VoLTE PUD Session Creation Call Flow – Step-by-Step Guide for Telecom Engineers
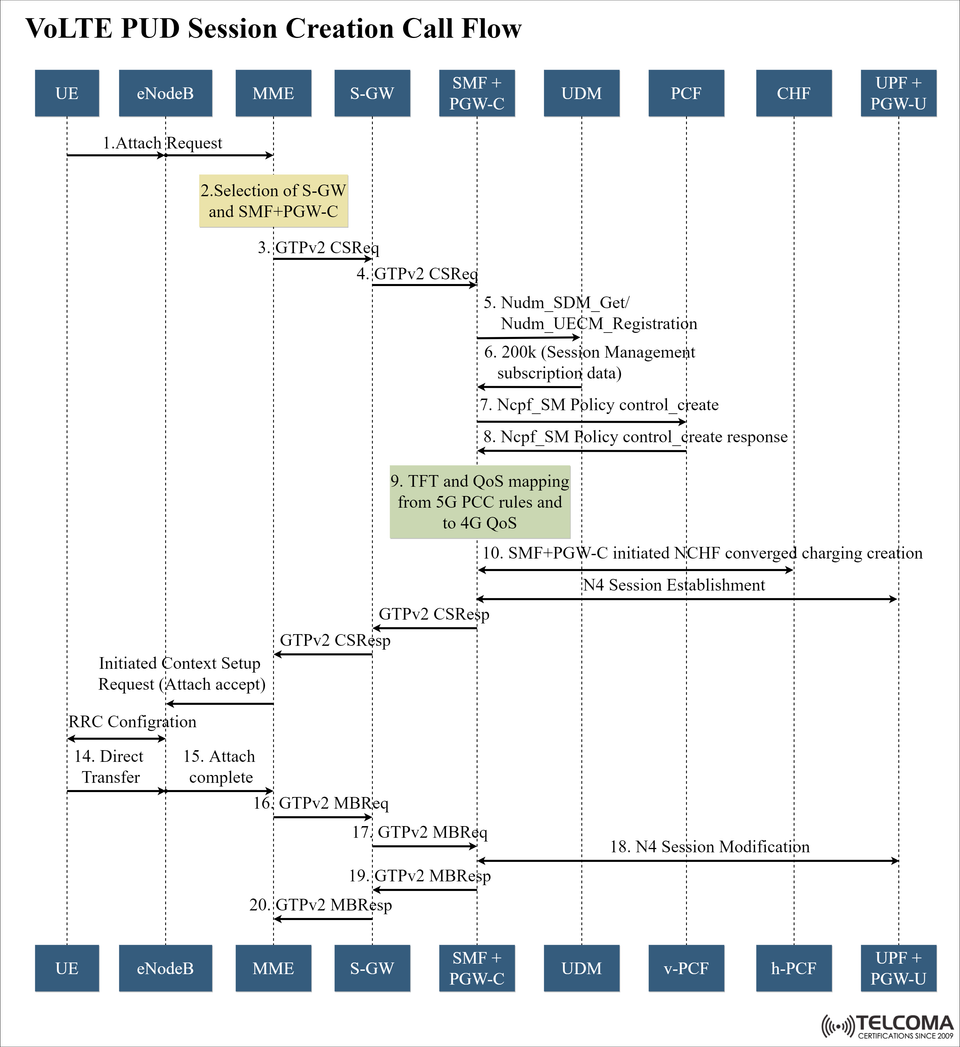

Understanding the VoLTE PUD Session Creation Call Flow
Voice over LTE, or VoLTE, has really changed the game for mobile voice services by using IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) over LTE networks instead of the old circuit-switched tech. In more advanced setups, VoLTE can run on E-UTRAN with 5G Core (5GC) support, which brings better policy control, charging functions, and Quality of Service (QoS) mapping.
The PUD Session Creation Call Flow is a key process that sets up the necessary connections, applies policy rules, and makes sure that the User Equipment (UE) is set for high-quality voice service. The diagram above illustrates how different network components work together to establish a VoLTE Packet Data Unit (PDU) session in a mixed LTE-5G environment.
Key Network Components in the Call Flow
Before we get into the details, it’s important to know the main players involved:
Entity|Function
UE|Mobile device requesting VoLTE session
eNodeB|LTE base station that handles radio signaling
MME|Mobility Management Entity – manages session control and bearer setup
S-GW|Serving Gateway – routes user data packets
SMF + PGW-C|Session Management Function + Packet Gateway Control – handles PDU session control in 5GC context
UDM|Unified Data Management – stores subscription data
PCF (vPCF/hPCF)|Policy Control Function – defines QoS and charging rules
CHF|Charging Function – oversees billing events
UPF + PGW-U|User Plane Function – forwards user plane traffic
Step-by-Step Breakdown of the VoLTE PUD Session Creation Call Flow
Step 1 – Attach Request
The UE kicks things off by sending an Attach Request to the eNodeB. This tells the network that the device wants to connect for services, including VoLTE.
