Understanding the NDL Architectural Context in Modern Telecom Networks
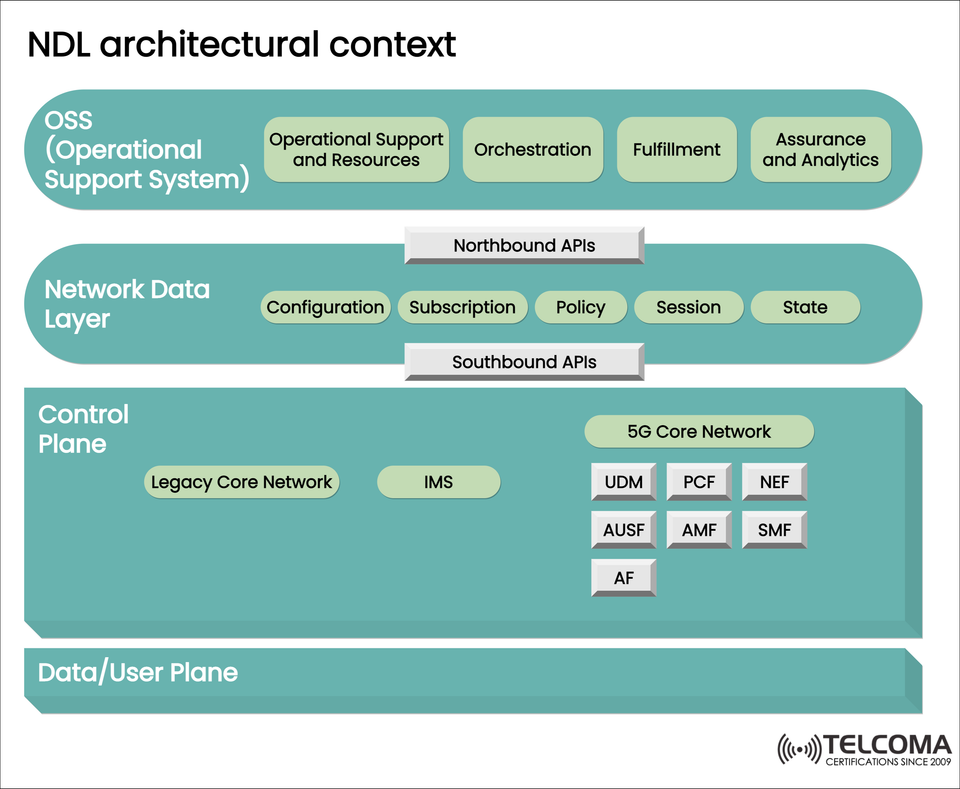

📡 NDL Architectural Context: The Data-Forward Structure for Next Generation Telecom
As telecom networks evolve towards software-defined, cloud-native and data-centric environments, the NDL architecture provides a significant foundation. This blog post explains the NDL architectural context, including a discussion of the layered architecture, interdependencies of the layers, and a description of how NDL will operate within the 5G core.
🧱 What is the NDL Architectural Context?
The NDL (Network Data Layer) is middleware between the Operational Support Systems (OSS) and the Control Plane in telecom architectures. NDL is designed to abstract and centralize all of the interactions with data for a telecom network. The NDL abstracts data interactions to provide immediate service provisioning, subscriber management and policy control, which is essential in any modern multi-domain networks.
🏗️ Layered Architecture Summary
The image above is a layered architecture that describes specific functional roles in each layer.
- OSS (Operational Support Systems)
OSS are responsible for end-to-end lifecycle management of valuable network services.
Operational Support and Resource
Infrastructure resource monitoring (compute, storage and bandwidth)
Orchestration
Workflow automations for deploying and scaling services.
Fulfillment
Validation of service activation and provision of service.
Assurance and Analytics
Real time detection of faults, SLA compliance and KPIs.
Core Components:
Configuration: Repository of network configurations
Subscription: Manages subscriber data and service definition
Policy: Defines and enforces usage policy
Session: State information around session-level states in access/core domains
State: System-wide state information
APIs:
Northbound APIs: Interfaces to OSS, service and resource orchestration
Southbound APIs: Interfaces to network functions/elements in the control plane
- Control Plane
Classic and also contemporary 5G implementations control and signal the network.
Classic Core Network: Circuit-switched & first-generation packet core systems
IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem): Orchestrates VoLTE, VoWiFi, rich communication services, etc.
