Hybrid Virtualization and Hybrid Cloud Orchestration: Seamless Path from VNF to CNF

Hybrid Virtualization and Cloud Orchestration: Your Go-To Guide
Telecommunications networks are quickly shifting from hardware-based setups to cloud-native structures. With 5G and edge computing on the rise, operators are moving from Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) to Cloud-Native Network Functions (CNFs).
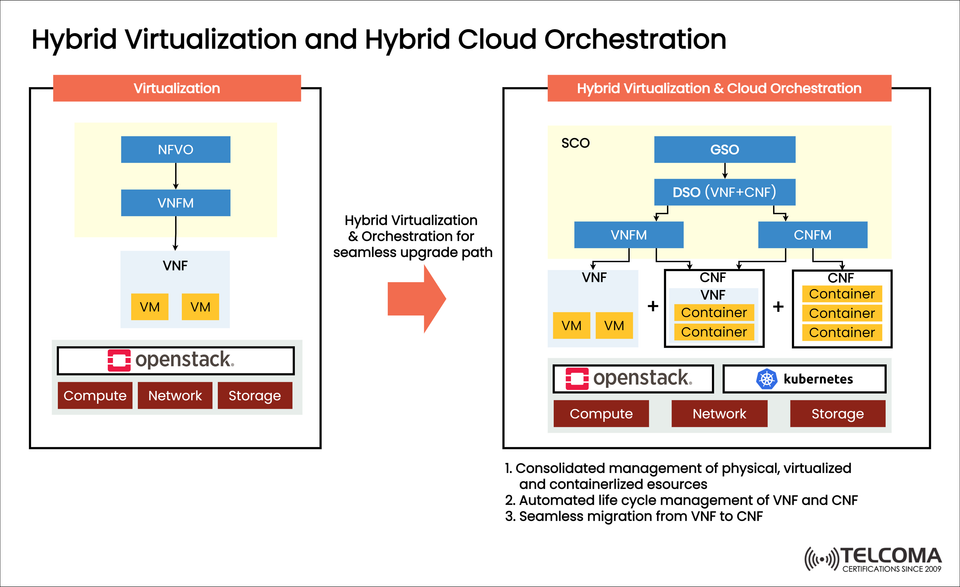
The diagram provided shows this transition, illustrating how hybrid virtualization and orchestration facilitate a smooth migration. This hybrid model merges VM-based virtualization with container-based orchestration, offering operators the flexibility, scalability, and efficiency needed in today’s networks.
Getting to Know the Basics
What is Virtualization?
Virtualization takes hardware resources—like compute, storage, and network—and turns them into virtual machines (VMs), allowing multiple VNFs to operate on a shared infrastructure. Traditionally, telecoms relied on OpenStack for managing virtualization.
VNF (Virtual Network Function): A software-based network function (think firewalls, EPC, or routers) that runs on VMs.
NFVO (Network Function Virtualization Orchestrator): This orchestrates VNFs, handling their deployment and the allocation of resources.
VNFM (VNF Manager): Responsible for managing the lifecycle of VNFs (like starting, scaling, and ending processes).
What is Cloud-Native Networking?
Cloud-native designs favor containers over VMs. Containers are lighter, quicker, and managed via Kubernetes. This change has paved the way for CNFs (Cloud-Native Network Functions), specifically designed for decentralized 5G, MEC, and IoT environments.
Hybrid Virtualization: The Best of Both Worlds
In practice, operators can't just ditch VNFs overnight. A hybrid model allows for the coexistence of VNFs and CNFs.
The diagram shows that:
VNFs still operate on VMs using OpenStack.
CNFs run within containers overseen by Kubernetes.
Orchestration layers (VNFM + CNFM + DSO) efficiently manage both setups.
This hybrid strategy guarantees that operators can transition gradually from VNFs to CNFs without interrupting services.
Main Elements of Hybrid Virtualization & Orchestration
- NFVO and VNFM (Virtualization)
NFVO coordinates network services within the VNF realm.
VNFM looks after the lifecycle management of VNFs.
VNFs operate on VMs managed by OpenStack.
- Hybrid Virtualization Layer
Supports both VM-based VNFs and container-based CNFs.
OpenStack manages the VM infrastructure.
Kubernetes takes care of containerized workloads.
