Understanding the Role of the Open RAN Node Integrator in 5G Deployments

The Role of the Open RAN Node Integrator in 5G Deployment
As the telecom industry pivots towards more open and flexible infrastructure, Open RAN (Radio Access Network) has emerged as a game-changer. One of the key players in this transformation is the Open RAN Node Integrator, a crucial role responsible for orchestrating the integration of disaggregated hardware and software components. This blog post unpacks the importance of the Node Integrator, its role in Open RAN architecture, and how it contrasts with traditional network deployment.
Traditional RAN vs. Open RAN Vision
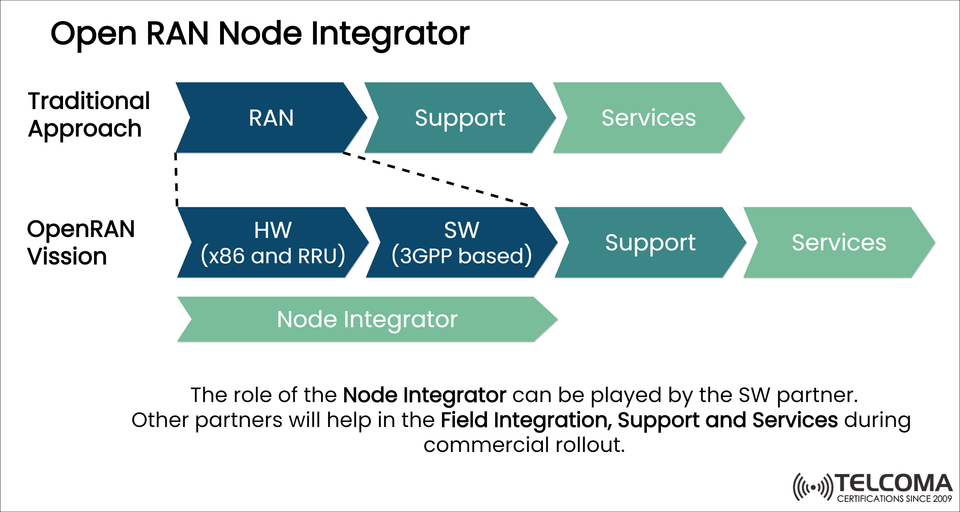
The image provided clearly distinguishes two approaches to deploying RAN infrastructure:
Traditional Approach OpenRAN Vision
Monolithic RAN solution Disaggregated components (HW and SW)
Vendor-provided integrated stack Open interfaces and multi-vendor environment
Limited flexibility Greater vendor diversity and innovation
Single vendor support/services Distributed support with shared responsibilities
Traditional Approach:
RAN, support, and services are tightly bundled and provided by a single vendor.
Integration is straightforward but limits flexibility and vendor choice.
Open RAN Vision:
Disaggregates the RAN into Hardware (HW) and Software (SW) components.
Hardware includes x86-based servers and Remote Radio Units (RRUs).
Software is 3GPP-compliant, allowing interoperability and modular upgrades.
Introduces a Node Integrator role to coordinate these components and ensure smooth deployment.
Open RAN Node Integrator — What is that?
Left to right: Node Integrator — this is the primary node in connecting hardware, software and services for Open RAN deployments. Traditional vendors would manage the entire stack, but Open RAN comes with multi-vendor interoperability requirements. This is why there will always be a role that can bridge this gap:
Commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) hardware
3GPP-based RAN software
Continued field support and service integration
Key Responsibilities:
Field Integration (FI): Test of readiness for hardware-software compatibility in the running life reality.
End-to-End Testing : Ensures cross-vendor interoperability at all the layers / tiers.
Coordination of Vendor-specific and third-party Support Models
Service Management: Managing lifecycle services of upgrades, patches and optimisations.
Who Can Play This Role?
PER: The Software partner as Node Integrator (this is often the case in partnerships) But note that other ecosystem players, such as system integrators and field service partners can provide integration, support & serve delivery during commercial roll-out.
Sponsored: The Node Integrator is Key to Successful 5G Rollouts
A move to Open RAN necessitates new deployment and operational frameworks. Node Integrator — helps telecom operators:
Time to Save in Market: Prepackaged modular components ready for integration.
Vendor Flexibility: Plug-and-play Architecture.
Enhanced Network Scalability — Dynamic resource allocation and scalezapmsbalIdealuse case:
OPEX & CAPEX Reduction: On COTS hardware and Open interfaces.
Building a Robust Open RAN Ecosystem — Summary
In contemporary disaggregated networks, the Open RAN Node Integrator is critical. Thus, it realizes the full benefits of that openness — vendor choice to gain increased flexibility and faster innovation in commercial rollouts. Tech enthusiasts and telecom professionals can use a primer on this role as they navigate the brave new world of emerging 5G infrastructure.
Key Takeaways:
Open RAN dedicates traditional RAN into HW and SW parts
Node Integrator for connecting everything, Peggy Gion. Bug-free Integration (Thorniness and completeness)
Those SW partners very often just act as Node Integrator.
Close coordination with ecosystem partners needed for field integration, support and services.
With this approach, 5G deployments can be more agile, cost-effective and scalable.
