Blockchain in 6G-enabled IoT: Transforming Connectivity, Trust, and Automation
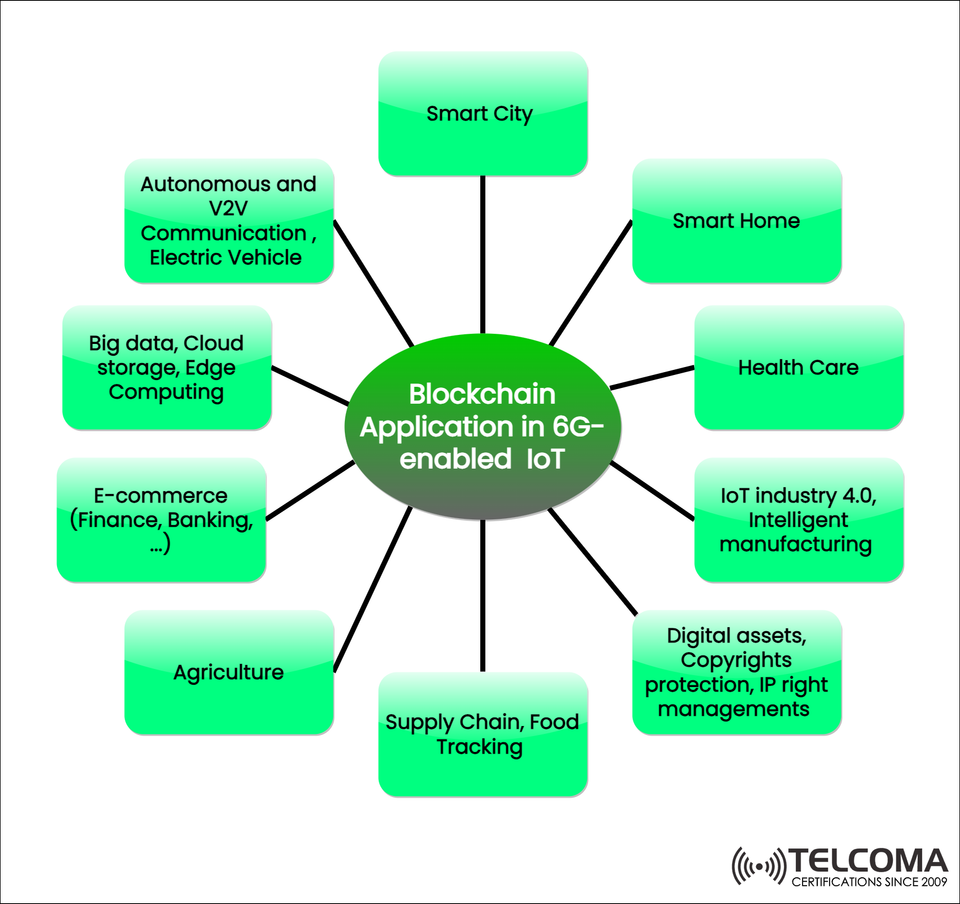

Blockchain Applications in 6G-enabled IoT: The Next Digital Revolution
The sixth generation of wireless technology (6G) is set to offer incredibly fast, smart, and secure connections, going beyond what 5G can do. With billions of devices interacting and sharing data in real-time, maintaining trust, transparency, and security is a huge challenge.
This is where blockchain technology comes into play, transforming the landscape. By weaving blockchain into the 6G-enabled Internet of Things (IoT) systems, telecom networks can establish decentralized trust frameworks that automate processes, secure transactions, and authenticate devices without needing human input.
The graphic above shows how blockchain can be applied across different 6G-IoT areas, like smart cities, healthcare, autonomous vehicles, e-commerce, and digital rights management.
The Foundation: Why Blockchain in 6G-enabled IoT Matters
Before exploring applications, it’s crucial to grasp the technological harmony between 6G and blockchain.
6G Capabilities Enabling IoT:
Terahertz communication: Offers ultra-high data rates that exceed 1 Tbps.
Sub-millisecond latency: Supports real-time communication between devices.
AI-driven networks: Help automate resource allocation and boost energy efficiency.
Massive IoT support: Can connect up to 10 million devices in a single square kilometer.
Blockchain’s Complementary Strengths:
Decentralized trust: Removes dependence on centralized authorities.
Immutable ledgers: Guarantee that data transactions are transparent and verifiable.
Smart contracts: Enable automatic, rule-based operations among IoT devices.
Security and identity: Safeguard devices against spoofing, tampering, and data theft.
Smart Cities: The Backbone of Connected Societies
In smart cities, millions of IoT sensors are constantly monitoring traffic, utilities, energy, and public safety. Blockchain provides the necessary trust framework for data integrity and transparency.
Key Use Cases:
Decentralized Data Sharing: Blockchain ensures that only authorized individuals can access sensor data, which is crucial for things like energy grids or transport systems.
Smart Governance: Public records—like licenses, permits, and citizen feedback—are kept on tamper-proof ledgers.
