Voice and Emergency Services in 5G EN-DC Explained

Voice and Emergency Services in 5G EN-DC
The shift to 5G New Radio (NR) has truly transformed mobile broadband, offering speeds that are lightning fast, ultra-low latency, and vast connectivity options. But when it comes to voice and emergency services, EN-DC (E-UTRAN New Radio – Dual Connectivity) plays a key role.
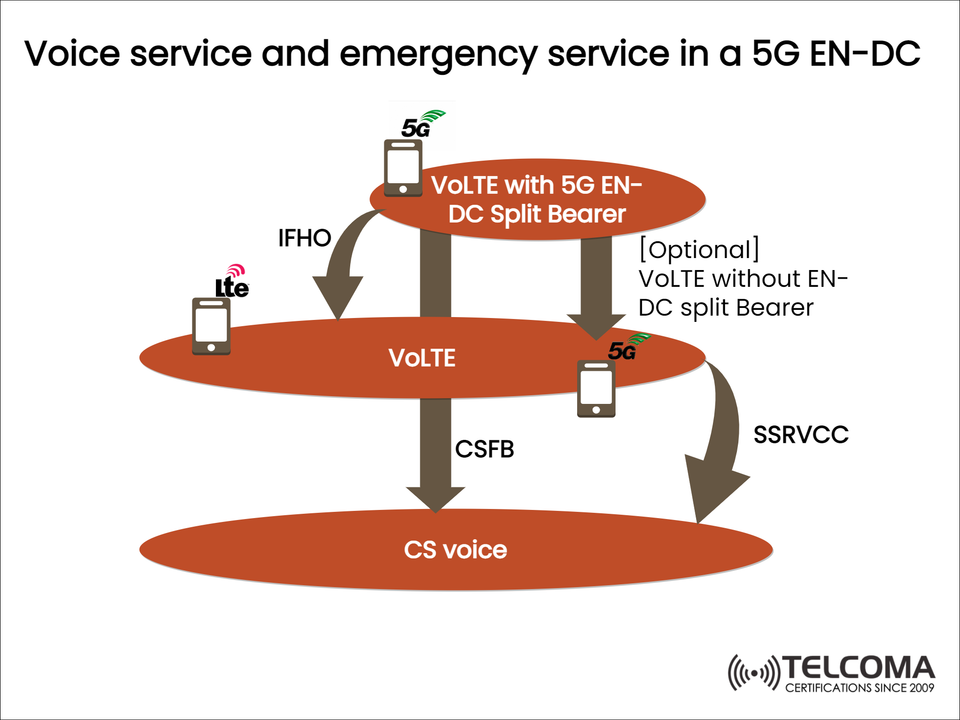
In the early days of 5G, networks and devices need EN-DC to mesh LTE and 5G together. This setup allows operators to deliver not just high-speed 5G data but also reliable LTE-based voice services (VoLTE). You can see in the diagram above how voice and emergency calls are managed in an EN-DC scenario, ensuring smooth connectivity across LTE, VoLTE, and older CS (circuit-switched) voice networks.
What is 5G EN-DC?
EN-DC (E-UTRAN NR Dual Connectivity) lets a device connect to both LTE (acting as the master node) and 5G NR (serving as the secondary node) at the same time.
LTE handles control plane and voice services.
5G NR boosts the user plane throughput for faster data.
This setup means that while 5G ramps up data performance, voice stays anchored in LTE with VoLTE, making EN-DC a bridge to full 5G Standalone (SA) voice solutions.
VoLTE in EN-DC
In an EN-DC network, Voice over LTE (VoLTE) is still the go-to solution for making voice calls.
There are two options:
VoLTE with EN-DC Split Bearer
The signaling and traffic for voice calls are anchored on LTE but can also tap into 5G NR resources.
This option offers better quality and manages voice and data services more effectively.
VoLTE without EN-DC Split Bearer (Optional)
Voice traffic operates solely over LTE.
5G NR is used only for data.
This can be handy if operators want to keep voice strictly on LTE.
With Vo LTE, users can expect smooth continuity and high-quality calls even in a dual connectivity setup.
Emergency Voice Support in EN-DC
A major aspect of EN-DC is making sure emergency voice services are always accessible. Regulations require that emergency calls are supported, no matter if the device is on 5G or LTE.
If the VoLTE with EN-DC split bearer is active, emergency calls can still go through using LTE.
