Deployment Options in Mobile Networks: Massive MIMO, Small Cells, DAS, and More

Deployment Options in Mobile Networks: The Backbone of 5G and Beyond
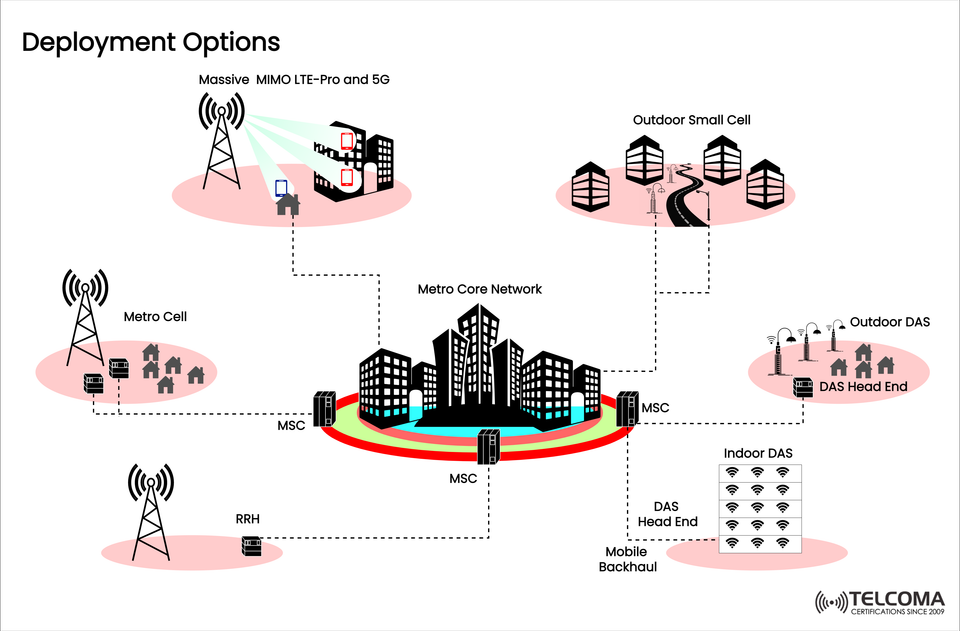
Rolling out advanced mobile networks like 5G and what’s coming next with 6G requires careful thought when it comes to deployment strategies. No single type of infrastructure can cover all bases regarding coverage, capacity, and performance needs. Instead, telecom operators use a mix of Massive MIMO, Metro Cells, Small Cells, DAS, RRHs, and mobile backhaul to ensure smooth connectivity.
The diagram shows how different deployment options link through the Metro Core Network (MCN), creating the backbone of today’s mobile ecosystems. Let’s dig into each option, what it does, and how they collaborate to provide efficient and high-quality connectivity.
What’s the Metro Core Network?
At the center of deployment is the Metro Core Network (MCN), which serves as the main hub that connects various components:
Macro-level coverage (through Massive MIMO and Metro Cells).
Dense urban coverage (thanks to Outdoor and Indoor DAS, Small Cells).
Rural and suburban coverage (using Remote Radio Heads).
Mobile Backhaul to link distributed access points.
The MCN makes sure that all traffic flows smoothly, supports scaling up, and enables advanced features like network slicing, real-time analytics, and low-latency communication.
Breaking Down Deployment Options
- Massive MIMO (LTE-Pro and 5G)
What it is: Massive Multiple Input, Multiple Output (MIMO) employs large antenna arrays to boost capacity and spectral efficiency.
Purpose: Vital for high-capacity urban areas, stadiums, and densely-packed environments.
Advantages: * Better spectral efficiency. * Beamforming cuts down on interference. * Allows high throughput for 5G services.
- Metro Cells
What it is: Medium-sized cells that bridge the gap between large macro cells and small cells.
Use Cases: Great for suburban areas, medium-density urban spots, or places where coverage is lacking.
Advantages: * Boosts network capacity and coverage. * A cost-friendly substitute for adding more macro towers.
- Remote Radio Heads (RRH)
What it is: Remote antennas linked to a baseband unit, often used in distributed base station setups.
