Understanding vRAN Architecture: Components, Functions, and Network Flow

vRAN Architecture Unraveled: Virtualizing the Radio Access Network
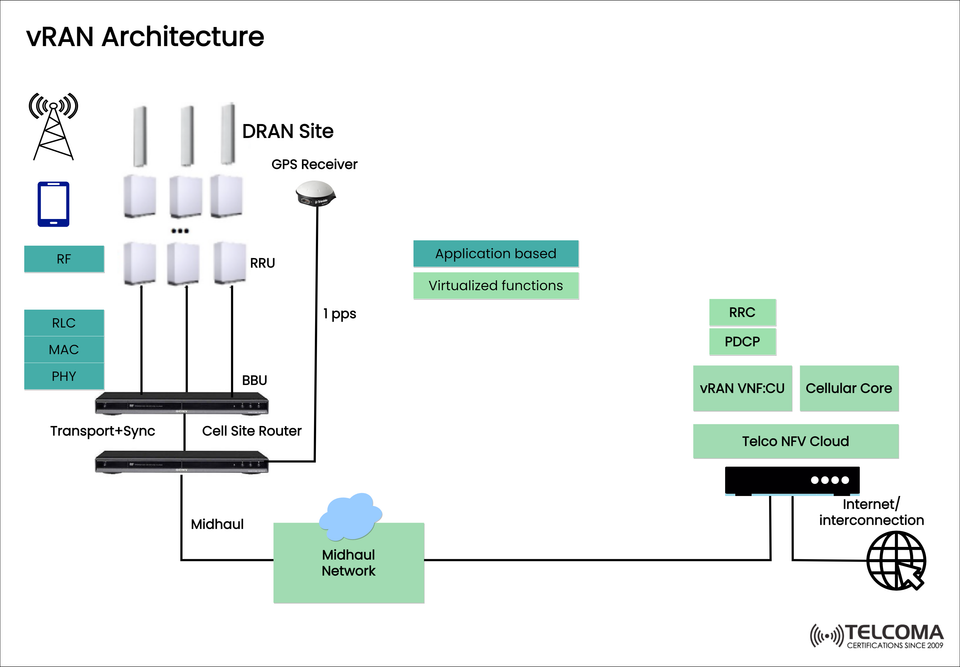
As 5G networks develop, telecom operators are rapidly moving to Virtualized Radio Access Networks (vRAN) for flexibility, scalability, and cost savings. The diagram above depicting the vRAN architecture shows the traditional base station components disaggregated and virtualized in a cloud-native way.
This blog will take a look at a vRAN system structure, components, and functions flows to those working in telecom, network engineers, or 5G strategists.
🧱 What is vRAN?
vRAN (Virtualized Radio Access Network) disaggregates traditional baseband hardware into software functions that run on commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) servers. Software functions are centralized and deployed in Telco NFV (Network Function Virtualization) cloud environments.
🏗️ vRAN Architecture Components
Here’s a simplified view of the vRAN components illustrated in the diagram:
DRAN Site (Distributed RAN)
User Equipment (UE): The mobile device which connects to the network.
Radio Frequency (RF): The section that transmits and receives Radio signals.
RRU (Remote Radio Unit): Converts digital signals from the BBU into analog RF signals and vice versa.
BBU (Baseband Unit): Responsible for Layer 1 (PHY), Layer 2 (MAC/RLC), and some Layer 3 functions.
Transport + Sync / Cell Site Router: Responsible for moving data and synchronizing all the above to the Network.
🌐 End-to-End Network Flow
When the UE connects to RF and RRU, the signals are processed in the BBU from PHY to MAC/RLC. The traffic is sent midhauled to the Telco NFV Cloud where the CU is functionally performing PDCP and RRC. Primary data sessions are anchored via the core network, allowing traffic to exit to the internet or interconnect with services external to the network (i.e. VNF).
🏁 Conclusion
vRAN represents a significant advancement in the creation of a mobile network fabric that is flexible, cost-driven, and high performance. The decentralization included in the virtualization of components in the RAN allows network operators the flexibility to support any number of use cases and variations that 5G brings to an ecosystem of applications including IoT and private 5G non-public networks, or ultra-reliable low-latency communication.
As illustrated in the vRAN architectural model, combining edge hardware, midhaul transport, centralized public cloud and cNFs with the vNF creates a strong and scalable RAN environment that paves the way for Open RAN and cloud-native networks.
