 6G networks, which will handle billions of interconnected devices and vital services.
Key security features in 6G include:
End-to-End Encryption: Safeguarding communications across both terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks.
Post-Quantum Cryptography: Protecting against future threats from quantum computing.
Identity and Access Management: Making sure only authorized devices and applications can access the network.
Resilience to Cyber Attacks: Ongoing monitoring to fend off service disruptions.
For telecom operators and businesses, maintaining trust is just as crucial as achieving high speeds.
Key Players in the 6G Ecosystem
At the center of the ecosystem are various stakeholders working together to make 6G a reality. Let’s take a look at them by category.
- Hardware and Technology Providers
Component Manufacturers: Create the basic materials and hardware elements (like semiconductors, sensors, and antennas).
6G Chipset & Technologies: Develop chipsets that can support terahertz frequencies, AI acceleration, and ultra-low power use.
Mobile Device Manufacturers: Make smartphones, wearables, and IoT devices that can take advantage of 6G features.
These players make sure the end-user devices and network equipment are ready for the future.
- Infrastructure and Connectivity
6G Infrastructure Vendors: Construct the radio access networks (RAN), base stations, and transport layers.
Mobile Carriers & Network Operators: Handle the backbone services, manage spectrum, and provide connection to users.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Streamline the delivery of data-heavy content like XR, VR, and holographic streams.
This part ensures that connectivity remains widespread, dependable, and high-performing.
- Computing and Cloud
Edge Devices & Servers: Bring computation closer to users, allowing for ultra-low latency applications.
Fog & Cloud Services: Provide distributed processing and storage for large-scale applications like AI training, gaming, and digital twins.
Data Centres: Huge facilities that store, analyze, and process massive amounts of data generated by 6G.
Together, they make up the computing fabric of 6G.
Policy, Standards, and R&D
At the base of the ecosystem are the organizations that set the rules for how everything connects:
Policy Makers: Formulate regulatory frameworks and manage spectrum allocation.
Standards Developers: Create global standards for interoperability and scalability.
Framework Developers: Design modular architectures for flexible setups.
R&D (Industry & Academia): Foster innovation through testing and pilot projects.
This ensures that 6G is fair, globally harmonized, and progressive.
- Users, IoT, and Applications
Lastly, at the end of the interaction chain, we find the Users and IoT devices. They’re the ones directly using the services from the 6G ecosystem.
Applications: Spanning from immersive XR and holographic communication to self-driving vehicles and industrial automation.
IoT Devices: Billions of connected sensors and machines across smart cities, healthcare, and logistics.
Essentially, users and IoT are both driving demand and reaping the benefits of 6G.
How the Ecosystem Connects
The 6G ecosystem isn’t separate. Every stakeholder and technology layer connects smoothly:
Mobile Carriers link users to the wider internet, collaborating with infrastructure vendors and data centers.
Device Manufacturers rely on chipset technologies and component suppliers.
Edge Devices work with fog and cloud services for efficient computing.
Applications flow through content networks, powered by data centers and secured by AI.
This interconnectedness turns 6G into a collaborative ecosystem, not just a simple supply chain.
6G Ecosystem Features and Benefits
Check out these standout features of the 6G ecosystem:
AI-Driven Automation – Reduces the need for human oversight in operations.
Zero-Trust Security – Guarantees resilience and data protection.
Terahertz Connectivity – Enables Tbps data rates for cutting-edge applications.
Distributed Computing – Combines edge and cloud for real-time responsiveness.
Cross-Sector Collaboration – Engages policymakers, academia, and industry alike.
These features allow for:
Ultra-reliable low latency communications (URLLC)
Holographic and tactile internet experiences
Intelligent infrastructure for cities and industries
Sustainable and energy-efficient networks
Comparison Table: Stakeholders and Their Roles in 6G
Stakeholder | Role in 6G Ecosystem | Impact Area
Component & Chipset Makers | Build advanced semiconductors and hardware | Devices, Efficiency, Cost
Device Manufacturers | Produce 6G-ready devices and IoT endpoints | User Experience, Scalability
Infrastructure Vendors | Deploy 6G RAN and transport systems | Coverage, Latency, Capacity
Carriers & Operators | Provide connectivity and spectrum management | Service Delivery, Reliability
CDNs & Data Centres | Handle content distribution and storage | Throughput, Performance
Edge & Cloud Providers | Enable distributed and real-time computing | Latency, Privacy, AI
Policymakers & Standards Bodies | Regulate, standardize, and harmonize frameworks | Interoperability, Compliance
Users & IoT Devices | Consume and generate data/services | Demand, Innovation
Why the 6G Ecosystem Is Essential for Telecom Professionals
For those in telecom, understanding the 6G ecosystem is vital because:
It reveals new collaboration opportunities across hardware, cloud, and AI.
It highlights security and regulatory focuses.
It gets operators ready for seamless integration of edge, cloud, and IoT.
It assists policymakers with ensuring sustainable and inclusive rollout.
In summary, getting the ecosystem perspective helps to prevent fragmented development and makes sure that 6G benefits society as a whole.
Conclusion
The 6G ecosystem is about more than just faster networks — it’s a layered collaboration that involves AI, security, infrastructure, cloud, devices, and policy. Every participant, from chipset manufacturers to mobile operators, plays a role in building a system that is smart, secure, sustainable, and user-focused.
For telecom experts, grasping this ecosystem is crucial for future-proofing strategies and aligning innovations with global 6G aspirations. By 2030, these intertwined elements will redefine not only how we connect, but also how we live, work, and interact in this digital age.
