NTT DOCOMO’s vRAN Architecture Explained: Components, Interfaces, and O-RAN Integration
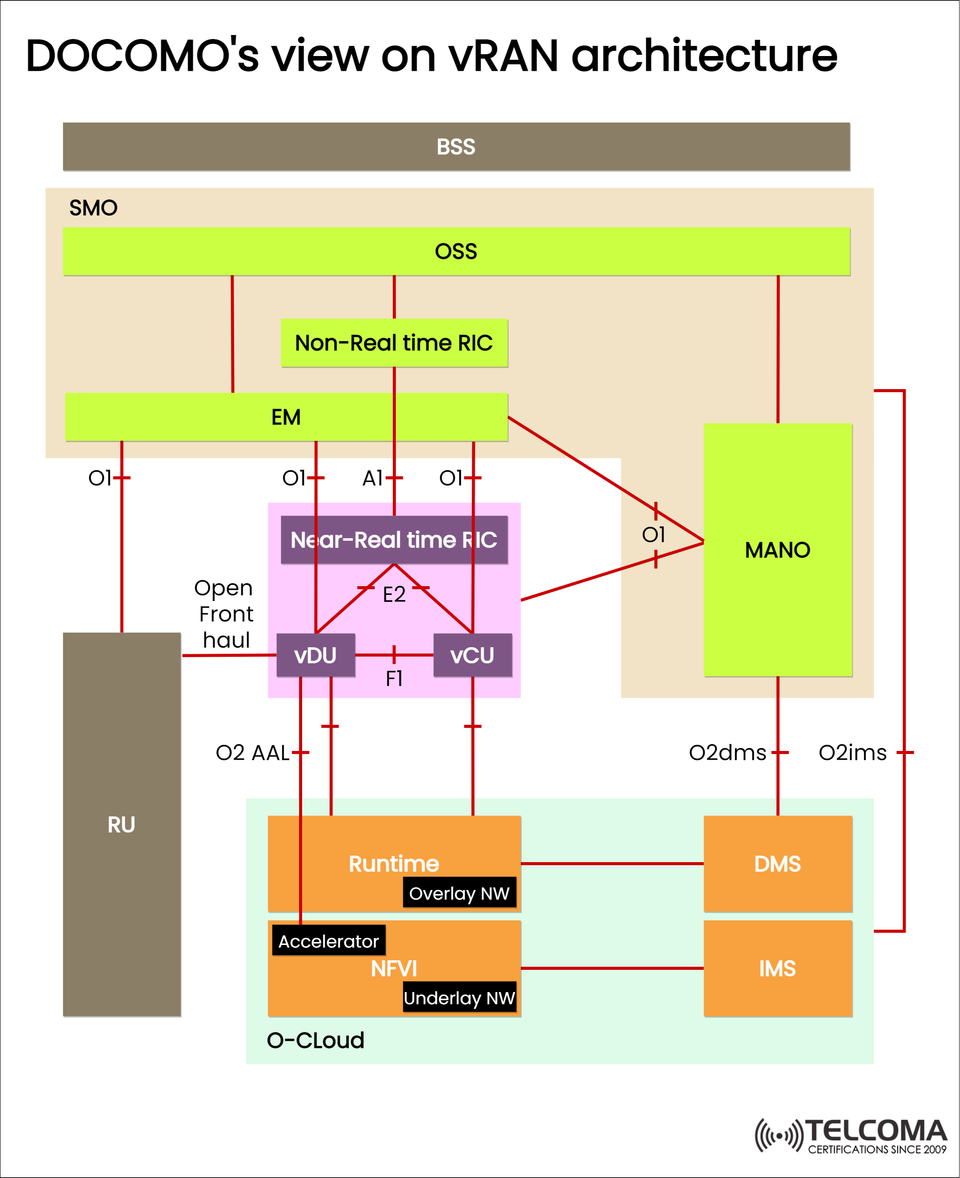

NTT DOCOMO’s Perspective on v RAN Architecture: A Closer Look at 5G Network Virtualization
Shifting from traditional RAN to v RAN (Virtualized Radio Access Network) is revolutionizing mobile networks, making them smarter, more open, and adaptable. NTT DOCOMO is at the forefront of this shift, being one of the early major operators to roll out O-RAN-based 5G networks.