Step 2 – Gateway Selection
Next, the MME picks the Serving Gateway (S-GW) and SMF + PGW-C based on factors like location, load, and subscription details to make sure the routing is efficient.
Step 3 – Create Session Request (GTPv2)
The MME then sends a Create Session Request (CSR) to the S-GW using GTPv2-C. This request includes session details like APN, QoS profile, and bearer identifiers.
Step 4 – Forwarding CSR to SMF + PGW-C
The S-GW passes along the Create Session Request to the SMF + PGW-C for more session management in the 5GC context.
Step 5 – UDM Interaction
The SMF gets in touch with the UDM using the Nudm_SDM_Get and Nudm_UECM_Registration interfaces to grab the UE’s subscription profile and confirm its registration status.
Step 6 – Subscription Data Fetch
The UDM comes back with session management subscription data, covering allowed services, QoS parameters, and policy information.
Step 7 – Policy Control Request
Next, the SMF reaches out to the Policy Control Function (PCF) with an Npcf_SM_PolicyControl_Create request to set up the policy and charging control rules for the VoLTE session.
Step 8 – Policy Control Response
The PCF replies with the policy rules, which include bearer QoS settings, ARP (Allocation Retention Priority), and any PCC (Policy and Charging Control) filters.
Step 9 – TFT and QoS Mapping
The SMF handles Traffic Flow Template (TFT) and QoS mapping, which converts 5G PCC rules to 4G QoS bearers. This step guarantees that LTE radio bearers can uphold the service quality parameters established by the 5G Core.
Example Mapping Table:
5G Parameter|Mapped 4G Equivalent
5QI (5G QoS Identifier)|QCI (QoS Class Identifier)
GBR (Guaranteed Bit Rate)|GBR bearer
ARP|ARP
Non-GBR|Non-GBR bearer
Step 10 – Charging Session Creation
The SMF + PGW-C fires up the CHF to start collecting charging data, ensuring accurate billing for the VoLTE call.
Step 11 – N4 Session Establishment
Now, the SMF establishes the N4 session with the UPF, setting up the user plane path to carry voice traffic.
Step 12 – CSR Response
The SMF sends a Create Session Response back through the S-GW to the MME, confirming that the bearer has been created and QoS is in place.
Step 13 – Initial Context Setup
The MME then sends an Initial Context Setup Request to the eNodeB, which includes the bearer parameters and the Attach Accept message.
Step 14 – RRC Configuration
The eNodeB sets up the UE’s Radio Resource Control (RRC) layer for the VoLTE bearer.
Step 15 – Attach Complete
The UE responds with an Attach Complete message, confirming that the session has been successfully established.
Step 16–19 – Bearer Modification
The MME sends Modify Bearer Requests to update session paths or QoS if needed. This could include reconfiguring bearers to reduce latency for VoLTE traffic.
Step 20 – Modify Bearer Response
The bearer modification is acknowledged, finalizing everything.
The Importance of QoS Mapping for VoLTE over 5GC
QoS mapping is essential to ensure that 5G-defined service quality is maintained when traffic is sent over LTE radio. Without this mapping, the voice quality could take a hit, leading to issues like jitter, packet loss, or even call drops.
Benefits of Proper QoS Mapping:
Keeps low latency for voice
Guarantees prioritization over data traffic
Maintains service-level agreements in mixed LTE/5G environments
The Role of Policy Control in VoLTE PUD Sessions
The PCF plays a crucial role in making sure that the VoLTE session follows the subscriber's plan, adapts to network conditions, and aligns with operator policies.
Key PCF functions in this flow include:
Defining bearer QoS levels
Implementing PCC filters for voice traffic
Working with CHF for real-time charging
Dynamically applying policy changes
Key Technical Considerations for Operators
When setting up VoLTE PUD session creation in a network that integrates 5G Core, operators should keep in mind:
Interoperability Testing – Making sure LTE eNodeB, MME, and SMF are all compatible
Policy Server Integration – Supporting both PCC (5G) and EPC policy formats
Latency Optimization – Strategically placing UPF to minimize call setup delays
Billing Accuracy – Checking CHF interactions for real-time billing
How to Troubleshoot Common Issues
Problem|Possible Cause|Resolution
Session creation failure|UDM subscription mismatch|Check UDM profile
Poor voice quality|QoS mapping errors|Validate TFT mapping
Delayed attach|N4 session delay|Optimize UPF connectivity
Billing discrepancies|CHF integration issues|Debug SMF–CHF interface
Conclusion
The VoLTE PUD Session Creation Call Flow is a foundational process for delivering high-quality, low-latency voice services in today’s LTE–5G hybrid networks. By grasping each signaling step—from attach request to QoS mapping—telecom engineers can facilitate efficient call setups, maintain voice quality, and ensure accurate billing.
As operators keep merging LTE radio access with 5G Core functionalities, mastering these processes becomes vital for network optimization, customer satisfaction, and staying ahead of the competition.