If LTE coverage starts to drop, fallback mechanisms like CSFB (Circuit-Switched Fallback) or SRVCC (Single Radio Voice Call Continuity) will keep things running smoothly.
This setup guarantees emergency readiness, even in places where 5G coverage might be spotty or VoLTE isn’t fully operational.
Key Mechanisms in 5G EN-DC Voice Services
- IFHO (Inter-Frequency Handover)
This comes into play when a device on LTE shifts between different frequency bands.
It ensures a smooth transition without dropped calls.
Quite crucial for users moving through mixed LTE-5G networks.
- CSFB (Circuit-Switched Fallback)
If Vo LTE isn’t working, the device can revert to using 2G/3G circuit-switched voice.
This secures basic voice calling capabilities.
However, it does mean longer wait times to set up calls compared to Vo LTE.
- SRVCC / SSRVCC (Single Radio Voice Call Continuity)
SRVCC allows for a seamless changeover from Vo LTE to circuit-switched (CS) networks.
SSRVCC (Single Step SRVCC) streamlines the process by making the switch in one step instead of going through several signaling stages.
This avoids dropped calls when moving from LTE/5G to 2G/3G.
Flow of Voice Services in EN-DC (Based on the Diagram)
Vo LTE with 5G EN-DC Split Bearer
The call starts in LTE but benefits from data support via 5G NR.
Optional Vo LTE without Split Bearer
The entire call is managed in LTE, while 5G NR is dedicated to data.
Inter-Frequency Handover (IFHO)
If the device shifts between LTE bands, the call remains stable.
CSFB
Should VoLTE be unavailable, the device can switch to CS voice (2G/3G).
SRVCC/SSRVCC
Ongoing VoLTE calls smoothly transition to CS voice if LTE coverage weakens.
This structured approach makes sure that both regular and emergency calls stay uninterrupted.
Benefits of EN-DC for Voice and Emergency Services
Seamless Continuity: Calls maintain stability between LTE, 5G, and older networks.
Emergency Reliability: Always-on fallback options ensure emergency calls can go through.
Enhanced Quality: VoLTE with split bearer allows for better voice and data handling.
Network Flexibility: Operators can roll out 5G data services without rushing towards VoNR.
Challenges in EN-DC Voice Implementation
Though EN-DC is a reliable interim solution, it has a few challenges:
Complexity: Managing dual connectivity means dealing with sophisticated signaling methods.
Coverage Gaps: Relying on LTE VoLTE might limit service in areas with weak LTE signals.
Latency: CSFB can lead to delays when setting up calls.
Transition Phase: EN-DC is just a stepping stone before native 5G voice (VoNR) becomes the norm.
Future of Voice Beyond EN-DC – Toward Vo NR
Ultimately, the aim for 5G networks is to support Voice over New Radio (Vo NR), which will run directly on the 5G Core (5GC).
Advantages of VoNR:
Lower latency compared to VoLTE.
Full integration with advanced 5G features (like AR/VR calls, network slicing).
Independence from LTE infrastructure.
Until then, EN-DC is crucial for operators to deliver dependable voice and emergency services while they expand 5G coverage.
Quick Reference Table
Mechanism Role in EN-DC Voice Key Advantage Limitation Vo LTE (with Split Bearer)Uses LTE anchor + 5G data Improved call/data performance Higher complexity Vo LTE (without Split Bearer)Pure LTE-based voice Stability & simplicity5G unused for voice IFHO LTE frequency handover Seamless mobility Requires robust LTE coverage CSFB Falls back to 2G/3G CS voice Legacy support Slower call setup SRVCC/SSRVCC Vo LTE → CS voice handover Call continuity Adds signaling overhead
Conclusion
5G EN-DC plays an essential role in connecting LTE voice with native 5G voice (Vo NR). By combining LTE as the backbone for control and voice alongside 5G NR for data throughput, EN-DC ensures that users benefit from the best of both worlds.
With mechanisms like Vo LTE (with or without EN-DC split bearer), IFHO, CSFB, and SRVCC/SSRVCC, EN-DC provides seamless voice continuity, emergency readiness, and a top-notch user experience.
As operators continue to transition towards complete 5G SA deployments featuring Vo NR, EN-DC will stay a fundamental part of early 5G rollouts, keeping users connected to crucial voice and emergency services.
