Self-Optimizing Networks (SON) in LTE and 5G: Automation for Coverage, Handover & Load Balancing

Self-Optimizing Networks (SON): Automating Network Performance in LTE and 5G
Automation is a key for keeping the performance optimized in today's fast-paced mobile networks. The concept of Self-Optimizing Networks (SON) is baked into the architecture of both LTE and 5G, enabling the system to self-configure, self-optimize and self-heal automatically with minimal input from a human operator.
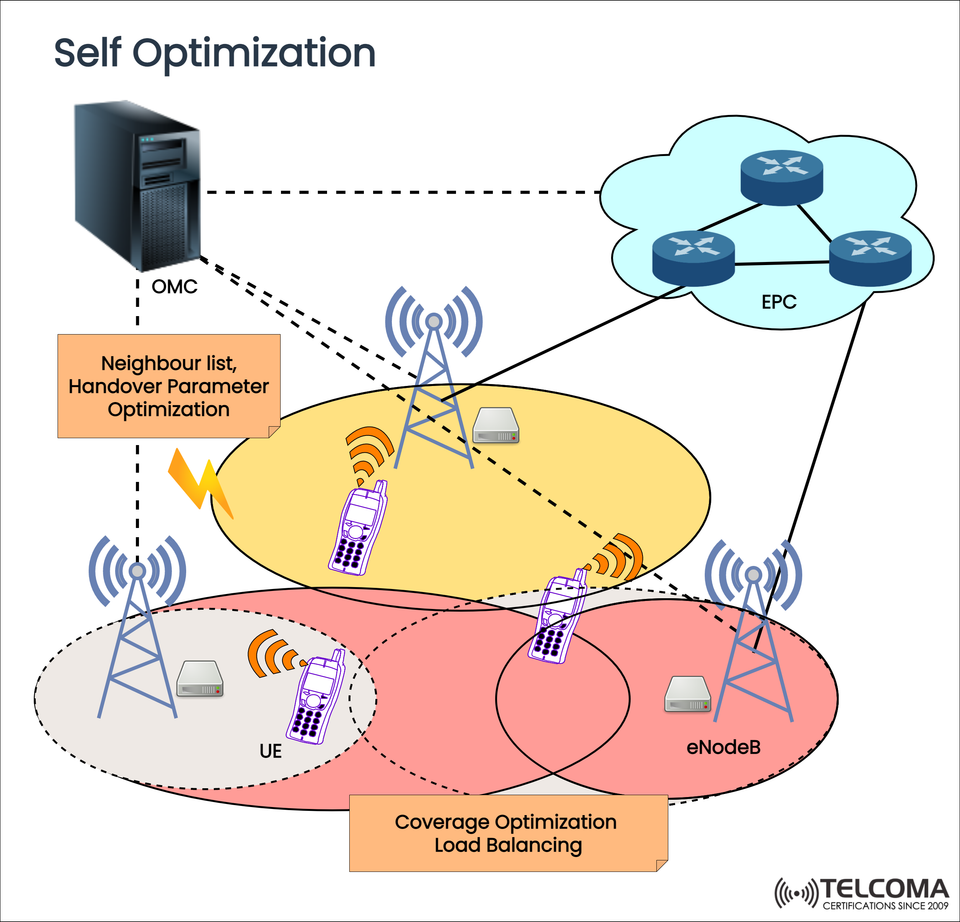
The image below depicts the functionality of SON taken from a live RAN and encapsulates examples such as the tuning of handover parameters, neighbor list optimization and load balancing which are dynamically controlled through an Operations and Maintenance center (OMC).
🧠What is SON (Self-Optimizing Networks)?
SON refers to a group of algorithms and automated features that can allow a mobile network to self-configure self-optimize and self-heal. SON is part of the overall self-organizing network concept that was developed for LTE and continues to evolve and progress in 5G.
SON has three primary functions, they are;
Self-Configuration
Self-Optimization
Self-Healing
📊What Does the Image Show?
In the diagram below, it shows the following SON function assignments:
OMC (Operations & Maintenance Center): The control point where SON logic is managed
eNodeBs (base stations): Connected to the Evolved Packet Core (EPC) and controlled from the OMC
Mobile users (UE): Moving through the cells generating handovers
Examples of optimizations:
Neighbor list & handover
🛰 Key areas of SON optimization that are illustrated Dynamic SON handover parameter optimization Dynamically optimizes or adjusts:
Time-to-Trigger (TTT)
Handover Margin (HOM)
These adjustments ensure appropriately smooth handovers between eNodeBs and reduce call drops and ping-pong handovers.
📡 Neighbor List Management Automatically detects and updates neighbor relationships based on:
User mobility (UE transition)
Signal measurements
Cell configuration changes
Properly detecting neighbor cells ensure handovers are not lost and handover failures do not occur.