🔗 How to Uncover Link Internals (for WordPress SEO)
Take this article and internal link your other relevant articles for increased engagement and time on session:
What is Open RAN and What is its Relation to vRAN
Investigating 5G Core Architecture and Network Slicing
BBU vs CU-DU Split in Next Gen Networks
NFV and SDN in 5G: Cloud-Native Infrastructure
Using interlinks helps the search engines better understand your site's hierarchy and they provide useful navigation guidance for users based on this logical road map of learning.
🖼️ Image Alt Text for SEO and Accessibility
Alt text example for uploaded image:
“vRAN architecture diagram depicting components of DRAN site such as RRU, BBU, GPS sync, and midhaul connection to Telco NFV Cloud comprised of virtualized functions.”
💼 vRAN in Action
vRAN has many active use cases today across a few different scenarios:
Urban 5G networks: Dynamic traffic and population density
Private enterprise networks: Manufacturers, mines, and logistics companies use localized vRAN to provide secure, low-latency communication to teams or devices
Rural connectivity: Virtualization to reduce costs of deployment and support in a low density area
Cloud-based mobile networks: Operators building their 5G RAN and core on public and hybrid cloud capabilities.
📊 Comparison: Traditional RAN vs. vRAN
Feature Traditional RAN vRAN
Architecture Hardware-based Software-defined
Flexibility Vendor-locked and inflexible Modular and scalable
O&M Manual-intensive Automated and centralized
Cost High CAPEX / OPEX Total cost lowered
Deployment Speed Slower Faster with cloud-native tools
💡vRAN Benefit Rapid Refresher
🛠️ Disaggregation allows flexible deployment models (centralized/distributed)
☁️ Cloud-Native Architecture enables fast scaling and service upgrades
🔐 Open Interfaces enable multi-vendor interoperability (key to Open RAN)
⚡ Low Latency Support for URLLC, edge computing, and 5G use cases
📘 Optional Schema Markup (For SEO Plugins like Yoast/RankMath)
Embed this in your blog header or with an SEO plugin:
json
Copy
Edit
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "TechArticle",
"headline": "Understanding vRAN Architecture: Components, Functions, and Network Flow",
"description": "This article will explain how vRAN will disaggregate traditional RAN functions and allow for cloud-native deployment with midhaul connectivity, a virtual CU, and integration into Telco NFV Cloud.",
"image": "URL_TO_IMAGE",
"author": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Telcoma"
},
"publisher": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Telcoma",
"logo": {
"@type": "ImageObject",
"url": "https://telcomaglobal.com/logo.png"
}
},
"datePublished": "2025-07-12",
"keywords": "vRAN architecture, virtualized RAN, 5G BBU and RRU, Telco NFV cloud, midhaul network, RRC PDCP CU, open RAN deployment"
}
(Remember to replace "URL_TO_IMAGE" with your image link for hosting)
🏁 Conclusion
As mobile operators deploy increasingly open and flexible mobile networks, vRAN is becoming a key part of 5G transformation because it enables automation, supports edge computing capabilities, and allows telco operators to deploy RAN functions as if they were any other cloud-native software application.
Familiarity with the architecture, from the radio frequency to the Telco NFV Cloud, allows engineers to make informed technology decisions that directly influence planning: CAPEX spending; and the ability to scale in the future.
🔁 Content Repurposing Recommendations
To get the most value out of your vRAN content, you can repurpose it into any of the following content formats:
Format Purpose Platform
Infographic Simple visual overview or summary of vRAN flow LinkedIn, SlideShare
Explainer video Visual walk through or journey of the architecture YouTube, training portals
Technical white paper Downloadable comprehensive guide Website or email marketing
Slide deck Can be used for webinars or internal training PowerPoint/PDF
Social media carousel post Can outline the benefits of vRAN Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn
🧾 WordPress Formatting Instructions (Block Editor)
Here’s how to format important things in WordPress Gutenberg editor:
Headings: Use H2 for primary subheadings and H3 for technical layers (eg. RRC, PDCP)
Bullet points and tables: Use "List" blocks and “Table” blocks to provide breakdown of components
Image Block: Upload the vRAN diagram under Block and use the provided alt text for accessibility and search engine optimization purposes
Call to Action Block: This would be a "Buttons" or "Group" block, to emphasize CTAs with customizable
