Understanding eSIM Security Architecture: SM-DP, SM-SR, and eUICC Explained

Getting to Know eSIM Security Architecture: The Key to Safe Connectivity
As telecom tech progresses, the Embedded SIM (eSIM) has emerged as a fundamental part of modern connectivity. Unlike regular SIM cards that need to be swapped out physically, an eSIM enables users to securely download and switch mobile network profiles over the air (OTA). This upgrade not only makes things easier for users but also bolsters the overall security and provisioning capabilities of the network.
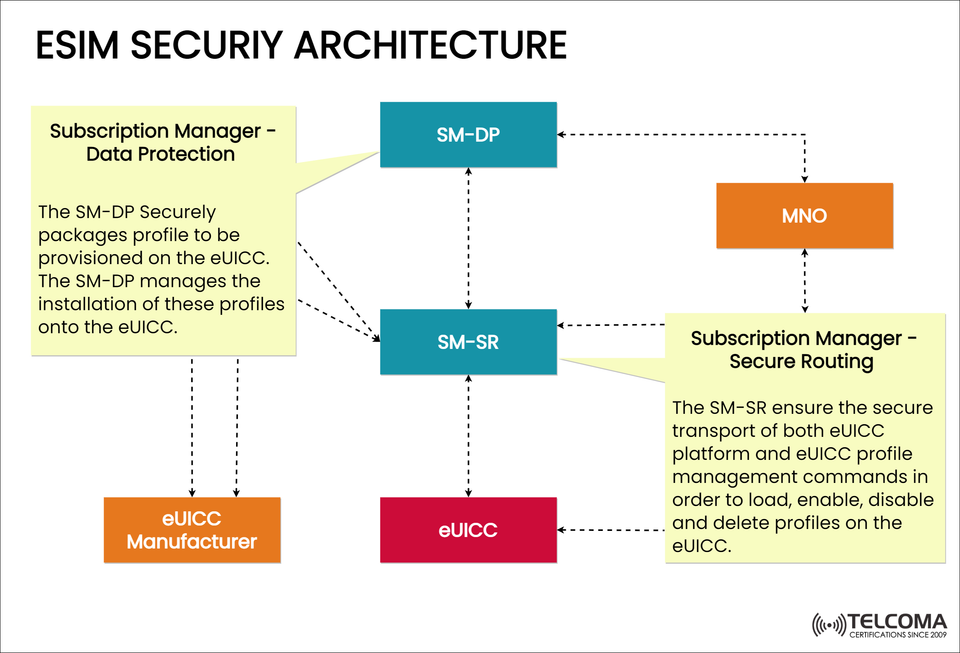
To make all this possible, eSIM technology depends on a solid security framework outlined by the GSMA (Global System for Mobile Communications Association). The diagram we've shared illustrates this architecture, showcasing the main components: SM-DP (Subscription Manager – Data Protection), SM-SR (Subscription Manager – Secure Routing), and the eUICC (Embedded Universal Integrated Circuit Card).
The Basics of eSIM Security
What’s an eSIM?
An eSIM (Embedded SIM) is a programmable chip inside a device that functions just like a removable SIM card. But instead of requiring physical handling, it supports remote provisioning, letting users activate, switch, or remove network profiles without needing to touch a SIM card.
The Importance of Security
Since eSIM profiles are downloaded and managed remotely, security is crucial to guarantee that:
Only authorized mobile network operators (MNOs) can set up profiles.
User data and credentials stay encrypted and safe from tampering.
Communication between network components is fully authenticated and secure.
Subscription Manager – Data Protection (SM-DP)
The SM-DP takes care of securely preparing and encrypting the operator’s profile before it gets downloaded onto the eUICC.
Key Functions of SM-DP:
Profile Packaging: It gathers the operator's subscription info (IMSI, authentication keys, etc.) and securely packages it for sending.
Provisioning: Oversees the secure installation of the profile on the eUICC.
Data Encryption: Encrypts sensitive data to keep it safe during transmission.
Integration with MNO: The SM-DP connects with the Mobile Network Operator to get the necessary credentials for provisioning.
The SM-DP acts like a secure vault, making sure all network data is encrypted before it reaches the user's device.
