VoIMS Architecture in LTE and 5G: Integration with IMS, EPC, and 5GC
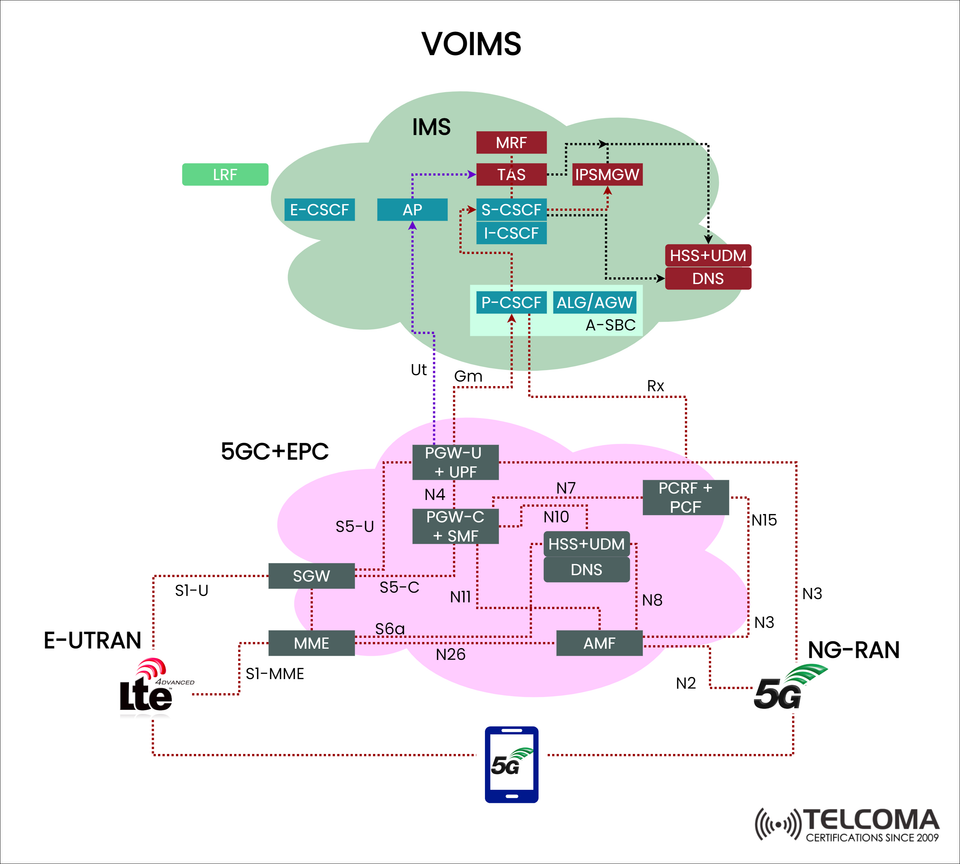

VoIMS Architecture in LTE and 5G Networks
Voice over IMS (VoIMS) is a key technology that provides high-quality voice services in LTE and 5G networks. Unlike older circuit-switched voice systems, VoIMS leverages the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) to deliver voice and multimedia services over an all-IP platform.
The diagram included shows how VoIMS operates within LTE (E-UTRAN + EPC) and 5G (NG-RAN + 5GC), highlighting its seamless interoperability. Let’s explore the architecture, interfaces, and main components of this system.
What is VoIMS?
VoIMS, or Voice over IMS, is an IP-based voice service that enables users on LTE and 5G networks to make voice calls using the IMS core. It serves as the base for both VoLTE (Voice over LTE) and VoNR (Voice over New Radio).
Some of the key features of VoIMS include:
IMS-based voice service tailored for LTE and 5G.
Guarantees service continuity during inter-RAT transitions (like moving from LTE to 5G).
Offers support for supplementary services such as call forwarding, call waiting, and conferencing.
Employs SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) signaling within IMS for call setup and management.
Major Components of VoIMS Architecture
The diagram illustrates several crucial network layers and entities:
- IMS Core (Green Cloud)
The IMS subsystem is responsible for managing signaling and call control.
P-CSCF (Proxy Call Session Control Function): The first point of contact for the UE in IMS.
I-CSCF (Interrogating CSCF): Manages SIP signaling routing within IMS.
S-CSCF (Serving CSCF): Key entity for call and session control.
E-CSCF (Emergency CSCF): Handles emergency call routing.
MRF (Media Resource Function): Provides conferencing, announcements, and media services.
TAS (Telephony Application Server): Supports various telephony services and call control features.
IP-SMGW (IP Multimedia Subsystem Gateway): Connects IMS to external IP networks.
HSS/UDM: Stores subscriber profiles and manages authentication.