Autonomous Resource Management: AI combined with blockchain smart contracts automatically manages street lighting, waste collection, and water usage according to real-time sensor data.
Smart Homes: Secure, Self-Managing Ecosystems
Smart homes represent the personal aspect of IoT. With 6G speed and blockchain-based identity systems, homes evolve into autonomous digital entities.
Applications:
Device Authentication: Blockchain verifies smart appliances, like thermostats, cameras, and locks, before they connect to the network.
Energy Trading: Homeowners can sell excess solar energy to neighbors using blockchain-based microgrids.
Data Privacy: Personal data, such as health stats and consumption patterns, is kept encrypted and accessible only to authorized devices or services.
Benefits:
Fewer security breaches
More efficient energy use
Clear and auditable device logs
Healthcare: Blockchain for Data Integrity and Telemedicine
Healthcare IoT involves constant data exchange among patients, hospitals, and insurers. Here, trust and data integrity are absolutely vital.
Use Cases:
Medical Record Security: Patient data is logged on blockchain ledgers, ensuring authenticity and controlled access.
IoT Device Monitoring: Wearable health sensors send encrypted and verifiable data over 6G networks.
Drug Traceability: Blockchain enables transparency in pharmaceutical supply chains to help prevent counterfeit medications.
Supply Chain and Food Tracking
Blockchain revolutionizes the supply chain by ensuring transparency from production to consumption.
Blockchain-Driven Enhancements:
Product Provenance: Each transaction—harvest, shipping, packaging—is logged with a timestamp.
Tamper-proof Tracking: 6G-connected IoT sensors keep track of temperature, location, and humidity in real-time.
Fraud Prevention: Blockchain verification stops fake goods and data manipulation.
Business Benefits:
Builds consumer trust through transparency
Improves logistics efficiency
Helps meet regulations with digital audit trails
With 6G’s global coverage and network slicing, businesses can achieve real-time visibility of goods across the globe, all backed by decentralized verification.
Digital Assets, Copyrights, and IP Management
As digital content and AI-generated assets grow, blockchain secures ownership and usage rights in 6G-enabled metaverse and content-sharing spaces.
Core Use Cases:
Digital Asset Tokenization: Transform intellectual property or media into NFTs (non-fungible tokens).
Copyright Protection: Immutable blockchain timestamps guarantee content originality and help prevent plagiarism.
Licensing Automation: Smart contracts automatically handle royalty payments when content is accessed.
E-commerce, Finance, and Banking
6G and blockchain are set to reshape financial transactions within IoT ecosystems by enabling instant, secure, and verifiable micro-payments.
Blockchain Applications:
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Peer-to-peer loans and insurance operate without middlemen.
IoT Micropayments: Devices can conduct transactions without human oversight, like a connected car paying for tolls.
Cross-border Settlements: Blockchain cuts down transaction costs and latency for international transfers.
Big Data, Cloud Storage, and Edge Computing
6G will produce vast amounts of IoT data, and blockchain ensures that this data is securely stored, shared, and monetized.
Blockchain Enhancements:
Distributed Cloud Storage: Data fragments are encrypted and spread across decentralized nodes.
Data Provenance: Blockchain timestamps confirm the authenticity and history of data.
Edge Analytics Validation: Smart contracts verify findings from AI-driven computations at the edge.
It all contributes to a trustworthy data marketplace, giving users control over how their information is utilized or sold.
Autonomous Vehicles and V2V Communication
Self-driving and electric vehicles (EVs) depend on instant communication between cars, infrastructure, and the cloud.
Blockchain Applications:
V2V Authentication: Blockchain verifies vehicle identities before any data exchange occurs.
Data Integrity: Driving data, location information, and sensor readings are logged immutably.
Energy Transactions: EVs can use blockchain to handle payments for charging services automatically.
6G Capabilities:
Millisecond latency allows for collision avoidance systems and AI-based traffic optimization.
Network slicing guarantees reliable bandwidth for networks that support autonomous driving.
With blockchain providing trust and auditability, and 6G delivering speed and intelligence, we have the foundation for safe and autonomous transportation systems.
Agriculture and Smart Farming
6G-enabled IoT sensors are transforming agriculture through real-time crop monitoring, weather analysis, and automated irrigation. Blockchain adds to this by ensuring traceability and transparency.
Use Cases:
Crop Lifecycle Tracking: From the seed stage to the retail shelf, every step is verified through blockchain.
Agricultural Finance: Smart contracts facilitate transparent distribution of subsidies and loans.
Food Authenticity: Consumers can verify product origins via blockchain QR codes.
6G enables connectivity in rural areas, while blockchain boosts efficiency and transparency in agriculture.
Conclusion: Blockchain + 6G = The Trust Layer for the Internet of Everything
The merging of 6G and blockchain is set to be the backbone of the next technological revolution. Together, they create an ecosystem where connectivity, intelligence, and trust work hand-in-hand.
From smart cities and healthcare to autonomous vehicles and digital finance, blockchain maintains transparency and integrity, while 6G enables real-time, AI-powered automation.