DOCOMO’s v RAN architecture, as illustrated in the image above, showcases how virtualization, open interfaces, and real-time intelligence come together to form a cloud-native and automated RAN ecosystem. Let’s break down this architecture step by step.
Understanding the Basics: What is v RAN?
v RAN separates traditional RAN components—baseband processing and radio units—into virtualized functions that operate on standard hardware.
Unlike the traditional setup, where hardware and software are closely linked, v RAN offers:
Scalability: Software functionalities can adjust dynamically.
Vendor flexibility: Open interfaces enable multiple vendors to work together.
Automation: AI and orchestration enhance network performance.
vRAN acts as a stepping stone toward Open RAN (O-RAN) — a standard set by the O-RAN Alliance for open and intelligent RAN ecosystems.
High-Level Overview of DOCOMO’s vRAN Architecture
The architecture includes several layers and functional blocks:
Layer Key Components Function RAN Layer RU, v DU, vCU Manages radio transmission and baseband processing RIC Layer Near-RT RIC, Non-RT RICAI-driven control and optimization Management & Orchestration (MANO)MANO, SMO, EM, OSS Automates lifecycle management Cloud Infrastructure (O-Cloud)NFVI, Runtime, Accelerator Provides computing and storage resources Service Layer DMS, IMS, BSS Offers telecom services and subscriber management
Each layer connects through standardized O-RAN interfaces (O1, O2, A1, E2, F1, etc.), ensuring that different vendors can work together seamlessly.
- The Radio Unit (RU)
The Radio Unit (RU) handles RF processing, which includes tasks like transmission, reception, and analog signal conversion.
It connects to the vDU using the Open Fronthaul interface defined by O-RAN.
This open interface allows operators to choose RUs from various vendors, boosting interoperability.
Key functions involve signal amplification, filtering, and managing antennas.
In DOCOMO’s network, the RU is positioned at the network’s edge, acting as the physical link between the digital side and radio signals.
- The Virtualized Distributed Unit (v DU)
The v DU oversees real-time Layer 1 (PHY) and part of Layer 2 (MAC) processing. It’s the first virtualized baseband function in the RAN setup.
Operates on O-Cloud infrastructure (through NFVI and runtime environments).
Communicates with the RU via the Open Fronthaul interface.
Connects to the v CU using the F1 interface.
The v DU allows for flexible scaling and quick processing, which is vital for edge-focused 5G applications like URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications).
- The Virtualized Central Unit (v CU)
The v CU takes care of non-real-time processing, including RLC, PDCP, and SDAP layers. It’s typically located in a centralized data center or regional hub.
Connects with v DU through the F1 interface.
Links to the Near-Real-Time RIC (RIC) via the E2 interface.
Connects to the core network (like through N2/N3 connections).
This separation helps DOCOMO centralize heavy computational tasks while keeping latency-sensitive operations close to the user edge.
- The Near-Real-Time RIC (RAN Intelligent Controller)
The Near-Real-Time RIC functions within a 10 ms to 1 s control loop.
It optimizes radio resources in real-time based on current network conditions.
Key Functions
Manages x Apps for tasks including radio resource management (RRM), handovers, and reducing interference.
Communicates with the v DU/v CU through the E2 interface.
Works with the Non-Real-Time RIC via the A1 interface for policy updates.
This setup allows DOCOMO to leverage AI-driven optimization almost in real-time, leading to better throughput, reduced latency, and improved spectral efficiency.
- The Non-Real-Time RIC
Operating on > 1 second control intervals, the Non-Real-Time RIC is part of the Service Management and Orchestration (SMO) framework.
Functions
Handles long-term network optimization, training machine learning models, and creating policies.