- Cloud-Native Orchestration Layer
SCO (Service Cloud Orchestrator): The top-level orchestrator that manages all resources.
GSO (Global Service Orchestrator): Ensures comprehensive orchestration across VNFs and CNFs.
DSO (Domain Service Orchestrator): Focuses on handling mixed environments (both VNF and CNF).
VNFM: Takes care of VNFs.
CNFM (CNF Manager): Manages network functions in containers.
- CNFs (Cloud-Native Network Functions)
Operate in lightweight containers.
Quickly scalable, robust, and optimized for distributed 5G networks.
How Hybrid Orchestration Functions
The hybrid model brings together physical, virtualized, and containerized resources under one management framework.
VNFs run on VMs (OpenStack).
CNFs operate on containers (Kubernetes).
Orchestration coordinates VNFs and CNFs through compute, storage, and network resources.
Lifecycle management is automated, cutting down on OPEX and human mistakes.
Advantages of Hybrid Virtualization & Orchestration
Smooth Migration Path * Operators can gradually transition from VNFs to CNFs. * Preserves existing investments in VNF infrastructure.
Unified Resource Management * Integrated management of physical, virtual, and cloud-native assets. * Enables holistic oversight of compute, storage, and network.
Automation & Agility * Automated lifecycle processes for both VNFs and CNFs. * Quicker service rollouts.
Cloud-Native Perks * CNFs bring flexibility, scalability, and resilience. * Perfect for 5G applications like network slicing, MEC, and IoT.
Future-Proofing * Hybrid orchestration readies networks for cloud-native growth without interrupting existing services.
Hybrid Virtualization in Telecom Use Cases
Use Case How Hybrid Virtualization Helps5G Core Networks Combination of VNFs (EPC) and CNFs (5G Core functions like AMF, SMF).MEC (Edge Computing)Deploying low-latency apps in containers alongside VM-based VNFs. Network Slicing Orchestration of VNFs and CNFs to form dynamic, isolated network slices. IoT Ecosystems Managing vast numbers of IoT connections with scalable CNFs while still using VNFs for legacy services. Enterprise Services Hybrid orchestration for enterprise VPNs, SD-WAN, and cloud-native security solutions.
Transitioning from VNF to CNF: Main Challenges
Even with hybrid orchestration easing the shift, hurdles remain:
Operational Complexity: Balancing VNFs and CNFs requires skilled teams.
Interoperability Issues: Vendor-specific VNFM and CNFM may not always mesh well.
Legacy Integration: Moving old VNFs to CNFs without downtime can be tricky.
Security Risks: Containerized systems introduce unique security challenges.
Why Hybrid Orchestration Matters for 5G
The 5G landscape requires extremely low latency, high scalability, and flexibility. Hybrid orchestration meets these demands by enabling:
Gradual migration: Operators can transition at a pace that suits them.
Distributed deployments: Edge and cloud-native applications can work together.
End-to-end automation: Leading to reduced OPEX and quicker market readiness.
Resilience: CNFs help maintain service continuity in the event of failures.
This hybrid model allows telecom networks to advance towards fully cloud-native 5G and 6G setups without interruptions.
Why Hybrid Virtualization is a Game-Changer
Hybrid virtualization and orchestration tackle one of the major challenges in telecom: finding the right mix of innovation and stability. Operators can’t just ditch their existing VNFs overnight—there's a ton of money tied up in those systems. Instead, hybrid architectures let them:
Modernize step-by-step without causing service interruptions.
Support new 5G applications while still keeping legacy VNFs in play.
Future-proof their operations and set the stage for a complete switch to CNFs.
This approach is especially important for global telecom deployments, where carriers need to effectively manage a mix of vendors and network generations without a hitch.
Wrap-Up
The shift from VNFs to CNFs is a significant leap for telecom networks. However, operators need to avoid rocky transitions. Hybrid virtualization and orchestration provide the ideal solution—allowing VNFs and CNFs to coexist, all managed through a cohesive orchestration framework.
This structure enables:
Integrated management of every resource.
Automated lifecycle management.
A seamless migration route toward cloud-native, 5G-ready networks.
For telecom experts, hybrid orchestration isn’t just a transition strategy; it’s the bedrock for future networks, fueling advancements in 5G, IoT, MEC, and more.
