Samsung 5G Network Automation Architecture Explained: Future of Intelligent Networks
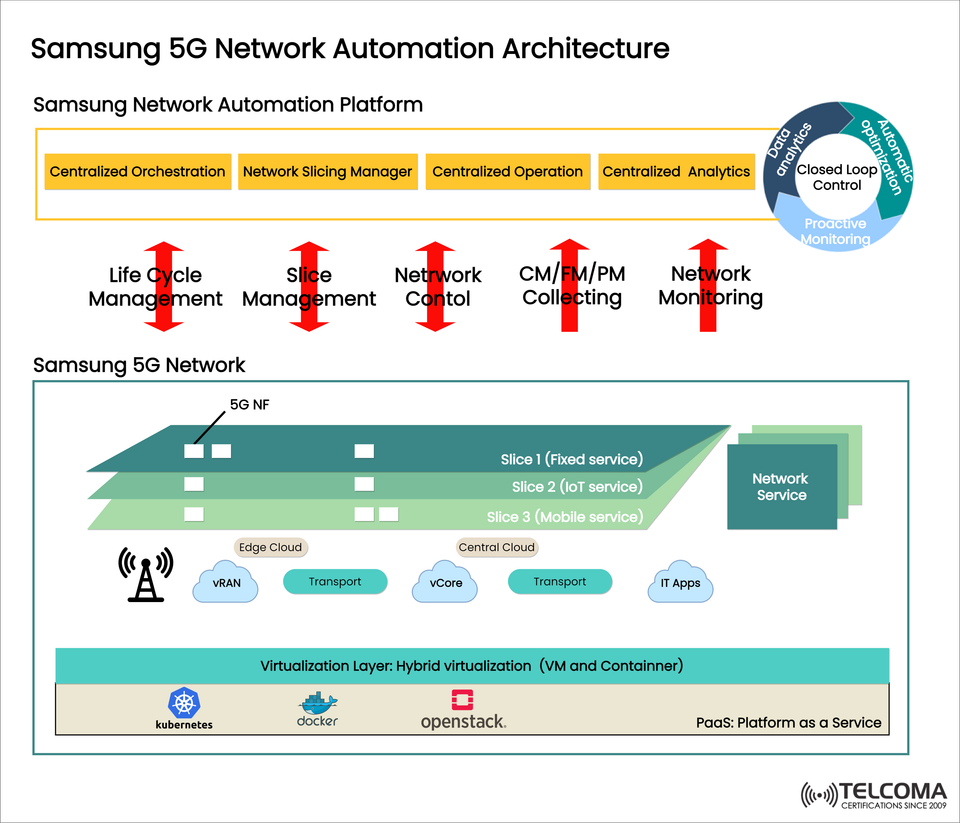

Samsung 5G Network Automation Architecture: Shaping the Future of Intelligent Networks
The new wave of telecom innovation is all about automation and intelligence. With the increasing complexities of 5G networks, relying on traditional management methods just won't cut it anymore. Samsung’s 5G Network Automation Architecture offers a cohesive, AI-driven platform that ensures smooth orchestration, efficient network slicing, proactive monitoring, and closed-loop control.
In this piece, we’ll unpack the architecture shown in the diagram, dive into its key components, and discuss why it’s a real game-changer for telecom operators and businesses alike.
Why 5G Needs Network Automation
5G networks are designed for ultra-low latency, massive device connectivity, and a variety of service needs. Unlike earlier generations, 5G must quickly adjust resources to accommodate different user types — from industrial IoT applications to mobile broadband.
Static configurations or manual setups just won’t be sufficient. That’s where automation comes in, offering:
Agility: Swift service provisioning.
Scalability: Ability to handle millions of IoT devices.
Reliability: Early fault detection and self-repair capabilities.
Efficiency: Better utilization of network resources.
Samsung tackles these issues with its Network Automation Platform, designed to intelligently oversee the entire 5G ecosystem.
Samsung Network Automation Platform
At the core of Samsung’s 5G framework is the Samsung Network Automation Platform (SNAP). This platform brings together several centralized functions:
Centralized Orchestration – Automates how network functions are deployed and scaled across edge and core.
Network Slicing Manager – Dynamically allocates and governs network slices based on different use cases.
Centralized Operation – Offers visibility and control throughout all network layers.
Centralized Analytics – Leverages AI/ML insights to boost performance, spot issues, and suggest optimizations.
These features work together through Closed Loop Control, where data analytics, ongoing monitoring, and automation optimization continually enhance the network in real time.
