CU/DU Virtualization and Open RAN Interfaces: Enabling Cloud-Native 5G Networks

CU/DU Virtualization and Open RAN Interfaces: Cloudification of RAN for Next-gen 5G
The importance of Centralized Units (CU) and Distributed Units (DU) in the current telecom industry is crucial as we move towards cloud-native 5G infrastructure. CU and DU are key components to create scalable, flexible and software-centric Radio Access Networks (RAN) on cloud with Open RAN interfaces, virtualization and cloudification. Operators will be able to move away from proprietary monolithic systems and proprietary systems and work towards disaggregated and interoperable network components.
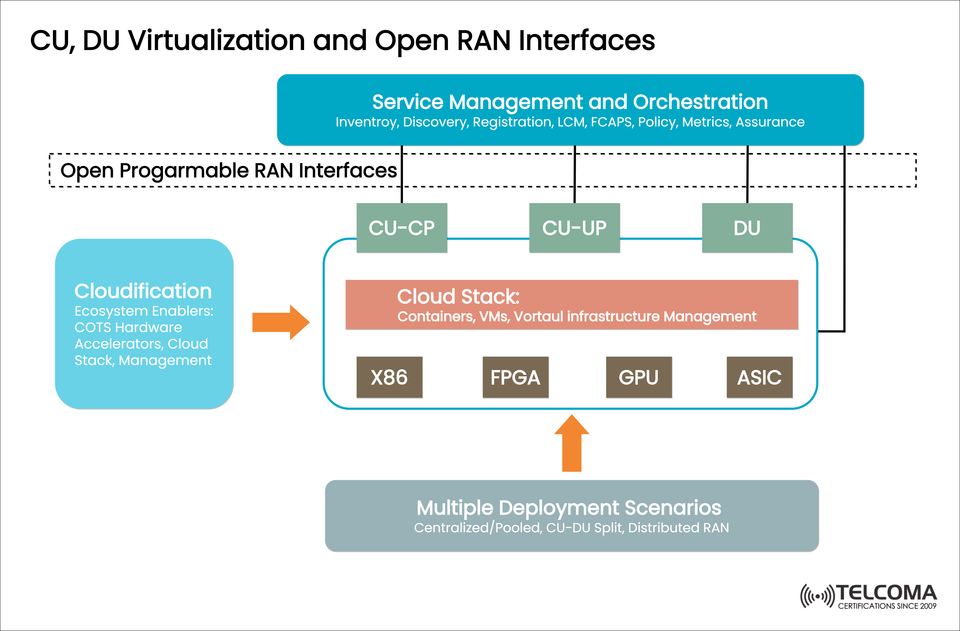
In the following, we deconstruct the architecture shown in the image above and review the effect of CU/DU virtualization on the RAN ecosystem.
☁️ What is CU/DU Virtualization?
CU/DU virtualization layers the RAN functions into software components on general-purpose hardware (COTS – Commercial Off-The-Shelf), orchestrated and managed from a cloud environment.
CU (Centralized Unit) completes non-real-time functions such as signaling and traffic.
CU-CP (Control Plane): RRC, signaling control
CU-UP (User Plane): SDAP, data forwarding
DU (Distributed Unit) performs real-time functions that will be processed closer to the edge (MAC, RLC, PHY-high )
Each function can be containerized or virtualized and deployed in cloud stacks supporting containers, VMs, all provisioned on the different virtualization platforms.
🧩 Multiple Deployment Scenarios
Open RAN with CU/DU virtualization allows for many deployment models:
Scenario Description
Centralized RAN CU and DU functions hosted in a centralized data center
CU-DU Split CU in the centralized cloud and DU at the edge (optimal for 5G latency initiatives)
Distributed RAN All functions distributed and placed close to users or enterprises
Pooled CU Shared CU resources for multiple DUs for best performance
Operators can choose deployment models from a latency, cost, performance, and geographic requirements perspective.