Sends control guidance to the Near-RT RIC through the A1 interface.
Gathers performance data from the network using O1 interfaces.
By incorporating AI/ML in this layer, DOCOMO ensures predictive analytics and long-term optimization, aligning with O-RAN’s goals for intelligent automation.
- The SMO (Service Management and Orchestration) and OSS
The SMO brings together OSS (Operations Support Systems) and Element Management (EM) to orchestrate and monitor the entire network.
Key Responsibilities
Managing Faults, Configuration, Accounting, Performance, and Security (FCAPS).
Orchestrating virtual resources using MANO.
Communicating with RICs, vRAN elements, and O-Cloud through interfaces like O1, A1, and O2.
DOCOMO’s SMO functions as the central hub coordinating all components, ensuring everything from virtual functions to cloud resources and AI controllers interacts smoothly.
- The MANO Layer (Management and Orchestration)
The MANO layer, following ETSI NFV specifications, coordinates:
The lifecycle of virtual network functions (VNFs).
Resource distribution in O-Cloud.
Deployment, scaling, and recovery of vCU/vDU functions.
Through the O2dms and O2ims interfaces, MANO connects with the DMS (Domain Management System) and IMS (Infrastructure Management System) to ensure comprehensive resource visibility.
- The O-Cloud (Open Cloud Infrastructure)
O-Cloud is the backbone that hosts virtualized RAN functions (vDU, vCU) along with related workloads.
It consists of:
NFVI (Network Function Virtualization Infrastructure) — supplying computing, network, and storage resources.
Runtime Environment — supporting VNFs and CNFs with overlay/underlay networking.
Accelerators (e.g., FPGA, GPU, SmartNIC) — boosting performance for PHY processing.
DOCOMO’s O-Cloud is built for carrier-grade performance, ensuring low latency and reliability.
- DMS, IMS, and BSS Layers
At the operational level, DOCOMO integrates service and business systems:
DMS (Domain Management System): Handles domain-level resources like computing or RAN clusters.
IMS (Infrastructure Management System): Offers visibility and control for both physical and virtual infrastructures.
BSS (Business Support Systems): Manages billing, customer care, and service activation.
These systems help ensure that v RAN operates effectively while also supporting business and operational objectives.
- Interfacing Framework in DOCOMO’s v RAN
InterfaceConnectsPurposeO1SMO ↔ Network Functions Management and monitoringO2O-Cloud ↔ MANO Orchestration and resource controlA1Non-RT RIC ↔ Near-RT RIC Policy guidance and ML updatesE2Near-RT RIC ↔ v DU/v CU Real-time control and feedbackF1vDU ↔ v CU Data/control plane split interface Open Fronthaul RU ↔ v DU Radio and baseband connection
These open interfaces adhere to O-RAN Alliance standards, ensuring interoperability, flexibility, and a variety of vendor options.
Advantages of DOCOMO’s v RAN Architecture
Vendor-neutral Interoperability thanks to O-RAN’s open interfaces.
Cloud-native Deployment that fully utilizes O-Cloud.
AI-driven Optimization through RICs for real-time and long-term control.
Automated Orchestration via SMO and MANO integration.
Scalability and Elasticity to meet the demands of 5G and beyond to 6G.
DOCOMO’s approach shows that vRAN can be both high-performance and adaptable when built around principles of openness, intelligence, and automation.
Conclusion
NTT DOCOMO’s vRAN architecture represents the next step in the evolution of mobile networks — intelligent, virtualized, and open.
By fusing:
Open RAN concepts,
AI-enhanced RIC controllers,
Cloud-native O-Cloud infrastructure, and
Automated SMO orchestration,
DOCOMO has laid down a blueprint for scalable, high-performance 5G networks — setting the stage for 6G-ready systems.
In summary, DOCOMO’s vision for vRAN illustrates how network intelligence and virtualization can come together to empower the future of mobile connectivity — making it efficient, flexible, and responsive to every user and service requirement.
