Mini-slot Transmission in 5G NR Downlink: Enabling Ultra-Low Latency Communication

Mini-slot Transmission in the 5G NR Downlink
One of the standout features of 5G New Radio (NR) is its ability to cater to a variety of service needs, ranging from enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) to Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC). To hit these lofty performance targets, 5G rolls out mini-slot transmission, which means data can be sent right away without having to wait for the next slot boundary.
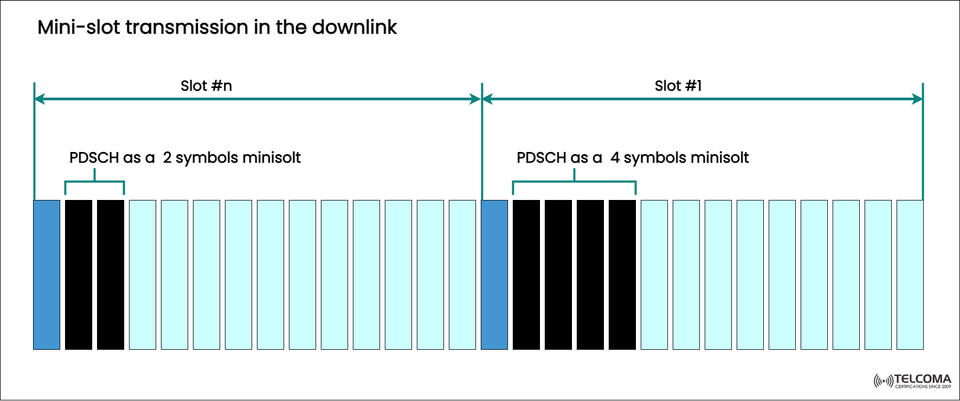
The accompanying image highlights this aspect really well; it shows how the Physical Downlink Shared Channel (PDSCH) can be sent using a 2-symbol or 4-symbol mini-slot within different slots. This kind of flexibility is crucial for meeting 5G’s tough latency and reliability benchmarks.
Understanding Mini-slot Transmission
In the older LTE systems, data is sent in fixed slot or subframe intervals, which can lead to higher latency for applications that need timely responses. In contrast, 5G NR introduces mini-slots that let transmissions kick off anytime, without being tied to slot timings.
What is a Mini-slot?
A mini-slot represents a short transmission time interval (TTI) that consists of 2, 4, or 7 OFDM symbols, as opposed to the usual 14-symbol full slot. With mini-slots, you can transmit data packets as soon as they are ready, which significantly cuts down on transmission delays.
Key Features of Mini-slots:
Made up of 2, 4, or 7 OFDM symbols.
Can start at any symbol boundary, not limited to slot boundaries.
Works for both uplink and downlink.
Perfect for URLLC and time-sensitive data.
Integrates smoothly with standard slot-based transmissions.
In the image, the left side showcases a mini-slot with 2 OFDM symbols, while the right side illustrates a 4-symbol mini-slot, both transmitting downlink data (PDSCH).
Why Mini-slots Matter in 5G
5G networks aim for ultra-low latency (as low as 1 ms) along with high reliability—a must for things like self-driving cars, industrial robots, and augmented reality. Mini-slots help achieve this by:
Cutting down scheduling delays: No more waiting for the next slot.
Enabling dynamic transmission: Great for sporadic or urgent data.
Enhancing radio resource use: Small packets get sent efficiently.
Allowing preemptive scheduling: URLLC packets can interrupt ongoing eMBB transmissions when necessary.
This kind of flexibility guarantees that critical data gets prioritized without needing to wait for fixed time intervals.
Full Slot vs. Mini-slot Transmission
To really understand mini-slot transmission, it’s helpful to compare it with traditional full-slot scheduling.
Aspect
| Full Slot Transmission | Mini-slot Transmission |
|----------------------------|----------------------------|
| Slot Duration | 14 OFDM symbols | 2, 4, or 7 symbols |
| Transmission Timing | Aligned with slot boundaries | Can start anytime |
| Latency | Higher | Ultra-low |
| Use Case | eMBB, mMTC | URLLC, low-latency control |
| Scheduling Flexibility | Fixed | Dynamic |
| Preemption Support | Not supported | Fully supported |
As you can see, mini-slots offer the detailed timing control and asynchronous scheduling that's crucial for the next wave of communication systems.
Mini-slot Transmission in the Downlink
In the downlink, mini-slot transmission primarily involves the Physical Downlink Shared Channel (PDSCH), which carries user data from the gNB (base station) to the UE (user equipment).