✅ Summary: Benefits of CU and DU virtualization in Open RAN
✅ Enables cloud-native RAN functions (containers, VMs, virtual infra)
✅ Increases agility and reduces CAPEX/OPEX
✅ Supports various types of hardware (X86, FPGA, GPU, ASIC)
✅ Enhances the flexibility of deployment models
✅ Creates automation through open interfaces
- How does cloudification help with 5G RAN?
Cloudification allows dynamic resource allocation, elastic scaling, increased automation, and switching between vendor-provided solutions on generic hardware. - How does open interfaces help in RAN?
They allow multi-vendor interoperability over O-RAN interfaces that reduce integration time, while also providing opportunities for multiple innovation efforts, and also allows programmable functionality. - 🔧 Best Practices for CU/DU Virtualization Implementation
To successfully implement CU/DU virtualization in an Open RAN architecture, operators and system integrators should follow a few guidelines:
🛠️ 1. Start With Cloud-Native Design Principles
Choose containers and microservices rather than a monolithic VNFs (Virtual Network Functions)
Prefer to orchestrate using Kubernetes or OpenStack
Try to decouple control/user planes early for independent scaling
🔌 2. Using Hardware Abstraction and Acceleration
Use x86 for general-purpose compute
Use FPGA/ASIC for high-throughput packet processing, or PHY layer acceleration
Consider GPU for AI/ML-driven RAN functions (e.g., traffic forecasting, anomaly detection)
🧠 3. Integrate AI/ML in the SMO Layer
Automate scaling of resources dependent upon real-time demand
Feed intelligent orchestration dependent upon the behavior of the network.
🔄 4. Enable CI/CD Pipelines
Use DevOps best practices for continuous or rapid-testing and delivery of CU/DU updates
Validate changes in a staging environment using a synthetic traffic model
🔗 Suggested Internal Links (for WordPress Blogs)
What Is Open RAN and Why It Matters
The Role of the RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC)
Top Hardware Accelerators for Virtualized RAN
🌍 External Resources & References
O-RAN Alliance Architecture White Papers
Linux Foundation Networking (LFN) ONAP Overview
ETSI NFV Standards and Use Cases
Intel Network Builders – vRAN Optimization
🎯 Final Client Action
Virtualization of CU/DU and the deployment of open interfaces are more than just technological advances for network operators. They strategically enable network operators to future-proof 5G (and beyond). Let your operating model be, whether you are an operator, vendor, or network architect, now is the time to:
- Update your RAN strategy
- Accept open multi-vendor
- Invest in automation and cloud-native infrastructure
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are CU-CP and CU-UP in a 5G Open RAN architecture?
CU-CP (Centralized Unit - Control Plane) performs the signaling functions within the RAN, including RRC (Radio Resources Control) and mobility control.CU-UP (Centralized Unit - User Plane) performs user data forwarding functions within the RAN, including SDAP (Service Data Adaptation Protocol) and PDCP (Packet Data Convergence Protocol). - Why is DU (Distributed Unit) virtualized in Open RAN?
Virtualizing DU allows it to be deployed on general purpose hardware, resulting in cost savings and flexibility and easier integration with edge cloud environments to attest to the low-latency requirements of 5G. - How does cloudification improve RAN operations?
Cloudification introduces automation, scalability, and dynamic resource allocation via the cloud-native technologies (containers, orchestration tool like Kubernetes, COTS hardware). - Can telecom operators use multiple hardware accelerators in Open RAN deployments?
Yes. Open RAN also embraces hardware abstraction and therefore allows the operator to use x86 for the general compute, FPGA or ASIC for offloading the physical layer operations and GPU
🏁 Final Summary
CU and DU virtualization, enabled by Open RAN interfaces, provides the foundation for an evolution toward cloud-native, automated, and scalable 5G networks. This architecture layer separates software from hardware, allowing the same CU/DU workload to be deployed in a range of deployment models, from a centralized cloud data center to an edge location, to support a wide variety of use cases in both public and private 5G markets.
The introduction of open and programmable interfaces, AI-based orchestration, and support for multiple hardware form factors (x86, GPU, FPGA, ASIC) gives telecom operators the tools to innovate faster, lower costs, and future-proof their RAN investments.