ALG/AGW (Access Gateway): Facilitates signaling and bearer interworking.
- Evolved Packet Core (EPC) – LTE (Pink Cloud)
MME (Mobility Management Entity): Manages signaling, authentication, and mobility.
SGW (Serving Gateway): Manages user plane traffic.
PGW-C + SMF (Control Plane): Ensures policy enforcement and session management.
PGW-U + UPF (User Plane): Routes user traffic.
- 5G Core (5GC) – Integrated with EPC
AMF (Access and Mobility Management Function): Manages 5G registration and mobility.
SMF (Session Management Function): Allocates resources for data sessions.
UPF (User Plane Function): Routes and forwards user data.
PCF (Policy Control Function): Replaces PCRF for managing policies in 5G.
UDM (Unified Data Management): Handles user authentication and subscription management.
- Radio Access Networks
E-UTRAN (LTE): The traditional LTE radio access network connecting to EPC.
NG-RAN (5G): The 5G New Radio network connecting to 5GC.
Interfaces in VoIMS
The diagram also details important interfaces:
Ut (UE ↔ AP): For supplementary services.
Gm (UE ↔ P-CSCF): SIP signaling for IMS registration and call setup.
S1-MME (E-UTRAN ↔ MME): LTE signaling interface.
N2, N3 (NG-RAN ↔ 5GC): Control and user plane interfaces for 5G.
N26 (MME ↔ AMF): Interworking for mobility between EPC and 5GC.
Rx (IMS ↔ PCRF/PCF): Interface for policy control.
How VoIMS Works Across LTE and 5G
User Registration: The device connects to IMS through P-CSCF using SIP, with authentication via HSS/UDM.
Call Setup: When a call is initiated, S-CSCF manages the session and may interact with TAS and MRF as required.
Data Transport: Voice packets travel through SGW/PGW in LTE or UPF in 5G.
Policy Enforcement: PCRF/PCF enforces QoS policies to maintain voice quality.
Inter-RAT Mobility: N26 ensures service continuity during transitions between LTE and 5G.
Advantages of VoIMS
Seamless voice continuity across LTE and 5G networks.
Improved call quality through dedicated QoS parameters.
Convergence of services (voice, video, messaging) within the IMS framework.
Future-proofing, as IMS supports VoLTE, VoNR, and rich communication services (RCS).
LTE vs 5G Integration in Vo IMS
Features LTE (Vo LTE)5G (Vo NR)CoreEPC5GCVoice Control IMS IMS Policy Control PCRFPCF Mobility Management MMEAMF User Plane SGW + PGWUPF Interworking EPC ↔ IMS5GC ↔ IMS
Suggested SEO Keywords for Vo IMS
Main Keywords (Top Priority):
VoIMS architecture
IMS in LTE and 5G
Voice over IMS (VoIMS)
VoLTE and VoNR integration
5G voice services
Supporting Keywords:
EPC and 5GC integration
IMS call flow
SIP signaling in IMS
LTE IMS core
5G VoNR architecture
Long-Tail Keywords (High CTR, Niche):
How does VoIMS work in 5G networks?
What's the difference between VoLTE and VoNR?
VoIMS interfaces explained
IMS integration with EPC and 5GC
The role of IMS in 5G voice services
Internal Linking Strategy (for WordPress Blog)
To boost your SEO, link this post to other related telecom topics on your blog or ones you plan to write about:
“What is IMS in Telecom?” → This article covers the basics of IMS before getting into VoIMS.
“VoLTE Call Flow Explained” → Provides a detailed analysis of SIP flow.
“5G Core Network Functions Explained” → Background info on AMF, SMF, and UPF.
“EPC vs 5GC: What’s the Difference?” → Helps readers grasp the interworking (N26 interface).
“VoNR: Voice over New Radio in 5G” → A logical follow-up piece.
External Linking Strategy
To enhance authority and technical reliability, link to credible sources like:
3GPP Specifications (like TS 23.228 for IMS and TS 23.502 for 5GC procedures).
GSMA Whitepapers on IMS and VoLTE/VoNR.
Technical blogs from vendors (Ericsson, Nokia, Qualcomm) covering VoIMS implementation.
Conclusion
VoIMS (Voice over IMS) is vital for ensuring voice continuity and quality across LTE and 5G networks. By utilizing IMS, alongside EPC and 5GC integration, operators can offer users smooth VoLTE and VoNR services, plus enriched multimedia experiences.
As networks move towards full 5G capabilities, VoIMS ensures backward compatibility with LTE while paving the way for an all-IP future in telecom services. For telecom engineers and enthusiasts, it’s crucial to grasp the VoIMS architecture to effectively manage 5G deployment and service assurance.