⚖️ Coverage and Load Balancing Adjusts the boundaries of the cell, and may align with neighbor cells by adjusting antenna tilt or transmit power. This allows traffic to be distributed evenly utilizing the neighbors in a more effective but equitable manner.
This can also serve to offload traffic from ET cell(s) that are overloaded and fill unused neighbors by taking the traffic off the overloaded cell.
🔧 SON Use Cases for Network Optimization
Optimization Task Benefit to Network
Handover Optimization Fewer dropped calls, better handover mobility
Load Balancing Greater throughput and better quality of experience (QoE)
Neighbor List Auto-Tuning More reliable and faster handovers
Coverage Shaping Better relative signal indoors and outdoors
Outage Detection and Recovery Faster fault detection and recovery.
🌐 SON in 5G: Taking SON to the Next Level
SON takes a more significant leap as 5G networks transition from SON automation directly into AI/ML enabled automation. Key features are:
Intent-based Networking - Network will tune and adjust itself based on service intent (for example, latency, capacity).
Predictive Optimization - Network will adjust coverage or capacity based on historical utilization data and metrics.
Energy Optimization - Network will actively power down underutilized cells to save energy.
🧰 SON Benefits for Operators
OPEX Reduction - Because SON relies less on human processes and intervention, the OPEX costs are reduced.
Faster Network Rollout - Self Configuration capabilities facilitate faster network roll out.
🏁 Wrap-Up
The image above shows how SON turns a traditional LTE/5G (mobile) network into a rationally intelligent self-aware infrastructure. By automating handovers, neighbor list updates, and load balancing, SON has advanced mobile networks' efficiencies of operation, reliability and overall scaling capabilities.
As the networks evolve to 5G-Advanced, and eventually sixth-generation (6G) networks, self-optimisation functionality will no longer be an option, but will be a necessity in supporting reliable performance and customer satisfaction levels.
🧠 SON Architecture: Centralized vs Distributed vs Hybrid
Centralized SON (C-SON)
SON is software hosted at a centralized location (OMC or core).
Simple to manage, easier to scale, suit legacy multi-vendor environments.
Best for:
• Policy-based optimization
• Global change based analytics
• Central controlling parameter changes
Distributed SON (D-SON)
SON logic is embedded on the individual network elements (eNodeB or gNode).
Provides faster reaction time, local decision autonomy.
Best for:
• Real-time handovers
• RACH optimizations
• Local fault recovery
Hybrid SON
Provides the best of both C-SON and D-SON.
Centralized control with localized agility.
Most modern networks deploy hybrid SON because most networks need a compromise between performance and manageability.
📍 Real SON deployment use cases
- Deployment Scenarios SON Functionality Applied Result
- Dense urban 4G/5G rollout Coverage optimization + auto-neighbor management Seamless mobility and increased throughput
- Event stadium / arena Load balancing during period of stressed resources - --Reduced call drops and better user level QoE
- Rural coverage Auto-configuration of new cells, software-defined configurability -Faster time to deploy and minimal operator input
- Disaster recovery / site failure Self healing SON for re-routes and neighbor updates Faster recovery and connectivity maintained
- Indoor small cell networks Coordination of interference avoidances & coverage shaping Delivery stable performance
🤖 Integration of AI/ML within SON A future with 5G and beyond means SON is moving from rules based automation to intelligent, predictive and autonomous processing.
🔍 How AI/ML adds value to SON:
Anomaly Detection is the ability to check for potential network issues before they impact network performance.
Predictive Optimization enables SON to forecast traffic patterns and take action based on expected conditions.
Root Cause Analysis automatically identifies the issue causing the degraded KPIs.
Closed Loop Automation integrates an orchestration tool (e.g. O-RAN SMO) to allow AI models to take corrective action continue processing in real-time.
[difference between SON capability vs. network orchestration capability must can and are completely different provide examples example below]
🔗 SON and Network Orchestration Platforms
In case you haven't noticed, SON is usually combined in orchestration layers in a cloud native 5G architecture. There are many roles that SON more than likely plays within those orchestration environments:
Layer SON Role on Integration
Service Management & Orchestration (SMO) Coordinates SON dealing with life cycle management.
NFV MANO Have the capability to deploy SON policy based on the behavior of the VNF.
OSS/BSS Uses the analytics from SON to modify billing & Qos tiers.
These various integrations with SON allow for service assurance end-to-end in usage of dynamic SLA's and overall customer experience
🏁 Final Wrap-Up: Why SON is Mission-Critical in current networks
Self-Optimizing Networks are no longer just an option but a strategy to better manage complex, high-performance network environments with:
Millions of endpoints
Massive IoT connectivity
Expectations to provide 24/7 service
SON provides:
✅ Agility to act in real-time
✅ Efficiency to lower operational cost
✅ Resilience to self-reconcile from failure
✅ Intelligence to