Subscription Manager – Secure Routing (SM-SR)
The SM-SR ensures that profiles are delivered securely to the eUICC. It serves as the communication link between the SM-DP and the eUICC.
Main Duties of SM-SR:
Secure Transport: Ensures management commands and profile data are sent securely.
Lifecycle Management: Looks after the entire lifecycle of a profile — including loading, enabling, disabling, and deleting.
Command Routing: Passes commands between the SM-DP and eUICC using secure channels.
Authentication & Integrity: Checks that all requests and responses come from legitimate sources.
In short, the SM-SR guarantees end-to-end integrity and confidentiality throughout all operations performed on the eSIM.
The eUICC – The Secure Component
The eUICC is the tiny embedded chip inside devices (like smartphones, IoT sensors, smartwatches, etc.) that stores and runs the eSIM profiles.
Key Roles of eUICC:
Profile Storage: Holds multiple operator profiles at the same time.
Profile Execution: Ensures that only one profile is active at any given moment, with others securely stored but inactive.
Secure Interface: Only communicates with authorized SM-DP and SM-SR entities.
Tamper Resistance: Built with secure hardware to shield against both physical and digital attacks.
The eUICC is essentially the trust anchor of the whole eSIM ecosystem.
Supporting Players
Mobile Network Operator (MNO)
Provides the subscription profile and user credentials.
Interacts with the SM-DP for the secure packaging of profile data.
Works with the SM-SR to manage activation or revocation requests.
eUICC Manufacturer
Develops and embeds the eUICC into devices during production.
Ensures compliance with the GSMA’s eSIM security and interoperability standards.
Works with SM-DP entities to preload or set up profiles ahead of device activation.
How eSIM Profile Provisioning Works
The process of managing eSIM profiles remotely consists of several secure interactions:
Profile Creation: The MNO prepares a profile that includes authentication keys, network access details, and subscription information.
Profile Packaging: The SM-DP encrypts and packages the profile securely for provisioning.
Profile Delivery: The SM-SR sets up a secure channel between the SM-DP and the eUICC.
Profile Installation: The eUICC downloads and installs the encrypted profile.
Profile Activation: After verification, the SM-SR activates the chosen profile on the eUICC.
Lifecycle Management: Profiles can later be updated, disabled, or deleted securely over-the-air.
This method ensures a smooth and secure Remote SIM Provisioning (RSP) experience for users across a range of devices and networks.
Security Features in eSIM Architecture
The entire system employs several layers of security, including:
End-to-End Encryption: All data exchanges between SM-DP, SM-SR, and eUICC are encrypted using top-tier algorithms.
Mutual Authentication: Each entity verifies the other before starting any transactions.
Digital Signatures: Help protect data integrity during transmission.
Role-Based Access Control: Only authorized parties can carry out profile operations.
GSMA Compliance: Follows the GSMA SGP.02 and SGP.22 guidelines for consumer and M2M eSIMs.
These protections work together to ensure that no unauthorized party can intercept, alter, or misuse subscription data.
Advantages of eSIM Security Architecture
For Users
Easier switching between mobile networks.
No physical SIM cards to misplace or damage.
Improved privacy and secure onboarding.
For Operators
Lower logistical costs (no physical SIM distribution).
Scalable remote provisioning options.
Better management of subscribers.
For IoT and Enterprise
Secure connectivity for IoT devices regardless of location.
Simple remote management of large fleets of devices.
Greater operational efficiency with less downtime.
Real-World Uses
The eSIM Security Architecture plays a vital role in:
Smartphones and Wearables: Supporting global connectivity without SIM swaps.
Automotive Industry: Offering always-on, location-based services.
Industrial IoT: Managing connected devices in areas like logistics, healthcare, and smart cities.
Enterprise Mobility: Optimizing connectivity management for employee devices.
Conclusion
The eSIM Security Architecture sets the standard for how digital connectivity can be secure, scalable, and flexible. Through the interaction of the SM-DP, SM-SR, and eUICC, it guarantees that every eSIM profile is managed with the highest levels of trust and protection.
For those in telecom, grasping this architecture is crucial as eSIM adoption ramps up across mobile, IoT, and enterprise spaces. The eSIM isn't just a handy tool—it's the bedrock for a secure, connected, and intelligent world.