How It Works:
Dynamic Scheduling: The gNB identifies a data packet that needs to go out right away.
Mini-slot Allocation: Instead of waiting for the next slot boundary, the gNB assigns a mini-slot (2, 4, or 7 symbols) starting at any symbol position.
Transmission: The PDSCH data gets sent immediately within that mini-slot.
UE Decoding: The UE processes the data once it gets a scheduling grant via the Physical Downlink Control Channel (PDCCH).
In the illustration:
Slot #n shows PDSCH as a 2-symbol mini-slot—a great example of a very quick, urgent downlink transmission.
Slot #1 shows PDSCH as a 4-symbol mini-slot, used when more data symbols are necessary while still keeping that low latency.
This flexibility supports mixed traffic handling—while one user could be getting eMBB data in a full slot, another might be receiving time-sensitive URLLC data through mini-slot transmission.
Numerology and Slot Duration
The performance of mini-slots in 5G NR is closely tied to numerology (μ), which sets the subcarrier spacing (SCS) and slot duration.
Numerology (μ)Subcarrier Spacing (kHz)Slot Duration (ms)Mini-slot Duration (2 Symbols)0151.00.141300.50.072600.250.03531200.1250.01842400.0625~0.009
As numerology increases, slot durations get shorter, making even quicker mini-slot transmissions possible—this is crucial for millimeter-wave (mmWave) frequencies where extremely low latency is key.
Mini-slot Scheduling and Preemption
In 5G NR, scheduling decisions are dynamic and adaptable. Mini-slot scheduling is based on the idea of preemption, which means urgent URLLC transmissions can cut in on ongoing lower-priority traffic.
Example:
If eMBB traffic is using a full slot and a URLLC packet comes in, the gNB can preempt the eMBB allocation midway, utilizing a mini-slot to send out the URLLC packet right away. The interrupted eMBB data can get transmitted again later using Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request (HARQ).
Benefits of Preemptive Mini-slots:
Guarantees mission-critical reliability.
Keeps latency below 1 ms.
Maintains overall throughput with HARQ recovery.
This approach is vital for URLLC support in 5G NR.
Applications of Mini-slot Transmission
Mini-slots are key in enabling 5G’s most demanding applications:
- Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC)
Applications like self-driving, remote surgeries, and robotic control rely on immediate data delivery.
Mini-slots ensure that communication is timely and predictable without delays typical of slots.
- Industrial Automation and Smart Manufacturing
In Industry 4.0, sensors and controllers need to respond in less than a millisecond.
Mini-slot transmissions keep reaction times rapid and reliable.
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB)
In busy areas, mini-slots can manage quick control bursts or dynamic scheduling within larger eMBB sessions.
- Mission-Critical IoT and Emergency Networks
Mini-slots allow for prioritized downlink data delivery for urgent alerts or network slicing activities.
Advantages of Mini-slot Transmission
Technical Benefits:
Ultra-Low Latency: Perfect for real-time operations.
High Flexibility: Lets you schedule at the symbol level.
Coexistence: Can run eMBB and URLLC transmissions at the same time.
Better Spectrum Use: Allocates just what’s needed.
Improved QoS Management: Adjusts to different traffic priorities.
Operational Gains:
Efficient Resource Scheduling: Less idle time and waiting.
Service Differentiation: Supports various latency and reliability needs on the same carrier.
Challenges and Implementation Considerations
Even with the advantages, mini-slot transmissions come with their own challenges:
Increased Scheduling Complexity: Needs super responsive resource management.
Higher Control Overhead: Frequent PDCCH signaling for mini-slots can put more strain on the system.
Interference Management: Need to be careful with overlapping eMBB and URLLC transmissions.
Device Design Complexity: User devices must track and decode these asynchronous allocations efficiently.
Research and optimization efforts within 3GPP Release 17 and beyond are ongoing to enhance these systems.
Conclusion
The concept of mini-slot transmission in the 5G NR downlink marks a significant leap toward achieving the low-latency, high-reliability, and flexible scheduling that 5G aims for. As shown, PDSCH data can be sent using 2-symbol or 4-symbol mini-slots within different slots, facilitating immediate data delivery without waiting for fixed boundaries.
This precise control over timing and resources enables 5G networks to support a wide range of applications—from immersive AR/VR experiences to crucial industrial automation—all with unmatched speed and responsiveness.
In short, mini-slot transmission is the heartbeat of real-time 5G NR, providing a performance level that connects human and machine communication like never before.