Purpose: Helps reach beyond in rural areas or hard-to-access zones.
Advantages: * Flexible and scalable. * Cuts down on power loss by positioning radios closer to antennas.
- Small Cells (Outdoor)
What it is: Low-power base stations designed to provide focused coverage in high-density settings.
Use Cases: Ideal for city centers, shopping malls, and transport hubs.
Advantages: * Relieves congestion on macro cells. * Delivers localized high-capacity coverage. * Facilitates seamless handoffs for mobile users.
- Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS)
DAS spreads cellular signals through multiple antennas to enhance coverage in tricky spots.
Indoor DAS: * Used in offices, stadiums, airports, and shopping centers. * Guarantees strong indoor coverage where structures can weaken signals.
Outdoor DAS: * Found in urban areas, campuses, or outdoor event spaces. * Helps expand macro network coverage and capacity.
Benefits of DAS:
Reliable indoor/outdoor coverage.
Scalable to meet demand.
Centralized management through a DAS Head End.
- Mobile Backhaul
What it is: The transport network connecting the radio access network (RAN) components (cells, DAS, RRHs) to the Metro Core Network.
Purpose: Keeps voice, video, and data traffic flowing seamlessly.
Technologies: Fiber, microwave links, and satellite.
Advantages: * High-speed, dependable transport layer. * Essential for those ultra-low-latency needs in 5G.
Comparing Deployment Options
Here’s a straightforward comparison of the different deployment strategies:
Deployment Option Coverage Area Capacity Best Use Cases Massive MIMO Large (Urban Macro)High Stadiums, dense cities Metro Cells Medium Medium Suburban/urban fill-ins RRH Wide (remote)Low-Medium Rural/remote areas Small Cells Very Small High Urban hot spots Indoor DAS Building-level High Airports, malls, offices Outdoor DAS Campus/urban areas High Events, city blocks Mobile Backhaul Backbone N/A Transport layer for all
Why We Need Multiple Deployment Options
Today’s networks have to serve diverse environments:
Urban: Need for high capacity using Massive MIMO, Small Cells, and DAS.
Suburban: Metro Cells help balance coverage and cost.
Rural/Remote: RRH extends coverage without needing large infrastructure.
Indoor Spaces: Indoor DAS ensures solid connectivity.
This heterogeneous network (HetNet) strategy prevents any single deployment method from becoming a bottleneck.
Benefits for Telecom Operators
📶 Optimized Coverage: Customized solutions for urban, suburban, and rural areas.
⚡ Enhanced Capacity: Efficient use of spectrum with MIMO and Small Cells.
🔒 Improved Reliability: Multiple paths through DAS and various layers increase dependability.
💰 Cost Efficiency: Balanced investment strategy by mixing macro and smaller scale deployments.
Challenges in Deployment
While these deployment options provide significant benefits, they also bring along some challenges:
Site Acquisition: Finding the right spots for small cells and DAS.
Backhaul Costs: Ensuring fast backhaul without breaking the bank.
Interference Management: Especially tricky in densely packed small cell networks.
Energy Consumption: Keeping power needs in check for large-scale setups.
Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating zoning laws and permits for tower setups.
Deployment Options in the 5G and 6G Era
As networks evolve, deployment strategies will shift:
5G: Heavily reliant on small cells, Massive MIMO, and DAS to achieve low latency, high capacity, and mmWave coverage.
6G: Expected to incorporate AI-driven self-optimizing networks, sub-THz frequencies, and satellite-terrestrial integration.
The future looks to integrate a smooth combination of terrestrial cells, DAS, and satellite components, managed by smart orchestration platforms.
Wrapping Up
Mobile networks depend on an array of deployment options to provide reliable, high-performance connectivity. From Massive MIMO and Small Cells to DAS, RRH, and Metro Cells, each part has a distinct role in the Het Net ecosystem.
By weaving these deployment strategies together with solid backhaul and Metro Core Networks, telecom operators can guarantee seamless coverage, increased capacity, and are well-prepared for 5G and beyond.
For those working in telecom or anyone interested, getting a grip on these deployment choices is key to designing, optimizing, and running the connected world of the future.