Key Functions of Samsung 5G Network Automation
The platform brings key functions essential for success:
Life Cycle Management (LCM) - Automates the process of onboarding, deployment, scaling, and retiring of network functions, cutting down on operational strain and errors.
Slice Management - Allocates virtual network slices for various use cases like fixed broadband, IoT, and mobile services, ensuring guaranteed QoS (Quality of Service) for each slice.
Network Control - Manages real-time traffic and resource allocation, supporting multi-cloud and hybrid setups.
CM/FM/PM Collection - Collects Configuration Management (CM), Fault Management (FM), and Performance Management (PM) data for predictive maintenance and self-healing.
Network Monitoring - Provides end-to-end visibility across both virtualized and physical infrastructure, enabling proactive detection and response to anomalies.
Samsung 5G Network Architecture Layers
Samsung's 5G Network architecture is structured in layers, offering both flexibility and scalability:
- Network Slices
Slice 1: Fixed Service – Supports broadband-like services for households and businesses.
Slice 2: IoT Service – Tailored for low-power, high-volume machine communications.
Slice 3: Mobile Service – Handles enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) with high throughput capabilities.
Each slice operates 5G Network Functions (5G NF) customized for specific service needs.
Edge & Central Cloud
Edge Cloud – Moves computing closer to end-users, enhancing experiences with ultra-low latency applications like AR/VR and self-driving cars.
Central Cloud – Manages heavy processing tasks and centralized control functions.
- Network Components
vRAN (Virtualized RAN) – Provides flexibility in deploying and scaling radio resources.
Transport – Guarantees seamless connections between edge, core, and cloud.
vCore (Virtualized Core) – Offers essential 5G core functions for session and mobility management.
IT Applications – Facilitates business and operational applications.
- Virtualization Layer
Samsung utilizes a hybrid virtualization model that merges:
Kubernetes – For container orchestration of cloud-native network functions (CNFs).
Docker – Light containerization for scalable deployments.
OpenStack – Virtual Machine (VM) management for legacy Virtual Network Functions (VNFs).
This hybrid strategy ensures backward compatibility while taking full advantage of cloud-native flexibility.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS makes it easier to develop and integrate applications, allowing operators to innovate quickly without needing to reinvent the infrastructure.
Closed-Loop Automation: The Core Advantage
The real power of Samsung’s architecture lies in Closed-Loop Automation, where the system continuously:
Monitors – Gathers real-time data from the entire network.
Analyzes – Leverages AI/ML analytics to identify anomalies or anticipate problems.
Optimizes – Automatically tweaks configurations, scales resources, or redirects traffic.
This self-repair capability improves reliability and optimizes costs.
Benefits for Telecom Operators
Telecom operators deploying Samsung’s 5G Network Automation Architecture can anticipate:
Lower OPEX thanks to automation and AI-driven efficiency.
Quicker Time-to-Market for new services like IoT, AR/VR, and enterprise 5G.
Better SLA Compliance with guaranteed QoS for each network slice.
Future-Proof Design that supports both VNFs and CNFs through hybrid virtualization.
Boosted Security with proactive monitoring and closed-loop controls.
Real-World Applications
Samsung’s 5G Network Automation isn’t just theoretical; it’s designed for real, high-demand situations:
Smart Cities – Real-time monitoring of traffic, energy grids, and safety systems.
Industry 4.0 – Private 5G networks for factories that enable robotics and automation.
Healthcare – Remote surgeries and telemedicine that need ultra-low latency.
Autonomous Vehicles – Edge computing for on-the-spot decision-making.
Enterprise Services – Dedicated slices for business applications with guaranteed performance.
Comparative View: Traditional vs. Automated 5G Networks
Feature Traditional Networks Samsung Automated 5G Networks Provisioning Manual, slow Automated, real-time Resource Allocation Static Dynamic, slice-based Monitoring Reactive Proactive, AI-driven Fault Recovery Manual trouble shooting Self-healing with closed-loop control Scalability Limited Cloud-native, hybrid virtualization
Conclusion
Samsung’s 5G Network Automation Architecture marks a significant leap forward in telecom development. By combining centralized orchestration, network slicing, hybrid virtualization, and closed-loop automation, it equips operators to meet the demanding needs of 5G and beyond.
For telecom professionals, this architecture means quicker deployments, lower costs, and more dependable services. For tech enthusiasts, it’s a sneak peek into how automation and AI will shape the networks of tomorrow.
As industries start to embrace 5G on a large scale, solutions like Samsung’s will be at the center of a truly connected world.