5G Core Network Functions:
o AMF (Access and Mobility Management Function)
o SMF (Session Management Function)
o AUSF (Authentication Server Function)
o PCF (Policy Control Function)
o UDM (Unified Data Management)
o NEF (Network Exposure Function)
o AF (Application Function)
🔍 Key Advantages of the NDL Framework
Benefits Description
Data Abstraction Offers an abstraction standard for data to be communicated and manipulated for orchestration and automation
API-Based Integration API supports emerging open standards for OSS <--> network communication
Real-Time Responsive Supports session, policy, and state tracking so updates/changes can be made in response to fluctuating service demands or loads
Multi
💡 Use Cases Enabled by NDL
Automated Network Slicing leveraging real time policy and session management
Context-Aware Charging and Billing based on state and subscription information
Zero-Touch Provisioning using orchestration-based southbound APIs
Service Assurance supported by data-based analytics and closed-loop feedback mechanisms
🔐 Integrated with 5G Core Network Functions
NDL provides an integration platform between OSS and the service-based architecture (SBA) of 5G. NDL offers flexible integration with:
UDM and PCF for dynamic policy enforcement
SMF and AMF for session and mobility management
NEF for securely exposing APIs to external applications
This supports use cases such as private 5G, network slicing, and B2B IoT instances.
📶 5G and Beyond: A Requirement vs. A Nice to Have
The NDL framework is not build for only the current eras of networks, it allows for the future:
5G SA (standalone): NDL architects allows for dynamic service onboarding and intent based orchestration
Edge Compute: The network now extends up to and including the edge nodes, allowing the maximal utilization of ultra low latency services
IoT: Rolling out services that scales at enterprise levels for billions of managed devices from the ability to manage subscribers and control sessions in real time.
🧭 Strategic Benefits for Operators
🔄 Accelerated Time-to-Market
Operators can launch new services, new network slices or a new form of monetization, without having to navigate significant changes to the underlying infrastructure. Because of the data and API abstraction available within the NDL architecture.
📊 Comprehensive or Unified Data Governance
Control of the state, configuration and policy is unified within the NDL architecture, which allows for even better compliance, auditing, multi-domain visibility and verification without friction points or risks. The enterprise level SLA is pivotal to sustain network services.
🤝 Ecosystem Enablement
With established northbound and southbound APIs, connectivity with:
External partner platforms (OTT partners, enterprise partners)
AI/ML Ingrid data and analytical engines
Portable customer self-service/via mobile app portals
📣 Final Thoughts
The Network Data Layer (NDL) is a fundamental building block that enables integration with modern OSS, real-time control and service innovation in 5G-based networks. For telecom engineers, architects and strategists, gaining a complete understanding of the NDL framework helps to more readily modernize their infrastructure as the telecom domain adapts to the next decade of connectivity.
🚀 Key Use Cases Enabled by NDL Architecture
The NDL architectural context is not a hypothetical scenario; it is truly delivering new use cases in telecom:
- Dynamic Network Slicing
NDL allows for real-time policy, subscription, and configuration management. This means being able to dynamically allocate network slices to industries (e.g., healthcare, autonomous vehicles, smart factories). - Closed Loop Automation
Once the NDL architecture incorporates orchestration and analytics modules into the OSS, NDL would provide the ability to automatically detect and repair network faults or fir SLA violations, thus allowing for OPEX reduction and improving customer satisfaction. - Subscriber-centric Services
NDL ingests subscription, session and policy data allowing for hyper-personalized experiences whether on demand bandwidth, zero touch provisioning, or on the fly Quality of Service (QoS) adjustment. - 5G Multi Vendor Integration
NDL disassociates service logic from some of the vendor-specific control plane functions, allowing for the multi-vendor integration of network equipment, which contributes to interoperability and open networking.
🤖 Role of AI and ML in the NDL Context
NDL provides structured, real time data to support having rich, continuous data sources, which is essential for AI/ML to work effectively in telecom networks. Here’s how:
Predictive Maintenance: AI models would analyze session and state data to predict outages or degradation.
Churn Prediction: Analytics generated from subscriber data and usage patterns would inform proactive strategies for retention.
Smart Orchestration: Using AI agents, NDL can perform sophisticated orchestration using contextual telemetry data.
🧠 Conclusion
The NDL (Network Data Layer) Architectural Context represents a strategic foundation in modern telecom networks. It closes the gap between OSS, the control plane, and user services, allowing 5G networks to be:
Programmable
Context aware
AI ready
Interoperable
